"If you liked it then you should have put a test on it", Beyonce rule
C++20 single header/single module, macro-free μ(micro)/Unit Testing Framework
Overview
- No dependencies (C++20 / Tested Compilers: GCC-9+, Clang-9.0+, MSVC-2019+*)
- Single header/module (boost/ut.hpp)
- Macro-free (How does it work?)
- Easy to use (Minimal API -
suite, test, expect) - Fast to compile/execute (Benchmarks)
- Features (Assertions, Suites, Tests, Sections, Parameterized, BDD, Matchers, Logging, Runners, Reporters, ...)
Tutorial
Step 0: Get it...
Get the latest latest header/module from here!
Include/Import
// #include <boost/ut.hpp> // single header
// import boost.ut; // single module (C++20)
int main() { }Compile & Run
$CXX main.cpp && ./a.out
All tests passed (0 assert in 0 test)
[Optional] Install it
cmake -Bbuild -H.
cd build && make # run tests
cd build && make install # install
Step 1: Expect it...
Let's write our first assertion, shall we?
int main() {
boost::ut::expect(true);
}All tests passed (1 asserts in 0 test)
Okay, let's make it fail now?
int main() {
boost::ut::expect(1 == 2);
}main.cpp:4:FAILED [false]
===============================================================================
tests: 0 | 0 failed
asserts: 1 | 0 passed | 1 failed
Notice that expression
1 == 2hasn't been printed. Instead we gotfalse?
Let's print it then?
int main() {
using namespace boost::ut;
expect(1_i == 2);
}main.cpp:4:FAILED [1 == 2]
===============================================================================
tests: 0 | 0 failed
asserts: 1 | 0 passed | 1 failed
Okay, now we have it!
1 == 2has been printed as expected. Notice the User Defined Literal (UDL)1_iwas used._iis a compile-time constant integer value
- It allows to override comparison operators 👍
- It disallow comparison of different types 👍
See the User-guide for more details.
Alternatively, other expression syntaxes can be used.
expect(1_i == 2); // UDL syntax
expect(1 == 2_i); // UDL syntax
expect(that % 1 == 2); // Matcher syntax
expect(eq(1, 2)); // eq/neq/gt/ge/lt/lemain.cpp:6:FAILED [1 == 2]
main.cpp:7:FAILED [1 == 2]
main.cpp:8:FAILED [1 == 2]
main.cpp:9:FAILED [1 == 2]
===============================================================================
tests: 0 | 0 failed
asserts: 4 | 0 passed | 4 failed
Okay, but what about the case if my assertion is fatal. Meaning that the program will crash unless the processing will be terminated. Nothing easier, let's just add
!before theexpectcall to make it fatal.
!expect(1 == 2_i); // fatal assertion
expect(1_i == 2); // not executedmain.cpp:6:FAILED [1 == 2]
===============================================================================
tests: 1 | 1 failed
asserts: 2 | 0 passed | 2 failed
But my expression is more complex than just simple comparisons. Not a problem, logic operators are also supported in the
expect👍.
expect(42l == 42_l and 1 == 2_i); // compound expressionmain.cpp:5:FAILED [(42 == 42 and 1 == 2)]
===============================================================================
tests: 0 | 0 failed
asserts: 1 | 0 passed | 1 failed
Can I add a custom message though? Sure,
expectcalls are streamable!
int main() {
expect(42l == 42_l and 1 == 2_i) << "additional info";
}main.cpp:5:FAILED [(42 == 42 and 1 == 2)] additional info
===============================================================================
tests: 0 | 0 failed
asserts: 1 | 0 passed | 1 failed
Step 2: Group it...
Assertions are great, but how to combine them into more cohesive units?
Test casesare the way to go! They allow to group expectations for the same functionality into coherent units.
"hello world"_test = [] { };All tests passed (0 asserts in 1 tests)
Notice
1 testsbut0 asserts.
Let's make our first end-2-end test case, shall we?
int main() {
"hello world"_test = [] {
int i = 42;
expect(42_i == i);
};
}Running "hello world"...
main.cpp:8:FAILED [42 == 43]
FAILED
===============================================================================
tests: 1 | 1 failed
asserts: 1 | 0 passed | 1 failed
👍 We are done here!
I'd like to nest my tests, though and share setup/tear-down. With lambdas used to represents tests we can easily achieve that. Let's just take a look at the following example.
int main() {
"[vector]"_test = [] {
std::vector<int> v(5);
!expect(5_ul == std::size(v));
"resize bigger"_test = [=]() mutable {
v.resize(10);
expect(10_ul == std::size(v));
};
!expect(5_ul == std::size(v));
"resize smaller"_test = [=]() mutable {
v.resize(0);
expect(0_ul == std::size(v));
};
}
}All tests passed (4 asserts in 1 tests)
Nice! That was easy, but I'm a believer into Behaviour Driven Development (BDD). Is there a support for that? Yes! Same example as above just with the BDD syntax.
int main() {
"vector"_test = [] {
given("I have a vector") = [] {
std::vector<int> v(5);
!expect(5_ul == std::size(v));
when("I resize bigger") = [=]() mutable {
v.resize(10);
then("The size should increase") = [=] {
expect(10_ul == std::size(v));
};
};
};
};All tests passed (2 asserts in 1 tests)
That's great, but how can call the same tests with different arguments/types to be DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself)? Parameterized tests to the rescue!
int main() {
"args"_test = [](const auto& arg) {
expect(arg > 0_i) << "all values greater than 0";
} | std::vector{1, 2, 3};
}All tests passed (3 asserts in 3 tests)
Check Examples for further reading.
