diff --git a/.gitmodules b/.gitmodules
index faaf0846c8..7991ab6c60 100644
--- a/.gitmodules
+++ b/.gitmodules
@@ -71,3 +71,6 @@
[submodule "external/xbyak"]
path = external/xbyak
url = https://github.com/herumi/xbyak.git
+[submodule "external/xxHash"]
+ path = external/xxHash
+ url = https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash.git
diff --git a/CMakeLists.txt b/CMakeLists.txt
index 8be1eba24b..6926753906 100644
--- a/CMakeLists.txt
+++ b/CMakeLists.txt
@@ -377,7 +377,7 @@ endif()
option(BUILD_SHARED_LIBS "Build shared library" OFF)
set(XXHASH_BUILD_XXHSUM OFF CACHE BOOL "Build the xxhsum binary")
-add_subdirectory(core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial)
+add_subdirectory(external/xxHash/cmake_unofficial)
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE xxHash::xxhash)
option(BUILD_SHARED_LIBS "Build shared library" OFF)
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/.gitattributes b/core/deps/xxHash/.gitattributes
deleted file mode 100644
index fbcf75b555..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/.gitattributes
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
-# Set the default behavior
-* text eol=lf
-
-# Explicitly declare source files
-*.c text eol=lf
-*.h text eol=lf
-
-# Denote files that should not be modified.
-*.odt binary
-
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/.gitignore b/core/deps/xxHash/.gitignore
deleted file mode 100644
index 2d6deb9f4a..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/.gitignore
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
-# objects
-*.o
-*.obj
-*.s
-
-# libraries
-libxxhash.*
-!libxxhash.pc.in
-
-# Executables
-*.exe
-xxh32sum
-xxh64sum
-xxh128sum
-xxhsum
-xxhsum32
-xxhsum_privateXXH
-xxhsum_inlinedXXH
-tests/generate_unicode_test
-
-# compilation chain
-.clang_complete
-
-# Mac OS-X artefacts
-*.dSYM
-.DS_Store
-
-# Wasm / emcc / emscripten artefacts
-*.html
-*.wasm
-*.js
-
-# CMake build directories
-build*/
-
-# project managers artifacts
-.projectile
-
-# analyzer artifacts
-infer-out
-
-# test artifacts
-.test*
-tmp*
-tests/*.unicode
-tests/unicode_test*
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/.travis.yml b/core/deps/xxHash/.travis.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index d960cce30c..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/.travis.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,113 +0,0 @@
-language: c
-
-# Dump CPU info before start
-before_install:
- - cat /proc/cpuinfo
-
-matrix:
- fast_finish: true
- include:
-
- - name: General linux tests (Xenial)
- dist: xenial
- arch: amd64
- addons:
- apt:
- packages:
- - clang
- - g++-multilib
- - gcc-multilib
- - cppcheck
- script:
- - make -B test-all
-
- - name: Check results consistency on x64
- arch: amd64
- script:
- - CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=0 make check # Scalar code path
- - make clean
- - CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=1 make check # SSE2 code path
- - make clean
- - CPPFLAGS="-mavx2 -DXXH_VECTOR=2" make check # AVX2 code path
- - make clean
- - CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_REROLL=1 make check # reroll code path (#240)
- - make -C tests/bench
-
- - name: ARM compilation and consistency checks (Qemu)
- dist: xenial
- arch: amd64
- addons:
- apt:
- packages:
- - qemu-system-arm
- - qemu-user-static
- - gcc-arm-linux-gnueabi
- - libc6-dev-armel-cross
- script:
- # arm (32-bit)
- - CC=arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=0 LDFLAGS=-static RUN_ENV=qemu-arm-static make check # Scalar code path
- - make clean
- # NEON (32-bit)
- - CC=arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=3 CFLAGS="-O3 -march=armv7-a -fPIC -mfloat-abi=softfp -mfpu=neon-vfpv4" LDFLAGS=-static RUN_ENV=qemu-arm-static make check # NEON code path
-
- - name: aarch64 compilation and consistency checks
- dist: xenial
- arch: arm64
- script:
- # aarch64
- - CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=0 LDFLAGS=-static make check # Scalar code path
- # NEON (64-bit)
- - make clean
- - CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=3 LDFLAGS=-static make check # NEON code path
-
- # We need Bionic here because the QEMU versions shipped in the older repos
- # do not support POWER8 emulation, and compiling QEMU from source is a pain.
