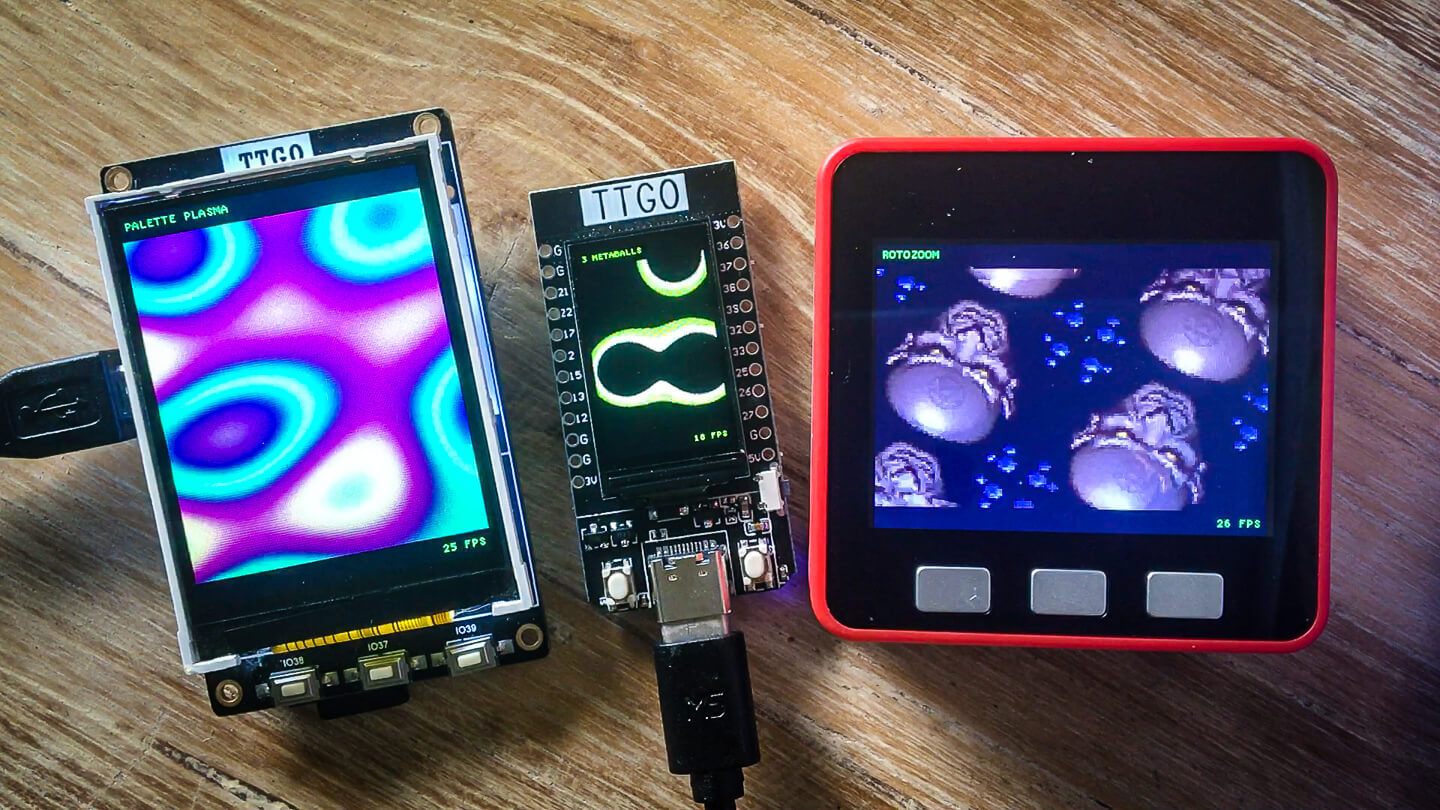
HAGL is a lightweight hardware agnostics graphics library. It supports basic geometric primitives, bitmaps, blitting, fixed width fonts. Library tries to stay lightweight but targets reasonably powerful microchips such as ESP32. There is no dynamic allocation.
This can still be considered work in progress. API should be 90% stable.
