-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 9
Value series generator
This page documents value series generator properties.
Value series generator is a common bit of code, that is used to generate series of values for various tools: LinearArray, PolarArray, ParaSeries.
The final result of Value series generator is the content of Values property. It is merely a list of floating-point values, the meaning of them depends on the actual feature.
Values can be typed in directly, sourced from a spreadsheed, or (default) generated in-place. The source is chosen with ValuesSource property.
Values property contains the final result of Value series generator, and are thereafter used by the feature. It is merely a list of floating-point values, the meaning of them depends on the actual feature.
For LinearArray, Values are distances in mm, measured along axis of the array.
For PolarArray, Values are angles in degrees.
For ParaSeries, Values contain the list of values for the parameter (unit depends on the parameter).
ValuesSource property sets, where to take the Values from. It can be:
- 'Values Property': Values property is editable directly; all other properties are ignored.
- 'Spreadsheet': the values are copied from a column in a spreadsheet.
- 'Generator': in-place series generator fills Values property.
These two properties define the column of a spreadsheet to collect the values from. SpreadsheetLink is the spreadsheet, and CellStart is the address (A1-style) of the topmost cell of the column.
The spreadsheet is scanned from CellStart (inclusive), downwards, till an empty cell is encountered.
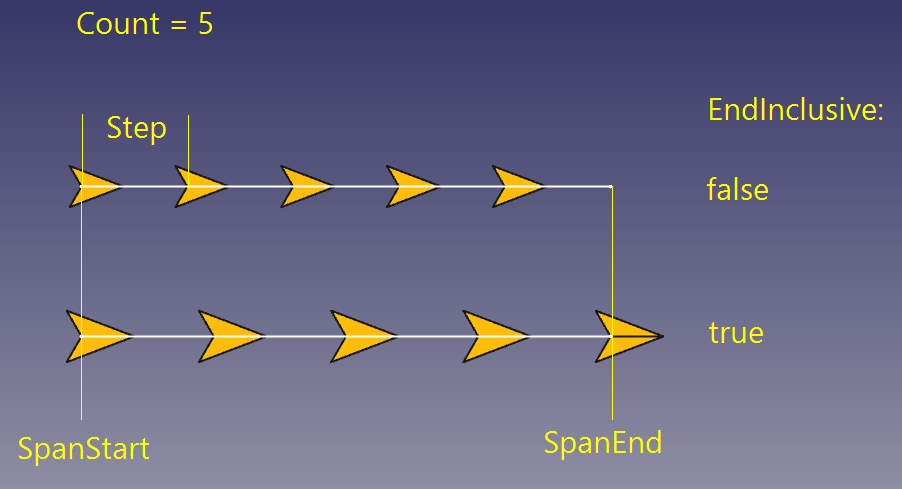
Sets the number of values to generate. If GeneratorMode is SpanStep, Count is read-only and determined from other properties.
Controls distribution of values in the interval.
- 'Linear' is the standard (values are distributed evenly along the interval).
- 'Exponential' makes the values be in a geometric progression. The meaning of Step property changes - it becomes the natural logarithm of ratio of adjacent values. In this mode, SpanStart and SpanEnd must have the same sign, and none of them is allowed to be zero.
If true, SpanEnd is treated as inclusive. The value equal to SpanEnd will end up into Values.
If false, SpanEnd is treated as not-inclusive. The value equal to SpanEnd is not dumped into Values, and not included in Count.
Controls, which properties are read-only, and which are driving.
Count, SpanStart, SpanEnd and Step are not independent. They are constrained by one relation, so one of them must be computed from others and be read-only.
- SpanN: fit Count values into SpanStart-SpanEnd interval. Step is computed (read-only).
- StepN: make Count values spaced by Step, starting from SpanStart. SpanEnd is computed (read-only).
- SpanStep: fill SpanStart-SpanEnd interval with values spaced by Step. Count is computed (read-only).
- Random: put Count random values into SpanStart-SpanEnd interval. Step is irrelevant (ignored).
Specifies additional offset to apply to all generated values. The value of 'Offset' is in fractions of 'Step'. Offset is applied after 'Alignment'.
The interval to put values into. If EndInclusive is false, the value equal to SpanEnd will not be included into Values and Count.
In case of Exponential distribution, SpanStart and SpanEnd nust be non-zero and of the same sign.
If GeneratorMode is StepN, SpanEnd only affects alignment.
Difference between adjacent values. If distribution is Exponential, Step is the natural logarithm of ratio of adjacent values. Step can be negative.
(new since rev. 233)
'Alignment' property sets, how to arrange values within span. This is a kind of post-processing step.
-
Low: default. Values start at SpanStart. -
Middle: Values are shifted to be in the middle of span. -
High: Values are shifted to make last value math SpanEnd. -
Justify: Step is increased to make the array fill Span completely (this effectively changesStepNintoSpanN; the mode is intended to make values fit into the interval nicely inSpanStepmode) -
Mirrored: For each value, an opposite (negated) value is inserted immediately after it (except if the value is zero - zero is not duplicated). This causes the number of values to increase, and not match 'Count'. This mode is aimed at making positive-negative scale bars.

Introduction to Lattice workbench
Boolean operations on arrays, Compound structure
Shape-driven arrays, Draft arrays in Lattice2
"Subsequencing" (sublink iteration, TopoSeries)
- (common pieces)
-- Common properties of placement features
-- Common properties of array generators
- (features)
-- Single Placement
-- Attached Placement
-- Array an attached Placement
-- Linear Array
-- Polar Array
-- Array From Shape
-- Invert placements
-- Join Arrays
-- Array Filter
-- Project Array
-- Resample Array
-- Populate With Copies
-- Populate With Children
-- Mirror
-- PartDesign Pattern
-- Downgrade
-- SubLink
-- Subsequence
-- Make Compound
-- Compound Filter
-- Fuse Compound
-- Bounding Box
-- Shape String
-- ParaSeries
-- TopoSeries
-- Shape info feature
- (tools)
-- Explode Array
-- Explode Compound
-- Inspect tool
-- Substitute Object
-- Expose links to subelements
-- Recompute controlling tools