-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 18
06 Build and Install
IMPORTANT OBAL is tested on Raspberry Pi OS Lite (Legacy), Although Ardupilot can run on Raspberry Bullseye-64bit after this PR-22418, but you need to recombile Linux kernel to enable CONFIG_STRICT_DEVMEM. for more details about this topic pleae check my article here.
Remaining steps are the same for both OS-Legacy or OS-64.
Download Binaries from here. Select vehicle type then search for OBAL. For obal copter version 4.2.2
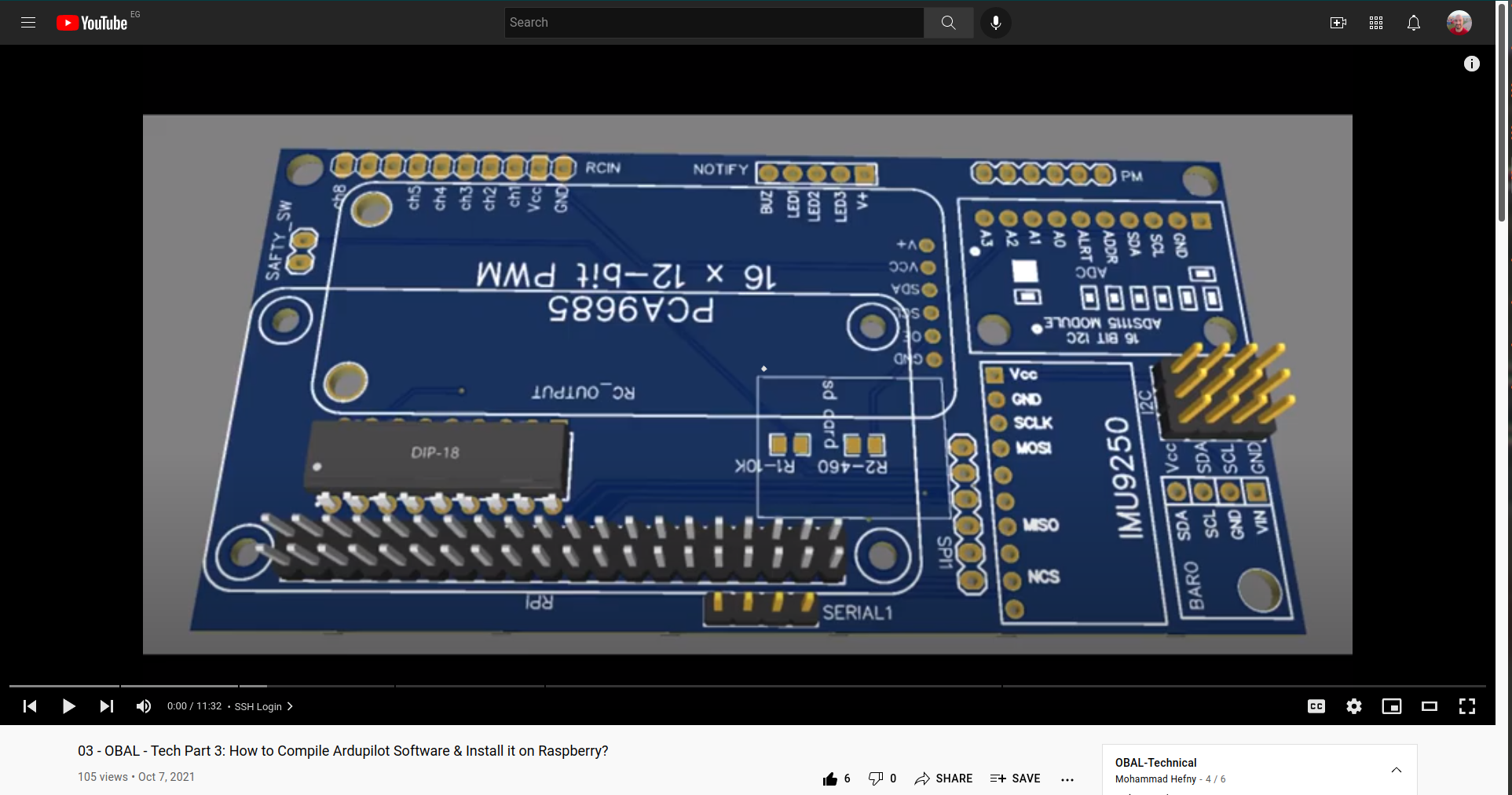
This board does not have any closed source or special drivers. Any Raspberry-Pi board will do the job. All you need is to compile Ardupilot from its main repository. It is straightforward.