To use HAGL you must provide a hardware absraction layer. The HAL must provide atleast a hagl_hal_put_pixel(x0, y0, color) function. If nothing else is provided all higher level graphical functions will use this function to draw the primitive. The HAL can override all functions if required (everything not implemented yet). While proper documentation is lacking see the example HAL implementations for GD, SDL2, ESP-IDF (Ilitek, Sitronix, Galaxycore), ESP-IDF (Solomon), Nuclei RISC-V SDK and Raspberry Pi Pico SDK.
High level functions are pretty self explanatory. For example applications see Pico Effects, ESP Effects, SDL2 Effects, ESP GFX, and GD32V Effects.
Before you start drawing you should call hagl_init(). Some HAL configurations require you to call hagl_flush() to update the contents of the screen. Before exiting your program it is good idea to call hagl_close()to clean things up.
#include <hagl_hal.h>
#include <hagl.h>
hagl_init();
/* Main loop. */
while (1) {
hagl_clear_screen();
hagl_load_image(0, 0, "/sdcard/hello.jpg");
hagl_flush();
};
hagl_close();HAL defines what kind of pixel format is used. Most common is RGB565 which is represented by two bytes. If you are sure you will be using only RGB565 colors you could use the following shortcut to create a random color.
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;To write portable code which can be run with different pixel formats use the following instead.
uint8_t r = rand() % 255;
uint8_t g = rand() % 255;
uint8_t b = rand() % 255;
color_t color = hagl_color(r, g, b);for (uint32_t i = 1; i < 100000; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_put_pixel(x0, y0, color);
}int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t pixel = hagl_get_pixel(x0, y0);Note that if requesting coordinates outside the clip window color black is returned. This behaviour is unoptimal and might change in the future.
for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 1000; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x1 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y1 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_draw_line(x0, y0, x1, y1, color);
}for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 1000; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x1 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y1 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_draw_line(x0, y0, x1, y1, color);
}for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 1000; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % (DISPLAY_WIDTH / 2);
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t width = rand() % (DISPLAY_WIDTH - x0);
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_draw_hline(x0, y0, width, color);
}for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 1000; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % (DISPLAY_HEIGHT / 2);
int16_t height = rand() % (DISPLAY_HEIGHT - y0);
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_draw_vline(x0, y0, height, color);
}for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 500; i++) {
int16_t x0 = DISPLAY_WIDTH / 2;
int16_t y0 = DISPLAY_HEIGHT / 2;
int16_t radius = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_draw_circle(x0, y0, radius, color);
}for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 500; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t radius = rand() % 100;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_fill_circle(x0, y0, radius, color);
}for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 500; i++) {
int16_t x0 = DISPLAY_WIDTH / 2;
int16_t y0 = DISPLAY_HEIGHT / 2;
int16_t rx = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t ry = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_draw_ellipse(x0, y0, rx, ry, color);
}for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 500; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t rx = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH / 4;
int16_t ry = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT / 4;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_fill_ellipse(x0, y0, rx, ry, color);
}int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x1 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y1 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x2 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y2 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_draw_triangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, color);int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x1 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y1 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x2 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y2 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_fill_triangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, color);for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 50; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x1 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y1 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_draw_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, color);
}for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x1 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y1 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_fill_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, color);
}for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 30; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x1 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y1 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t r = 10
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_draw_rounded_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, r, color);
}for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 30; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x1 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y1 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t r = 10
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_fill_rounded_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, r, color);
}You can draw polygons with unlimited number of vertices which are passed as an array. Pass the number of vertices as the first argument.
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x1 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y1 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x2 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y2 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x3 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y3 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x4 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y4 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
int16_t vertices[10] = {x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4};
hagl_draw_polygon(5, vertices, color);You can draw filled polygons with up to 64 vertices which are passed as an array. First argument is the number of vertices. Polygon does not have to be concave.
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x1 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y1 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x2 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y2 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x3 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y3 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t x4 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y4 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
int16_t vertices[10] = {x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4};
hagl_fill_polygon(5, vertices, color);The library supports Unicode fonts in fontx format. It only includes three fonts by default. You can find more at tuupola/embedded-fonts repository.
for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 10000; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
char code = rand() % 255;
hagl_put_char(code, x0, y0, color, font8x8);
}The library supports Unicode fonts in fontx format. It only includes three fonts by default. You can find more at tuupola/embedded-fonts repository.
for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 10000; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_put_text(u"YO! MTV raps.", x0, y0, color, font6x9);
}Blit copies a bitmap to the screen. This example uses a glyph bitmap which is extracted from a font.