- - name: PowerPC + PPC64 compilation and consistency checks (Qemu on Bionic)
- dist: bionic
- arch: amd64
- addons:
- apt:
- packages:
- - qemu-system-ppc
- - qemu-user-static
- - gcc-powerpc-linux-gnu
- - gcc-powerpc64-linux-gnu
- - libc6-dev-powerpc-cross
- - libc6-dev-ppc64-cross
- script:
- - CC=powerpc-linux-gnu-gcc RUN_ENV=qemu-ppc-static LDFLAGS=-static make check # Scalar code path
- - make clean
- - CC=powerpc64-linux-gnu-gcc RUN_ENV=qemu-ppc64-static CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=0 CFLAGS="-O3" LDFLAGS="-static -m64" make check # Scalar code path
- - make clean
- # VSX code
- - CC=powerpc64-linux-gnu-gcc RUN_ENV="qemu-ppc64-static -cpu power8" CFLAGS="-O3 -maltivec -mvsx -mcpu=power8 -mpower8-vector" LDFLAGS="-static -m64" make check # Auto code path
- - make clean
-
- - name: PPC64LE compilation and consistency checks
- dist: xenial
- arch: ppc64le
- script:
- # Scalar (universal) code path
- - CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=0 LDFLAGS=-static make check
- # VSX code path (64-bit)
- - make clean
- - CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=4 CFLAGS="-O3 -maltivec -mvsx -mpower8-vector -mcpu=power8" LDFLAGS="-static" make check
-
- - name: IBM s390x compilation and consistency checks
- dist: bionic
- arch: s390x
- script:
- # Scalar (universal) code path
- - CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=0 LDFLAGS=-static make check
- # s390x code path (64-bit)
- - make clean
- - CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_VECTOR=4 CFLAGS="-O3 -march=arch11 -mzvector" LDFLAGS="-static" make check
-
- - name: cmake build test
- script:
- - cd cmake_unofficial
- - mkdir build
- - cd build
- - cmake ..
- - make
-
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/CHANGELOG b/core/deps/xxHash/CHANGELOG
deleted file mode 100644
index aa9d6ffb17..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/CHANGELOG
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
-v0.7.3
-- perf: improved speed for large inputs (~+20%)
-- perf: improved latency for small inputs (~10%)
-- perf: s390x Vectorial code, by @easyaspi314
-- cli: improved support for Unicode filenames on Windows, thanks to @easyaspi314 and @t-mat
-- api: `xxhash.h` can now be included in any order, with and without `XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY` and `XXH_INLINE_ALL`
-- build: xxHash's implementation transferred into `xxhash.h`. No more need to have `xxhash.c` in the `/include` directory for `XXH_INLINE_ALL` to work
-- install: created pkg-config file, by @bket
-- install: VCpkg installation instructions, by @LilyWangL
-- doc: Highly improved code documentation, by @easyaspi314
-- misc: New test tool in `/tests/collisions`: brute force collision tester for 64-bit hashes
-
-v0.7.2
-- Fixed collision ratio of `XXH128` for some specific input lengths, reported by @svpv
-- Improved `VSX` and `NEON` variants, by @easyaspi314
-- Improved performance of scalar code path (`XXH_VECTOR=0`), by @easyaspi314
-- `xxhsum`: can generate 128-bit hashes with the `-H2` option (note: for experimental purposes only! `XXH128` is not yet frozen)
-- `xxhsum`: option `-q` removes status notifications
-
-v0.7.1
-- Secret first: the algorithm computation can be altered by providing a "secret", which is any blob of bytes, of size >= `XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN`.