Step 3: Scale it...
Okay, but my project is more complex than that. How can I scale?
Test suiteswill make that possible. By usingut::suitein translation unitstestsdefined inside will be automatically registered 👍
boost::ut::suite _ = [] {
"suite"_test = [] {
"should be equal"_test = [] { expect(42_i == 42); };
"should not be equal "_test = [] { expect(1_i != 2); };
};
}
int main() { }All tests passed (2 asserts in 1 tests)
What's next?
Examples
Assertions
// operators
expect(0_i == sum());
expect(2_i != sum(1, 2));
expect(sum(1) >= 0_i);
expect(sum(1) <= 1_i);
// message
expect(3_i == sum(1, 2)) << "wrong sum";
//expressions
expect(0_i == sum() and 42_i == sum(40, 2));
expect(0_i == sum() or 1_i == sum()) << "compound";
// that
expect(that % 0 == sum());
expect(that % 42 == sum(40, 2) and that % (1 + 2) == sum(1, 2));
expect(that % 1 != 2 or 2_i > 3);
// eq/neq/gt/ge/lt/le
expect(eq(42, sum(40, 2)));
expect(neq(1, 2));
expect(eq(sum(1), 1) and neq(sum(1, 2), 2));
expect(eq(1, 1) and that % 1 == 1 and 1_i == 1);
// floating points
expect(42.1_d == 42.101) << "epsilon=0.1";
expect(42.10_d == 42.101) << "epsilon=0.01";
expect(42.10000001 == 42.1_d) << "epsilon=0.1";
// constant
constexpr auto compile_time_v = 42;
auto run_time_v = 99;
expect(constant<42_i == compile_time_v> and run_time_v == 99_i);
// fatal
std::vector v{1, 2, 3};
!expect(std::size(v) == 3_ul) << "fatal assertion";
expect(v[0] == 1_i);
expect(v[1] == 2_i);
expect(v[2] == 3_i);
// failure
expect(1_i == 2) << "should fail";
expect(sum() == 1_i or 2_i == sum()) << "sum?";assertions.cpp:53:FAILED [1 == 2] should fail
assertions.cpp:54:FAILED [(0 == 1 or 2 == 0)] sum?
===============================================================================
tests: 0 | 0 failed
asserts: 24 | 22 passed | 2 failed
Tests
Run/Skip
"run"_test = [] {
expect(42_i == 42);
};
skip | "don't run"_test = [] {
expect(42_i == 43) << "should not fire!";
};All tests passed (1 asserts in 1 tests)
1 tests skipped
Sections
"[vector]"_test = [] {
std::vector<int> v(5);
!expect(5_ul == std::size(v));
"resize bigger"_test = [=]() mutable {
v.resize(10);
expect(10_ul == std::size(v));
};
!expect(5_ul == std::size(v));
"resize smaller"_test = [=]() mutable {
v.resize(0);
expect(0_ul == std::size(v));
};
};All tests passed (4 asserts in 1 tests)
Parameterized
"args"_test =
[](const auto& arg) {
expect(arg >= 1_i);
}
| std::vector{1, 2, 3};
"types"_test =
[]<class T> {
expect(std::is_integral_v<T>) << "all types are integrals";
}
| std::tuple<bool, int>{};
"args and types"_test =
[]<class TArg>(const TArg& arg) {
!expect(std::is_integral_v<TArg>);
expect(42_i == arg or true_b == arg);
expect(type<TArg> == type<int> or type<TArg> == type<bool>);
}
| std::tuple{true, 42};All tests passed (11 asserts in 7 tests)
Behavior Driven Development (BDD)
"scenario"_test = [] {
given("I have...") = [] {
when("I run...") = [] {
then("I expect...") = [] { expect(1_i == 1); };
then("I expect...") = [] { expect(1 == 1_i); };
};
};
};All tests passed (2 asserts in 1 tests)
Suites
namespace ut = boost::ut;
ut::suite _ = [] {
using namespace ut;
"equality/exceptions"_test = [] {
"should equal"_test = [] {
expect(42_i == 42);
};
"should throw"_test = [] {
expect(throws([]{throw 0;}));
};
};
};
int main() { }All tests passed (2 asserts in 1 tests)
Misc
Logging
"logging"_test = [] {
log << "pre";
expect(42_i == 43) << "message on failure";
log << "post";
};Running "logging"...