bitmap_t bitmap;
bitmap.buffer = (uint8_t *) malloc(6 * 9 * sizeof(color_t));
for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 20000; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
uint16_t code = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_get_glyph(code, color, &bitmap, font6x9);
hagl_blit(x0, y0, &bitmap);
}Scale blit copies and scales a bitmap to the screen. This example uses a glyph bitmap which is extracted from a font.
bitmap_t bitmap;
bitmap.buffer = (uint8_t *) malloc(6 * 9 * sizeof(color_t));
for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 20000; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
uint16_t code = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_get_glyph(code, color, &bitmap, font6x9);
hagl_scale_blit(x0, y0, 24, 36, &bitmap);
}You can restrict the area of drawing by setting a clip window.
hagl_set_clip_window(0, 40, DISPLAY_WIDTH, DISPLAY_HEIGHT - 40);
for (uint16_t i = 1; i < 500; i++) {
int16_t x0 = rand() % DISPLAY_WIDTH;
int16_t y0 = rand() % DISPLAY_HEIGHT;
int16_t radius = rand() % 100;
color_t color = rand() % 0xffff;
hagl_fill_circle(x0, y0, radius, color);
}If you want to cleant the contents of the clip window instead of clearing the whole screen call:
hagl_clear_clip_window()First table numbers are operations per second with double buffering enabled. Bigger number is better. T-Display and M5StickC have higher numbers because they have smaller resolution. Smaller resolution means less bytes to push to the display.
| T4 | T-Display | M5Stack | M5StickC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hagl_put_pixel() | 304400 | 304585 | 340850 | 317094 |
| hagl_draw_line() | 10485 | 14942 | 12145 | 31293 |
| hagl_draw_circle() | 15784 | 16430 | 17730 | 18928 |
| hagl_fill_circle() | 8712 | 9344 | 9982 | 13910 |
| hagl_draw_ellipse() | 8187 | 8642 | 9168 | 10019 |
| hagl_fill_ellipse() | 3132 | 3457 | 3605 | 5590 |
| hagl_draw_triangle() | 3581 | 5137 | 4160 | 11186 |
| hagl_fill_triangle() | 1246 | 1993 | 1654 | 6119 |
| hagl_draw_rectangle() | 22759 | 30174 | 26910 | 64259 |
| hagl_fill_rectangle() | 2191 | 4849 | 2487 | 16146 |
| hagl_draw_rounded_rectangle() | 17660 | 21993 | 20736 | 39102 |
| hagl_fill_rounded_rectangle() | 2059 | 4446 | 2313 | 13270 |
| hagl_draw_polygon() | 2155 | 3096 | 2494 | 6763 |
| hagl_fill_polygon() | 692 | 1081 | 938 | 3295 |
| hagl_put_char() | 29457 | 29131 | 32429 | 27569 |
| hagl_flush() | 32 | 76 | 32 | 96 |
Second table numbers are operations per second with double buffering disabled.
| T4 | T-Display | M5Stack | M5StickC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hagl_put_pixel() | 16041 | 15252 | 16044 | 24067 |
| hagl_draw_line() | 113 | 172 | 112 | 289 |
| hagl_draw_circle() | 148 | 173 | 145 | 230 |
| hagl_fill_circle() | 264 | 278 | 261 | 341 |
| hagl_draw_ellipse() | 84 | 103 | 85 | 179 |
| hagl_fill_ellipse() | 114 | 128 | 116 | 191 |
| hagl_draw_triangle() | 37 | 54 | 37 | 114 |
| hagl_fill_triangle() | 72 | 111 | 72 | 371 |
| hagl_draw_rectangle() | 2378 | 2481 | 2374 | 3482 |
| hagl_fill_rectangle() | 91 | 146 | 91 | 454 |
| hagl_draw_rounded_rectangle() | 458 | 535 | 459 | 808 |
| hagl_fill_rounded_rectangle() | 87 | 139 | 79 | 400 |
| hagl_draw_polygon() | 21 | 33 | 19 | 71 |
| hagl_fill_polygon() | 43 | 66 | 49 | 228 |
| hagl_put_char) | 4957 | 4264 | 4440 | 2474 |
| hagl_flush() | x | x | x | x |
You can run the speed tests yourself by checking out the speedtest repository.
The MIT License (MIT). Please see License File for more information.