-- `seed` is still available, and acts as a secret generator
-- updated `ARM NEON` variant by @easyaspi314
-- Streaming implementation is available
-- Improve compatibility and performance with Visual Studio, with help from @aras-p
-- Better integration when using `XXH_INLINE_ALL`: do not pollute host namespace, use its own macros, such as `XXH_ASSERT()`, `XXH_ALIGN`, etc.
-- 128-bit variant provides helper functions for comparison of hashes.
-- Better `clang` generation of `rotl` instruction, thanks to @easyaspi314
-- `XXH_REROLL` build macro to reduce binary size, by @easyaspi314
-- Improved `cmake` script, by @Mezozoysky
-- Full benchmark program provided in `/tests/bench`
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/LICENSE b/core/deps/xxHash/LICENSE
deleted file mode 100644
index bf27305e1b..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/LICENSE
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
-xxHash Library
-Copyright (c) 2012-present, Yann Collet
-All rights reserved.
-
-BSD 2-Clause License (https://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php)
-
-Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification,
-are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
-
-* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
- list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
-
-* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this
- list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or
- other materials provided with the distribution.
-
-THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND
-ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
-WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
-DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR
-ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
-(INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
-LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON
-ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
-(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS
-SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
-
-----------------------------------------------------
-
-xxhsum command line interface
-Copyright (c) 2013-present, Yann Collet
-All rights reserved.
-
-GPL v2 License
-
-This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
-it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
-the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
-(at your option) any later version.
-
-This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
-but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
-MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
-GNU General Public License for more details.
-
-You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
-with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
-51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/Makefile b/core/deps/xxHash/Makefile
deleted file mode 100644
index 30e92278a0..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/Makefile
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,407 +0,0 @@
-# ################################################################
-# xxHash Makefile
-# Copyright (C) Yann Collet 2012-present
-#
-# GPL v2 License
-#
-# This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
-# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
-# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