pre
logging.cpp:8:FAILED [42 == 43] message on failure
post
FAILED
===============================================================================
tests: 1 | 1 failed
asserts: 1 | 0 passed | 1 failed
Matchers
"matchers"_test = [] {
constexpr auto is_between = [](auto lhs, auto rhs) {
return matcher([=](auto value) {
return that % value >= lhs and that % value <= rhs;
});
};
expect(is_between(1, 100)(42));
expect(not is_between(1, 100)(0));
};All tests passed (1 asserts in 1 tests)
Exceptions/Aborts
"exceptions/aborts"_test = [] {
expect(throws<std::runtime_error>([]{throw std::runtime_error{""};}))
<< "throws runtime_error";
expect(throws([]{throw 0;})) << "throws any exception";
expect(nothrow([]{})) << "doesn't throw";
expect(aborts([] { assert(false); }));
};All tests passed (4 asserts in 1 tests)
Config
Runner
namespace ut = boost::ut;
namespace cfg {
class runner {
public:
template <class... Ts> auto on(ut::events::test<Ts...> test) { test(); }
template <class... Ts> auto on(ut::events::skip<Ts...>) {}
template <class TLocation, class TExpr>
auto on(ut::events::assertion<TLocation, TExpr>) -> bool { return true; }
auto on(ut::events::fatal_assertion) {}
template <class TMsg> auto on(ut::events::log<TMsg>) {}
};
} // namespace cfg
template<> auto ut::cfg<ut::override> = cfg::runner{};Reporter
namespace ut = boost::ut;
namespace cfg {
class reporter {
public:
auto on(ut::events::test_begin) -> void {}
auto on(ut::events::test_run) -> void {}
auto on(ut::events::test_skip) -> void {}
auto on(ut::events::test_end) -> void {}
template <class TMsg> auto on(ut::events::log<TMsg>) -> void {}
template <class TLocation, class TExpr>
auto on(ut::events::assertion_pass<TLocation, TExpr>) -> void {}
template <class TLocation, class TExpr>
auto on(ut::events::assertion_fail<TLocation, TExpr>) -> void {}
auto on(ut::events::fatal_assertion) -> void {}
auto on(ut::events::exception) -> void {}
auto on(ut::events::summary) -> void {}
};
} // namespace cfg
template <>
auto ut::cfg<ut::override> = ut::runner<cfg::reporter>{};User Guide
API
export module boost.ut; /// __cpp_modules
namespace boost::ut::inline v1_1_1 {
/**
* Represents test suite object
*/
struct suite final {
/**
* Creates and executes test suite
* @example suite _ = [] {};
* @param suite test suite function
*/
constexpr explicit(false) suite(auto suite);
};
/**
* Creates a test
* @example "test name"_test = [] {};
* @return test object to be executed
*/
constexpr auto operator""_test;
/**
* Behaviour Driven Development (BDD) helper functions
* @param name step name
* @return test object to be executed
*/
constexpr auto given = [](auto name);
constexpr auto when = [](auto name);
constexpr auto then = [](auto name);
/**
* Evaluates an expression
* @example expect(42 == 42_i and 1 != 2_i);
* @param expr expression to be evaluated
* @param location [source code location](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/source_location))
* @return stream
*/
constexpr OStream& expect(
Expression expr,
const std::source_location& location = std::source_location::current()
);
struct {
/**
* @example (that % 42 == 42);
* @param expr expression to be evaluated
*/
[[nodiscard]] constexpr auto operator%(Expression expr) const;
} that{};
/**
* @example auto gt_0 = matcher([](auto arg){ return that % arg > 0; })
*/
struct matcher {
/**
* @param expr matcher expression
*/
constexpr explicit(true) matcher_(Expression expr);
/**
* Executes matcher expression
* @param args arguments to be passed to a matcher expression
*/
[[nodiscard]] constexpr auto operator()(const Args&... args) const;
};
inline namespace literals {
/**
* User defined literals to represent constant values
* @example 42_i, 0_uc, 1.23_d
*/
constexpr auto operator""_i; /// int
constexpr auto operator""_s; /// short
constexpr auto operator""_c; /// char
constexpr auto operator""_l; /// long
constexpr auto operator""_ll; /// long long
constexpr auto operator""_u; /// unsigned
constexpr auto operator""_uc; /// unsigned char
constexpr auto operator""_us; /// unsigned short
constexpr auto operator""_ul; /// unsigned long
constexpr auto operator""_f; /// float
constexpr auto operator""_d; /// double
constexpr auto operator""_ld; /// long double
/**
* Represents dynamic values
* @example _i(42), _f(42.)