git clone https://github.com/ArduPilot/ardupilot.git
cd ardupilot
git submodule update --init --recursive
make obal
For Raspberry-Zero you can download its cross-tool from here
you can compile using the following command
./waf configure --toolchain=/opt/cross-pi-gcc/bin/arm-linux-gnueabihf --board obal
./waf rover
./waf copter
./waf plane
IMPORTANT: If you are using OBAL_GY91 you need to apply patch
- Copy ardupilot binary to /home/pi .
- Create empty file /home/pi/ardupilot.parm using
touch /home/pi/ardupilot.parmyou can add any initialization parameters to this file. For example for Quadcopter X configuration:
create ardupilot.parm with the following data.
SYSID_THISMAV 1
FRAME_CLASS 1
FRAME_TYPE 1
ArduCopter:
sudo /home/pi/arducopter (plus parameter)
ArduPlane:
sudo /home/pi/arduplane (plus parameter)
ArduRover:
sudo /home/pi/ardurover (plus parameter)
ArduSub:
sudo /home/pi/ardusub (plus parameter)
| Start Parameter | ArduPilot Serial Port |
|---|---|
| -A | SERIAL0 |
| -B | SERIAL3 |
| -C | SERIAL1 |
| -D | SERIAL2 |
| -E | SERIAL4 |
| -F | SERIAL5 |
Check http://ardupilot.org/copter/docs/parameters.html#serial0-baud-serial0-baud-rate to set the right value for SERIALx_BAUD and SERIALx_PROTOCOL
To connect a MAVLink groundstation with IP 192.168.1.123 add -C udp:192.168.1.123:14550
To use MAVLink via radio connected to Serial0 add -C /dev/serial0.
If there is a GPS connected to Serial1 add -B /dev/serial1.
Note: OBAL board default port is serial 0
Example: MAVLink groundstation with IP 192.168.178.26 on port 14550 via wifi and GPS connected to /dev/serial0 and telemetry via OTG /dev/serial1.
sudo /home/pi/arducopter -A udp:192.168.1.123:14550 -B /dev/serial0 -C serial1
create service file and edit it
sudo nano /lib/systemd/system/ardurover.service
[Unit]
Description=ArduPilot-Rover for Linux OPAL Board
After=systemd-modules-load.service
Documentation=https://docs.obal.com/page.html
Conflicts=arduplane.service arducopter.service ardurover.service
[Service]
Type=single
ExecStart=/home/pi/ardurover -A udp:**YourTargetIP**:14550:bcast -B /dev/serial0
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Above file is for running rover but you can replace ardurover with other binaries e.g. arducopter & arduplane.
sudo systemctl enable ardurover.service
sudo systemctl start ardurover.service
When running RPI-4 or **RPI-Zero 2W **and using Camera or running other software with ardupilot, it is recommended to give ardupilot 1 or 2 dedicated CPUs to run on. This enhannce Ardupilot schedule timing as we are not running Linux-RT.
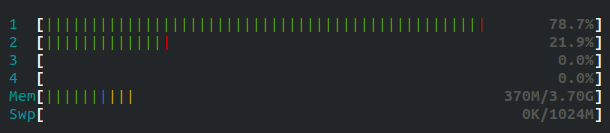
The below image shows cpu status using htop when cpu 3 & 4 are isolated using isocpus=2,3
yes values 2 & 3 are mapped to cpu 3 & 4yes values 2 & 3 are mapped to cpu 3 & 4
First free one or more cpus in RPI by adding isolcpus to /boot/cmdline.txt for example below is execution of
cat /boot/cmdline.txtconsole=tty1 root=PARTUUID=d9b3f436-02 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline fsck.repair=yes rootwait modules-load=dwc2,g_ether quiet splash plymouth.ignore-serial-consoles isolcpus=2,3You need to reboot here.
sudo reboot now
in Ardupilot you need to add parameter -c or --cpu-affinity for example:
/home/pi/ardurover -A udp:**YourTargetIP**:14550:bcast -B /dev/serial0 -c 2,3