-# (at your option) any later version.
-#
-# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
-# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
-# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
-# GNU General Public License for more details.
-#
-# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
-# with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
-# 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
-#
-# You can contact the author at:
-# - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
-# - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
-# ################################################################
-# xxhsum: provides 32/64 bits hash of one or multiple files, or stdin
-# ################################################################
-
-# Version numbers
-LIBVER_MAJOR_SCRIPT:=`sed -n '/define XXH_VERSION_MAJOR/s/.*[[:blank:]]\([0-9][0-9]*\).*/\1/p' < xxhash.h`
-LIBVER_MINOR_SCRIPT:=`sed -n '/define XXH_VERSION_MINOR/s/.*[[:blank:]]\([0-9][0-9]*\).*/\1/p' < xxhash.h`
-LIBVER_PATCH_SCRIPT:=`sed -n '/define XXH_VERSION_RELEASE/s/.*[[:blank:]]\([0-9][0-9]*\).*/\1/p' < xxhash.h`
-LIBVER_MAJOR := $(shell echo $(LIBVER_MAJOR_SCRIPT))
-LIBVER_MINOR := $(shell echo $(LIBVER_MINOR_SCRIPT))
-LIBVER_PATCH := $(shell echo $(LIBVER_PATCH_SCRIPT))
-LIBVER := $(LIBVER_MAJOR).$(LIBVER_MINOR).$(LIBVER_PATCH)
-
-CFLAGS ?= -O3
-DEBUGFLAGS+=-Wall -Wextra -Wconversion -Wcast-qual -Wcast-align -Wshadow \
- -Wstrict-aliasing=1 -Wswitch-enum -Wdeclaration-after-statement \
- -Wstrict-prototypes -Wundef -Wpointer-arith -Wformat-security \
- -Wvla -Wformat=2 -Winit-self -Wfloat-equal -Wwrite-strings \
- -Wredundant-decls -Wstrict-overflow=2
-CFLAGS += $(DEBUGFLAGS)
-FLAGS = $(CFLAGS) $(CPPFLAGS) $(MOREFLAGS)
-XXHSUM_VERSION = $(LIBVER)
-
-# Define *.exe as extension for Windows systems
-ifneq (,$(filter Windows%,$(OS)))
-EXT =.exe
-else
-EXT =
-endif
-
-# OS X linker doesn't support -soname, and use different extension
-# see: https://developer.apple.com/library/mac/documentation/DeveloperTools/Conceptual/DynamicLibraries/100-Articles/DynamicLibraryDesignGuidelines.html
-ifeq ($(shell uname), Darwin)
- SHARED_EXT = dylib
- SHARED_EXT_MAJOR = $(LIBVER_MAJOR).$(SHARED_EXT)
- SHARED_EXT_VER = $(LIBVER).$(SHARED_EXT)
- SONAME_FLAGS = -install_name $(LIBDIR)/libxxhash.$(SHARED_EXT_MAJOR) -compatibility_version $(LIBVER_MAJOR) -current_version $(LIBVER)
-else
- SONAME_FLAGS = -Wl,-soname=libxxhash.$(SHARED_EXT).$(LIBVER_MAJOR)
- SHARED_EXT = so
- SHARED_EXT_MAJOR = $(SHARED_EXT).$(LIBVER_MAJOR)
- SHARED_EXT_VER = $(SHARED_EXT).$(LIBVER)
-endif
-
-LIBXXH = libxxhash.$(SHARED_EXT_VER)
-
-
-.PHONY: default
-default: ## generate CLI and libraries in release mode (default for `make`)
-default: DEBUGFLAGS=
-default: lib xxhsum_and_links
-
-.PHONY: all
-all: lib xxhsum xxhsum_inlinedXXH
-
-xxhsum: xxhash.o xxhsum.o ## generate command line interface (CLI)
- $(CC) $(FLAGS) $^ $(LDFLAGS) -o $@$(EXT)
-
-xxhsum32: CFLAGS += -m32 ## generate CLI in 32-bits mode
-xxhsum32: xxhash.c xxhsum.c ## do not generate object (avoid mixing different ABI)
- $(CC) $(FLAGS) $^ $(LDFLAGS) -o $@$(EXT)
-
-xxhash.o: xxhash.c xxhash.h xxh3.h
- $(CC) $(FLAGS) -c $< -o $@
-xxhsum.o: xxhsum.c xxhash.h
- $(CC) $(FLAGS) -c $< -o $@
-
-.PHONY: xxhsum_and_links
-xxhsum_and_links: xxhsum xxh32sum xxh64sum xxh128sum