*/
constexpr auto _b(bool);
constexpr auto _c(char);
constexpr auto _s(short);
constexpr auto _i(int);
constexpr auto _l(long);
constexpr auto _ll(long long);
constexpr auto _u(unsigned);
constexpr auto _uc(unsigned char);
constexpr auto _us(unsigned short);
constexpr auto _ul(unsigned long);
constexpr auto _f(float);
constexpr auto _d(double);
constexpr auto _ld(long double);
/**
* Logical representation of constant values
*/
constexpr auto true_b; /// true
constexpr auto false_b; /// false
} // namespace literals
inline namespace operators {
/**
* Comparison functions to be used in expressions
* @example eq(42, 42), neq(1, 2)
*/
constexpr auto eq(Operator lhs, Operator rhs); /// ==
constexpr auto neq(Operator lhs, Operator rhs); /// !=
constexpr auto gt(Operator lhs, Operator rhs); /// >
constexpr auto ge(Operator lhs, Operator rhs); /// >=
constexpr auto lt(Operator lhs, Operator rhs); /// <
constexpr auto le(Operator lhs, Operator rhs); /// <=
/**
* Overloaded comparison operators to be used in expressions
* @example (42_i != 0)
*/
constexpr auto operator==;
constexpr auto operator!=;
constexpr auto operator>;
constexpr auto operator>=;
constexpr auto operator<;
constexpr auto operator<=;
/**
* Overloaded logic operators to be used in expressions
* @example (42_i != 0 and 1 == 2_i)
*/
constexpr auto operator and;
constexpr auto operator or;
constexpr auto operator not;
/**
* Executes parameterized tests
* @example "parameterized"_test = [](auto arg) {} | std::tuple{1, 2, 3};
*/
constexpr auto operator|;
} // namespace operators
/**
* Creates skippable test object
* @example skip | "don't run"_test = [] { };
*/
struct { } skip{};
struct {
/**
* @example log << "message!";
* @param msg stringable message
*/
auto& operator<<(Msg msg);
} log{};
/**
* Default execution flow policy
*/
class runner {
public:
/**
* @example cfg<override> = { .filter = "test.section.*", .dry_run = true };
* @param options.filter runs all tests which names matches test.section.* filter
* @param options.dry_run if true then print test names to be executed without running them
*/
auto operator=(options);
/**
* @example suite _ = [] {};
* @param suite() executes suite
*/
template<class TSuite>
auto on(ut::events::suite<TSuite>);
/**
* @example "name"_test = [] {};
* @param test.type ["test", "given", "when", "then"]
* @param test.name "name"
* @param test.arg parameterized argument
* @param test() executes test
*/
template<class... Ts>
auto on(ut::events::test<Ts...>);
/**
* @example skip | "don't run"_test = []{};
* @param skip.type ["test", "given", "when", "then"]
* @param skip.name "don't run"
* @param skip.arg parameterized argument
*/
template<class... Ts>
auto on(ut::events::skip<Ts...>);
/**
* @example file.cpp:42: expect(42_i == 42);
* @param assertion.location { "file.cpp", 42 }
* @param assertion.expr 42_i == 42
* @return true if expr passes, false otherwise
*/
template <class TLocation, class TExpr>
auto on(ut::events::assertion<TLocation, TExpr>) -> bool;
/**
* @example !expect(2_i == 1)
* @note triggered by `!expect`
* should std::exit
*/
auto on(ut::events::fatal_assertion);
/**
* @example log << "message"
* @param log.msg "message"
*/
template<class TMsg>
auto on(ut::events::log<TMsg>);
};
/**
* Default reporter policy
*/
class reporter {
public:
/**
* @example "name"_test = [] {};
* @param test_begin.type ["test", "given", "when", "then"]
* @param test_begin.name "name"
*/
auto on(ut::events::test_begin) -> void;
/**
* @example "name"_test = [] {};
* @param test_run.type ["test", "given", "when", "then"]
* @param test_run.name "name"
*/
auto on(ut::events::test_run) -> void;
/**
* @example "name"_test = [] {};
* @param test_skip.type ["test", "given", "when", "then"]
* @param test_skip.name "name"
*/
auto on(ut::events::test_skip) -> void;
/**
* @example "name"_test = [] {};
* @param test_end.type ["test", "given", "when", "then"]
* @param test_end.name "name"
*/
auto on(ut::events::test_end) -> void;
/**
* @example log << "message"
* @param log.msg "message"
*/
template<class TMsg>
auto on(ut::events::log<TMsg>) -> void;
/**
* @example file.cpp:42: expect(42_i == 42);
* @param assertion_pass.location { "file.cpp", 42 }
* @param assertion_pass.expr 42_i == 42
*/
template <class TLocation, class TExpr>
auto on(ut::events::assertion_pass<TLocation, TExpr>) -> void;
/**
* @example file.cpp:42: expect(42_i != 42);
* @param assertion_fail.location { "file.cpp", 42 }
* @param assertion_fail.expr 42_i != 42
*/
template <class TLocation, class TExpr>
auto on(ut::events::assertion_fail<TLocation, TExpr>) -> void;
/**
* @example !expect(2_i == 1)
* @note triggered by `!expect`
* should std::exit
*/
auto on(ut::events::fatal_assertion) -> void;
/**
* @example "exception"_test = [] { throw std::runtime_error{""}; };
*/
auto on(ut::events::exception) -> void;
/**
* @note triggered on destruction of runner
*/
auto on(ut::events::summary) -> void;
};
/**
* Used to override default running policy
* @example template <> auto cfg<override> = runner<reporter>{};
*/
struct override {};
/**
* Default UT execution policy
* Can be overwritten with override
*/
template <class = override> auto cfg = runner<reporter>{};
} // namespace boost::utConfiguration
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
BOOST_UT_VERSION |
Current version | 1'1'1 |
BOOST_UT_FORWARD |
Optionally used in .cpp files to speed up compilation of multiple suites |
|
BOOST_UT_IMPLEMENTATION |
Optionally used in main.cpp file to provide ut implementation (have to be used in combination with BOOST_UT_FORWARD) |
FAQ
How does it work?