-
-xxh32sum xxh64sum xxh128sum: xxhsum
- ln -sf $<$(EXT) $@$(EXT)
-
-xxhsum_inlinedXXH: CPPFLAGS += -DXXH_INLINE_ALL
-xxhsum_inlinedXXH: xxhsum.c
- $(CC) $(FLAGS) $^ -o $@$(EXT)
-
-
-# library
-
-libxxhash.a: ARFLAGS = rcs
-libxxhash.a: xxhash.o
- $(AR) $(ARFLAGS) $@ $^
-
-$(LIBXXH): LDFLAGS += -shared
-ifeq (,$(filter Windows%,$(OS)))
-$(LIBXXH): CFLAGS += -fPIC
-endif
-$(LIBXXH): xxhash.c
- $(CC) $(FLAGS) $^ $(LDFLAGS) $(SONAME_FLAGS) -o $@
- ln -sf $@ libxxhash.$(SHARED_EXT_MAJOR)
- ln -sf $@ libxxhash.$(SHARED_EXT)
-
-.PHONY: libxxhash
-libxxhash: ## generate dynamic xxhash library
-libxxhash: $(LIBXXH)
-
-.PHONY: lib
-lib: ## generate static and dynamic xxhash libraries
-lib: libxxhash.a libxxhash
-
-pkgconfig:
- @sed -e 's|@PREFIX@|$(PREFIX)|' \
- -e 's|@VERSION@|$(LIBVER)|' \
- libxxhash.pc.in >libxxhash.pc
-
-# helper targets
-
-AWK = awk
-GREP = grep
-SORT = sort
-
-.PHONY: list
-list: ## list all Makefile targets
- @$(MAKE) -pRrq -f $(lastword $(MAKEFILE_LIST)) : 2>/dev/null | $(AWK) -v RS= -F: '/^# File/,/^# Finished Make data base/ {if ($$1 !~ "^[#.]") {print $$1}}' | $(SORT) | egrep -v -e '^[^[:alnum:]]' -e '^$@$$' | xargs
-
-.PHONY: help
-help: ## list documented targets
- @$(GREP) -E '^[0-9a-zA-Z_-]+:.*?## .*$$' $(MAKEFILE_LIST) | \
- $(SORT) | \
- $(AWK) 'BEGIN {FS = ":.*?## "}; {printf "\033[36m%-30s\033[0m %s\n", $$1, $$2}'
-
-.PHONY: clean
-clean: ## remove all build artifacts
- @$(RM) -r *.dSYM # Mac OS-X specific
- @$(RM) core *.o *.$(SHARED_EXT) *.$(SHARED_EXT).* *.a libxxhash.pc
- @$(RM) xxhsum$(EXT) xxhsum32$(EXT) xxhsum_inlinedXXH$(EXT)
- @$(RM) xxh32sum$(EXT) xxh64sum$(EXT) xxh128sum$(EXT)
- @echo cleaning completed
-
-
-# =================================================
-# tests
-# =================================================
-
-# make check can be run with cross-compiled binaries on emulated environments (qemu user mode)
-# by setting $(RUN_ENV) to the target emulation environment
-.PHONY: check
-check: xxhsum ## basic tests for xxhsum CLI, set RUN_ENV for emulated environments
- # stdin
- $(RUN_ENV) ./xxhsum$(EXT) < xxhash.c
- # multiple files
- $(RUN_ENV) ./xxhsum$(EXT) xxhash.* xxhsum.*
- # internal bench
- $(RUN_ENV) ./xxhsum$(EXT) -bi1
- # file bench
- $(RUN_ENV) ./xxhsum$(EXT) -bi1 xxhash.c
- # 32-bit
- $(RUN_ENV) ./xxhsum$(EXT) -H0 xxhash.c
- # 128-bit
- $(RUN_ENV) ./xxhsum$(EXT) -H2 xxhash.c
- # request incorrect variant
- $(RUN_ENV) ./xxhsum$(EXT) -H9 xxhash.c ; test $$? -eq 1
-
-.PHONY: test-unicode
-test-unicode:
- $(MAKE) -C tests test_unicode
-
-.PHONY: test-mem
-VALGRIND = valgrind --leak-check=yes --error-exitcode=1
-test-mem: RUN_ENV = $(VALGRIND)
-test-mem: xxhsum check
-
-.PHONY: test32
-test32: clean xxhsum32
- @echo ---- test 32-bit ----
- ./xxhsum32 -bi1 xxhash.c
-
-.PHONY: test-xxhsum-c
-test-xxhsum-c: xxhsum
- # xxhsum to/from pipe
- ./xxhsum xxh* | ./xxhsum -c -
- ./xxhsum -H0 xxh* | ./xxhsum -c -
- # xxhsum -q does not display "Loading" message into stderr (#251)
- ! ./xxhsum -q xxh* 2>&1 | grep Loading
- # xxhsum to/from file, shell redirection
- ./xxhsum xxh* > .test.xxh64
- ./xxhsum -H0 xxh* > .test.xxh32
- ./xxhsum -H2 xxh* > .test.xxh128
- ./xxhsum -c .test.xxh64
- ./xxhsum -c .test.xxh32
- ./xxhsum -c .test.xxh128
- # read list of files from stdin
- ./xxhsum -c < .test.xxh64
- ./xxhsum -c < .test.xxh32
- # xxhsum -c warns improperly format lines.
- cat .test.xxh64 .test.xxh32 | ./xxhsum -c - | $(GREP) improperly
- cat .test.xxh32 .test.xxh64 | ./xxhsum -c - | $(GREP) improperly
- # Expects "FAILED"
- echo "0000000000000000 LICENSE" | ./xxhsum -c -; test $$? -eq 1
- echo "00000000 LICENSE" | ./xxhsum -c -; test $$? -eq 1
- # Expects "FAILED open or read"
- echo "0000000000000000 test-expects-file-not-found" | ./xxhsum -c -; test $$? -eq 1
- echo "00000000 test-expects-file-not-found" | ./xxhsum -c -; test $$? -eq 1
- @$(RM) .test.xxh32 .test.xxh64 .test.xxh128
-
-.PHONY: armtest
-armtest: clean
- @echo ---- test ARM compilation ----
- CC=arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc MOREFLAGS="-Werror -static" $(MAKE) xxhsum
-
-.PHONY: clangtest
-clangtest: clean
- @echo ---- test clang compilation ----
- CC=clang MOREFLAGS="-Werror -Wconversion -Wno-sign-conversion" $(MAKE) all
-
-.PHONY: cxxtest
-cxxtest: clean
- @echo ---- test C++ compilation ----
- CC="$(CXX) -Wno-deprecated" $(MAKE) all CFLAGS="-O3 -Wall -Wextra -Wundef -Wshadow -Wcast-align -Werror -fPIC"
-
-.PHONY: c90test
-ifeq ($(NO_C90_TEST),true)
-c90test:
- @echo no c90 compatibility test
-else
-c90test: CPPFLAGS += -DXXH_NO_LONG_LONG
-c90test: CFLAGS += -std=c90 -Werror -pedantic
-c90test: xxhash.c
- @echo ---- test strict C90 compilation [xxh32 only] ----
- $(RM) xxhash.o
- $(CC) $(FLAGS) $^ $(LDFLAGS) -c
- $(RM) xxhash.o
-endif
-
-.PHONY: usan
-usan: CC=clang
-usan: CXX=clang++
-usan: ## check CLI runtime for undefined behavior, using clang's sanitizer
- @echo ---- check undefined behavior - sanitize ----
- $(MAKE) clean
- $(MAKE) test CC=$(CC) CXX=$(CXX) MOREFLAGS="-g -fsanitize=undefined -fno-sanitize-recover=all"
-
-.PHONY: staticAnalyze
-SCANBUILD ?= scan-build
-staticAnalyze: clean ## check C source files using $(SCANBUILD) static analyzer
- @echo ---- static analyzer - $(SCANBUILD) ----
- CFLAGS="-g -Werror" $(SCANBUILD) --status-bugs -v $(MAKE) all
-
-CPPCHECK ?= cppcheck
-.PHONY: cppcheck
-cppcheck: ## check C source files using $(CPPCHECK) static analyzer
- @echo ---- static analyzer - $(CPPCHECK) ----
- $(CPPCHECK) . --force --enable=warning,portability,performance,style --error-exitcode=1 > /dev/null
-
-.PHONY: namespaceTest
-namespaceTest: ## ensure XXH_NAMESPACE redefines all public symbols
- $(CC) -c xxhash.c
- $(CC) -DXXH_NAMESPACE=TEST_ -c xxhash.c -o xxhash2.o
- $(CC) xxhash.o xxhash2.o xxhsum.c -o xxhsum2 # will fail if one namespace missing (symbol collision)
- $(RM) *.o xxhsum2 # clean
-
-MD2ROFF ?= ronn
-MD2ROFF_FLAGS ?= --roff --warnings --manual="User Commands" --organization="xxhsum $(XXHSUM_VERSION)"
-xxhsum.1: xxhsum.1.md xxhash.h
- cat $< | $(MD2ROFF) $(MD2ROFF_FLAGS) | sed -n '/^\.\\\".*/!p' > $@
-
-.PHONY: man
-man: xxhsum.1 ## generate man page from markdown source
-
-.PHONY: clean-man
-clean-man:
- $(RM) xxhsum.1
-
-.PHONY: preview-man
-preview-man: man
- man ./xxhsum.1
-
-.PHONY: test
-test: DEBUGFLAGS += -DDEBUGLEVEL=1
-test: all namespaceTest check test-xxhsum-c c90test test-tools
-
-.PHONY: test-inline
-test-inline:
- $(MAKE) -C tests test_multiInclude
-
-.PHONY: test-all
-test-all: CFLAGS += -Werror