suite
/**
* Reperesents suite object
* @example suite _ = []{};
*/
struct suite final {
/**
* Assigns and executes test suite
*/
[[nodiscard]] constexpr explicit(false) suite(Suite suite) {
suite();
}
};
test
/**
* Creates named test object
* @example "hello world"_test
* @return test object
*/
[[nodiscard]] constexpr Test operator ""_test(const char* name, std::size_t size) {
return test{{name, size}};
}/**
* Represents test object
*/
struct test final {
std::string_view name{}; /// test case name
/**
* Assigns and executes test function
* @param test function
*/
constexpr auto operator=(const Test& test) {
std::cout << "Running... " << name << '\n';
test();
}
};
expect
/**
* Evaluates an expression
* @example expect(42_i == 42);
* @param expr expression to be evaluated
* @param location [source code location](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/source_location))
* @return stream
*/
constexpr OStream& expect(
Expression expr,
const std::source_location& location = std::source_location::current()
) {
if (not static_cast<bool>(expr) {
std::cerr << location.file()
<< ':'
<< location.line()
<< ":FAILED: "
<< expr
<< '\n';
}
return std::cerr;
}/**
* Creates constant object for which operators can be overloaded
* @example 42_i
* @return integral constant object
*/
template <char... Cs>
[[nodiscard]] constexpr Operator operator""_i() -> integral_constant<int, value<Cs...>>;/**
* Overloads comparison if at least one of {lhs, rhs} is an Operator
* @example (42_i == 42)
* @param lhs Left-hand side operator
* @param rhs Right-hand side operator
* @return Comparison object
*/
[[nodiscard]] constexpr auto operator==(Operator lhs, Operator rhs) {
return eq{lhs, rhs};
}/**
* Comparison Operator
*/
template <Operator TLhs, Opeartor TRhs>
struct eq final {
TLhs lhs{}; // Left-hand side operator
TRhs rhs{}; // Right-hand side operator
/**
* Performs comparison operatation
* @return true if expression is succesful
*/
[[nodiscard]] constexpr explicit operator bool() const {
return lhs == rhs;
}
/**
* Nicely prints the operation
*/
friend auto operator<<(OStream& os, const eq& op) -> Ostream& {
return (os << op.lhs << " == " << op.rhs);
}
};Can I still use macros?
#define EXPECT(...) ::boost::ut::expect(::boost::ut::that % __VA_ARGS__)