-test-all: test test32 clangtest cxxtest usan test-inline listL120 trailingWhitespace staticAnalyze test-unicode
-
-.PHONY: test-tools
-test-tools:
- CFLAGS=-Werror $(MAKE) -C tests/bench
- CFLAGS=-Werror $(MAKE) -C tests/collisions
-
-.PHONY: listL120
-listL120: # extract lines >= 120 characters in *.{c,h}, by Takayuki Matsuoka (note: $$, for Makefile compatibility)
- find . -type f -name '*.c' -o -name '*.h' | while read -r filename; do awk 'length > 120 {print FILENAME "(" FNR "): " $$0}' $$filename; done
-
-.PHONY: trailingWhitespace
-trailingWhitespace:
- ! $(GREP) -E "`printf '[ \\t]$$'`" xxhsum.1 *.c *.h LICENSE Makefile cmake_unofficial/CMakeLists.txt
-
-
-# =========================================================
-# make install is validated only for the following targets
-# =========================================================
-ifneq (,$(filter $(shell uname),Linux Darwin GNU/kFreeBSD GNU OpenBSD FreeBSD NetBSD DragonFly SunOS))
-
-DESTDIR ?=
-# directory variables: GNU conventions prefer lowercase
-# see https://www.gnu.org/prep/standards/html_node/Makefile-Conventions.html
-# support both lower and uppercase (BSD), use uppercase in script
-prefix ?= /usr/local
-PREFIX ?= $(prefix)
-exec_prefix ?= $(PREFIX)
-libdir ?= $(exec_prefix)/lib
-LIBDIR ?= $(libdir)
-includedir ?= $(PREFIX)/include
-INCLUDEDIR ?= $(includedir)
-bindir ?= $(exec_prefix)/bin
-BINDIR ?= $(bindir)
-datarootdir ?= $(PREFIX)/share
-mandir ?= $(datarootdir)/man
-man1dir ?= $(mandir)/man1
-
-ifneq (,$(filter $(shell uname),FreeBSD NetBSD DragonFly))
-PKGCONFIGDIR ?= $(PREFIX)/libdata/pkgconfig
-else
-PKGCONFIGDIR ?= $(LIBDIR)/pkgconfig
-endif
-
-ifneq (,$(filter $(shell uname),OpenBSD FreeBSD NetBSD DragonFly SunOS))
-MANDIR ?= $(PREFIX)/man/man1
-else
-MANDIR ?= $(man1dir)
-endif
-
-ifneq (,$(filter $(shell uname),SunOS))
-INSTALL ?= ginstall
-else
-INSTALL ?= install
-endif
-
-INSTALL_PROGRAM ?= $(INSTALL)
-INSTALL_DATA ?= $(INSTALL) -m 644
-
-
-.PHONY: install
-install: lib pkgconfig xxhsum ## install libraries, CLI, links and man page
- @echo Installing libxxhash
- @$(INSTALL) -d -m 755 $(DESTDIR)$(LIBDIR)
- @$(INSTALL_DATA) libxxhash.a $(DESTDIR)$(LIBDIR)
- @$(INSTALL_PROGRAM) $(LIBXXH) $(DESTDIR)$(LIBDIR)
- @ln -sf $(LIBXXH) $(DESTDIR)$(LIBDIR)/libxxhash.$(SHARED_EXT_MAJOR)
- @ln -sf $(LIBXXH) $(DESTDIR)$(LIBDIR)/libxxhash.$(SHARED_EXT)
- @$(INSTALL) -d -m 755 $(DESTDIR)$(INCLUDEDIR) # includes
- @$(INSTALL_DATA) xxhash.h $(DESTDIR)$(INCLUDEDIR)
- @$(INSTALL_DATA) xxh3.h $(DESTDIR)$(INCLUDEDIR)
- @echo Installing pkgconfig
- @$(INSTALL) -d -m 755 $(DESTDIR)$(PKGCONFIGDIR)/
- @$(INSTALL_DATA) libxxhash.pc $(DESTDIR)$(PKGCONFIGDIR)/
- @echo Installing xxhsum
- @$(INSTALL) -d -m 755 $(DESTDIR)$(BINDIR)/ $(DESTDIR)$(MANDIR)/
- @$(INSTALL_PROGRAM) xxhsum $(DESTDIR)$(BINDIR)/xxhsum
- @ln -sf xxhsum $(DESTDIR)$(BINDIR)/xxh32sum
- @ln -sf xxhsum $(DESTDIR)$(BINDIR)/xxh64sum
- @ln -sf xxhsum $(DESTDIR)$(BINDIR)/xxh128sum
- @echo Installing man pages
- @$(INSTALL_DATA) xxhsum.1 $(DESTDIR)$(MANDIR)/xxhsum.1
- @ln -sf xxhsum.1 $(DESTDIR)$(MANDIR)/xxh32sum.1
- @ln -sf xxhsum.1 $(DESTDIR)$(MANDIR)/xxh64sum.1