#define SUITE ::boost::ut::suite _ = []
#define TEST(name) ::boost::ut::detail::test{"test", name} = [=]() mutable
SUITE {
TEST("suite") {
EXPECT(42 == 42);
};
};
int main() {
TEST("macro") {
EXPECT(1 != 2);
};
TEST("vector") {
std::vector<int> v(5);
!EXPECT(5u == std::size(v)) << "fatal";
TEST("resize bigger") {
v.resize(10);
EXPECT(10u == std::size(v));
};
};
}All tests passed (4 asserts in 3 tests)
Benchmarks
| Framework | Version | Standard | License | Linkage | Test configuration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boost.Test | 1.71.0 | C++03 | Boost 1.0 | single header/library | static library |
| GoogleTest | 1.10.0 | C++11 | BSD-3 | library | static library |
| Catch | 2.10.2 | C++11 | Boost 1.0 | single header | CATCH_CONFIG_FAST_COMPILE |
| Doctest | 2.3.5 | C++11 | MIT | single header | DOCTEST_CONFIG_SUPER_FAST_ASSERTS |
| μt | 1.1.0 | C++20 | Boost 1.0 | single header/module |
| Include / 0 tests, 0 asserts, 1 cpp file | |||
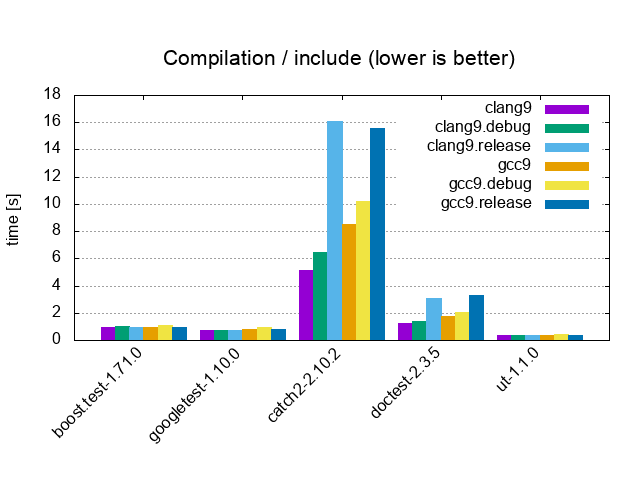 |
|||
| Assert / 1 test, 1'000'000 asserts, 1 cpp file | |||
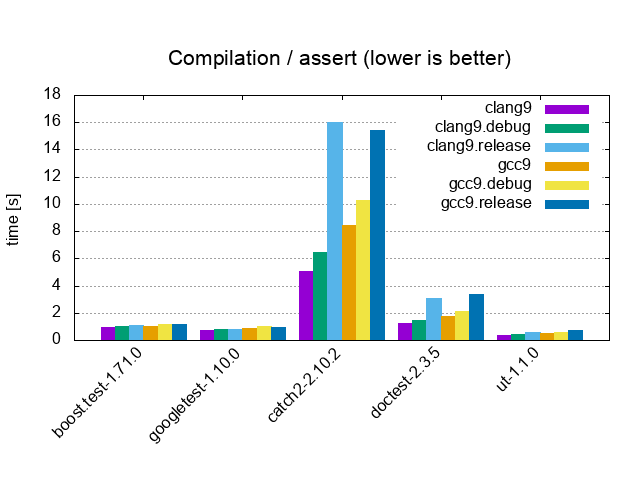 |
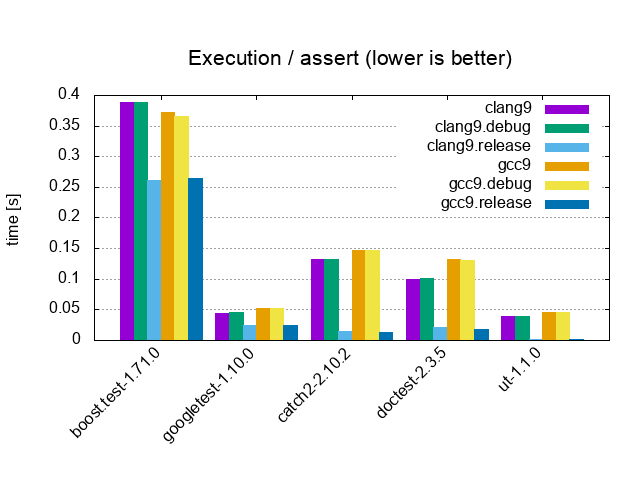 |
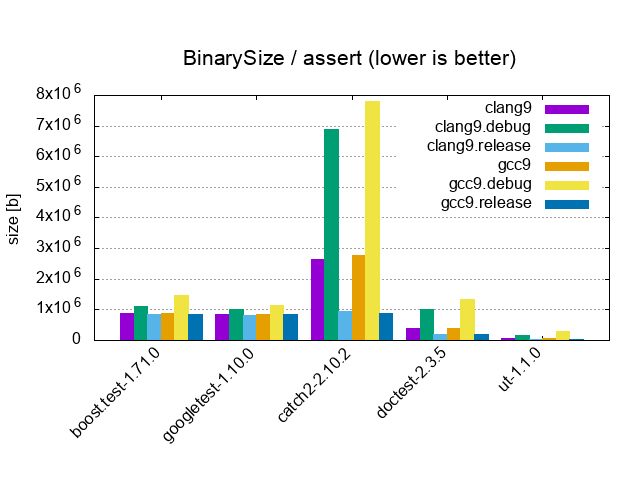 |
|
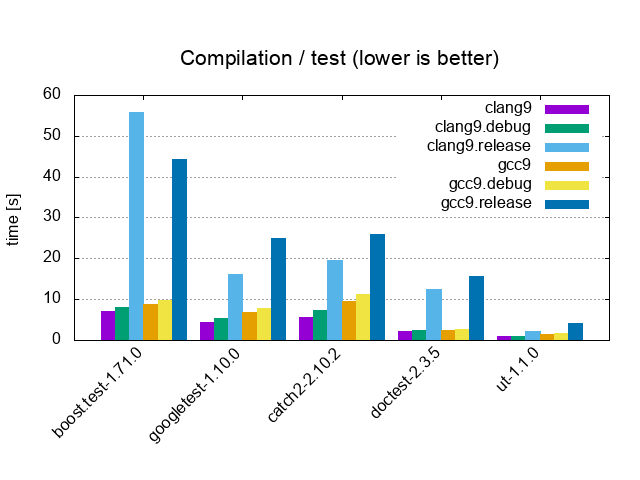
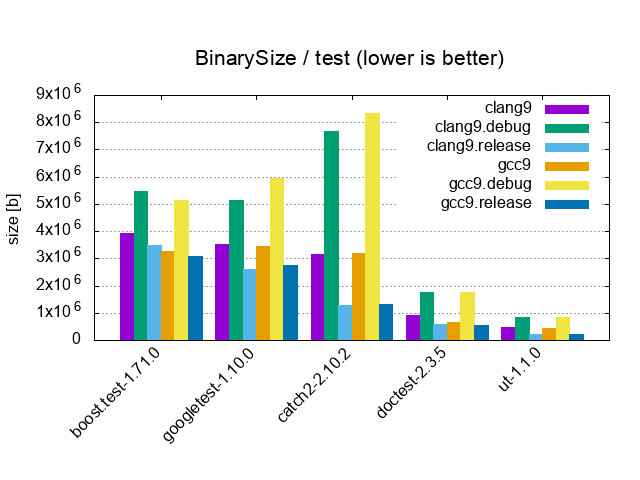
| Test / 1'000 tests, 0 asserts, 1 cpp file | |||
 |
 |
 |
|
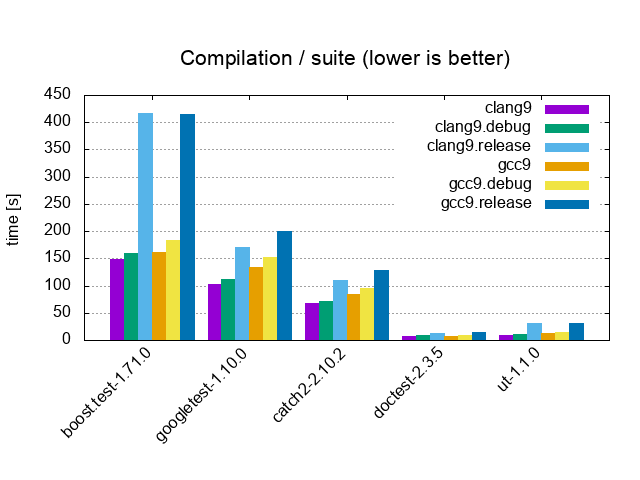
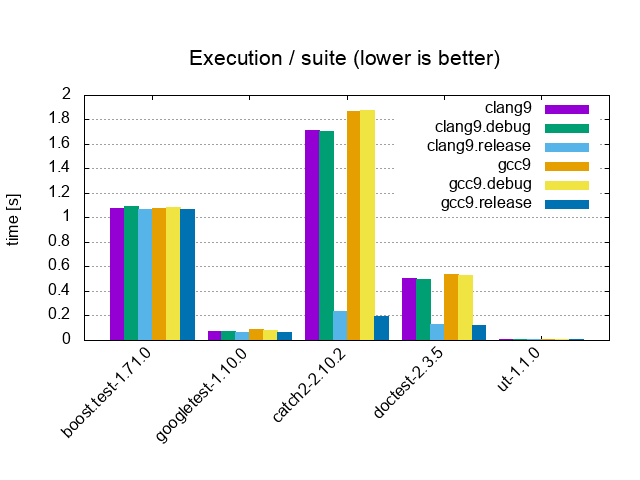
| Suite / 10'000 tests, 0 asserts, 100 cpp files | |||
 |
 |
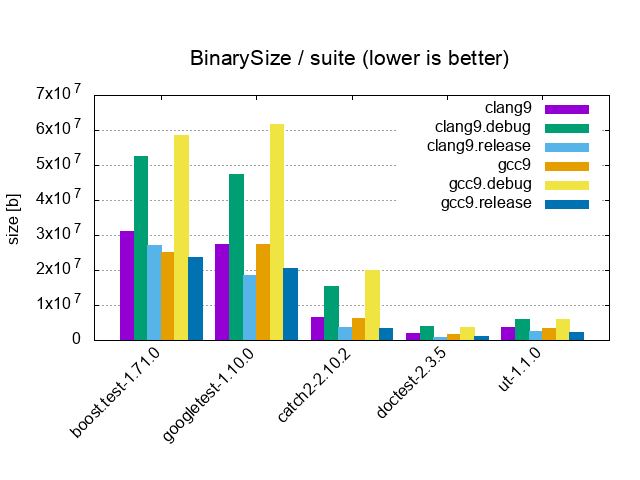 |
|
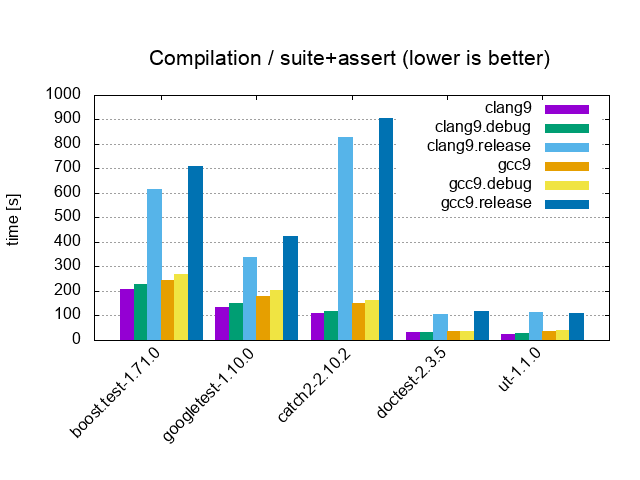
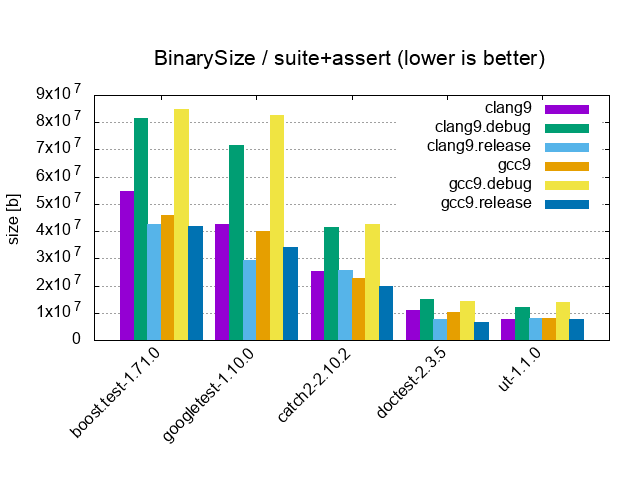
| Suite+Assert / 10'000 tests, 40'000 asserts, 100 cpp files | |||
 |
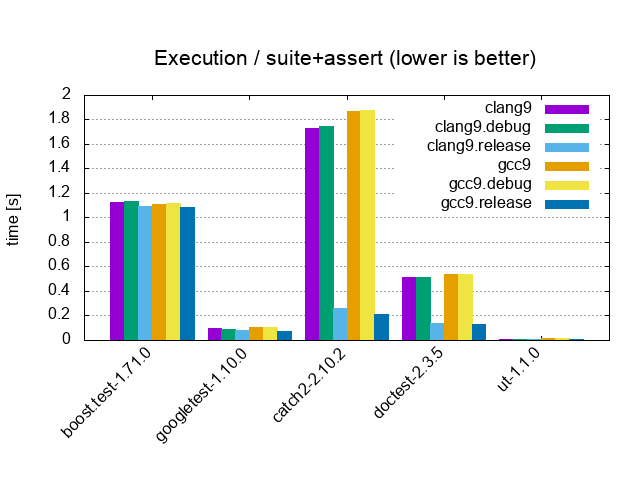 |
 |
|
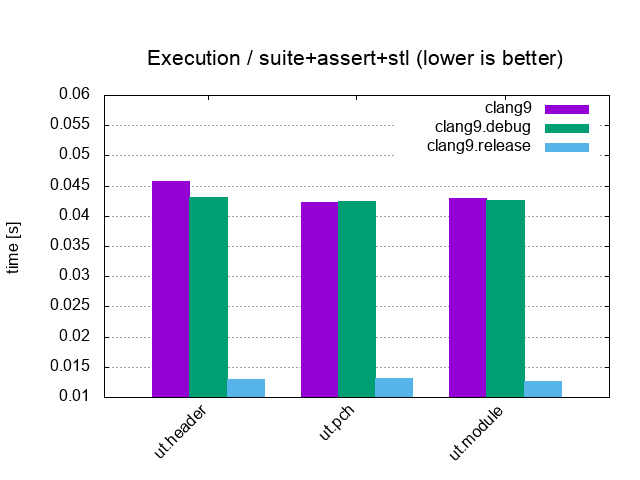
| Suite+Assert+STL / 10'000 tests, 20'000 asserts, 100 cpp files | |||
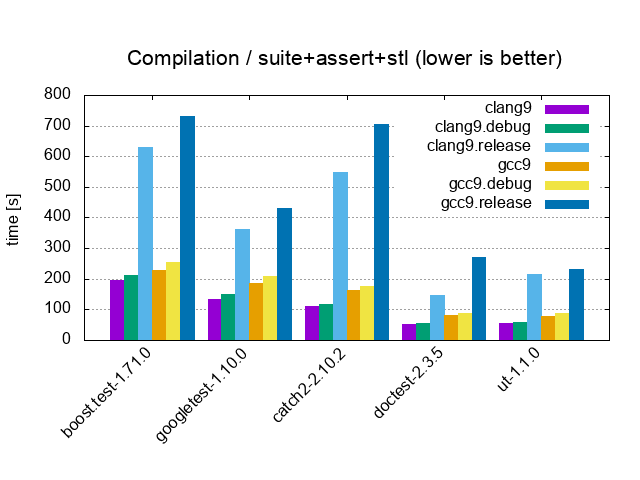 |
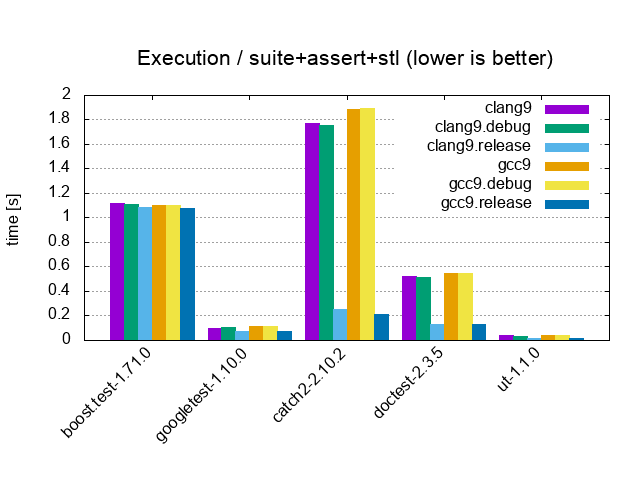 |
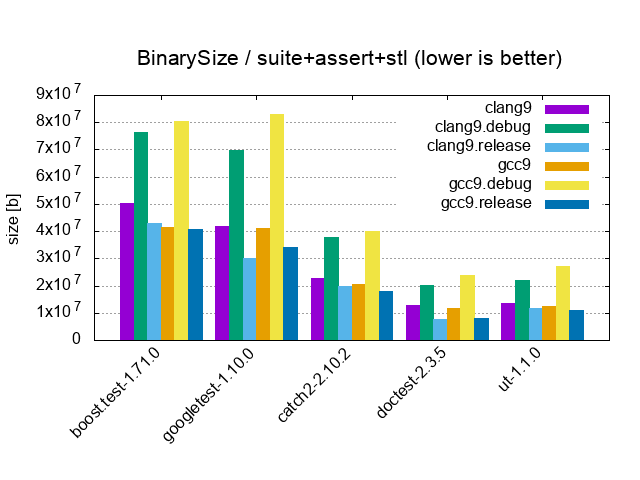 |
|
|
Suite+Assert+STL / 10'000 tests, 20'000 asserts, 100 cpp files (Headers vs Precompiled headers vs C++20 Modules) |
|||
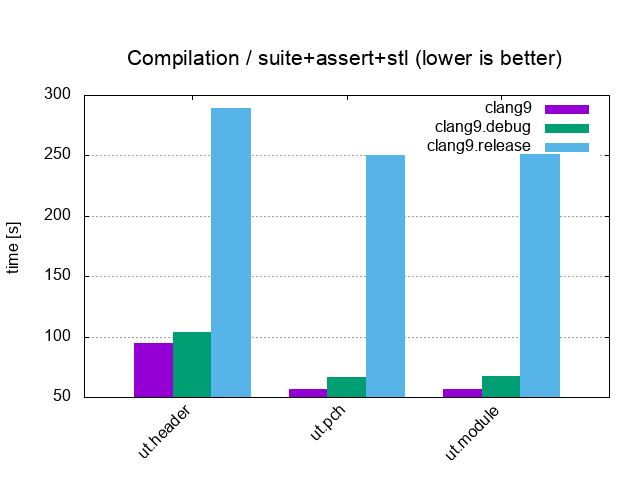 |
 |
 |
|
Disclaimer [Boost].UT is not an official Boost library.