- @ln -sf xxhsum.1 $(DESTDIR)$(MANDIR)/xxh128sum.1
- @echo xxhash installation completed
-
-.PHONY: uninstall
-uninstall: ## uninstall libraries, CLI, links and man page
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(LIBDIR)/libxxhash.a
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(LIBDIR)/libxxhash.$(SHARED_EXT)
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(LIBDIR)/libxxhash.$(SHARED_EXT_MAJOR)
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(LIBDIR)/$(LIBXXH)
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(INCLUDEDIR)/xxhash.h
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(PKGCONFIGDIR)/libxxhash.pc
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(BINDIR)/xxh32sum
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(BINDIR)/xxh64sum
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(BINDIR)/xxh128sum
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(BINDIR)/xxhsum
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(MANDIR)/xxh32sum.1
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(MANDIR)/xxh64sum.1
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(MANDIR)/xxh128sum.1
- @$(RM) $(DESTDIR)$(MANDIR)/xxhsum.1
- @echo xxhsum successfully uninstalled
-
-endif
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/README.md b/core/deps/xxHash/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 4b27accf11..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,205 +0,0 @@
-xxHash - Extremely fast hash algorithm
-======================================
-
-
-xxHash is an Extremely fast Hash algorithm, running at RAM speed limits.
-It successfully completes the [SMHasher](https://code.google.com/p/smhasher/wiki/SMHasher) test suite
-which evaluates collision, dispersion and randomness qualities of hash functions.
-Code is highly portable, and hashes are identical on all platforms (little / big endian).
-
-|Branch |Status |
-|------------|---------|
-|master | [](https://travis-ci.org/Cyan4973/xxHash?branch=master) |
-|dev | [](https://travis-ci.org/Cyan4973/xxHash?branch=dev) |
-
-
-
-Benchmarks
--------------------------
-
-The benchmark uses SMHasher speed test, compiled with Visual 2010 on a Windows Seven 32-bit box.
-The reference system uses a Core 2 Duo @3GHz
-
-
-| Name | Speed | Quality | Author |
-|---------------|--------------------|:-------:|-------------------|
-| [xxHash] | 5.4 GB/s | 10 | Y.C. |
-| MurmurHash 3a | 2.7 GB/s | 10 | Austin Appleby |
-| SBox | 1.4 GB/s | 9 | Bret Mulvey |
-| Lookup3 | 1.2 GB/s | 9 | Bob Jenkins |
-| CityHash64 | 1.05 GB/s | 10 | Pike & Alakuijala |
-| FNV | 0.55 GB/s | 5 | Fowler, Noll, Vo |
-| CRC32 | 0.43 GB/s † | 9 | |
-| MD5-32 | 0.33 GB/s | 10 | Ronald L.Rivest |
-| SHA1-32 | 0.28 GB/s | 10 | |
-
-[xxHash]: https://www.xxhash.com
-
-Note †: SMHasher's CRC32 implementation is known to be slow. Faster implementations exist.
-
-Q.Score is a measure of quality of the hash function.
-It depends on successfully passing SMHasher test set.
-10 is a perfect score.
-Algorithms with a score < 5 are not listed on this table.
-
-A more recent version, XXH64, has been created thanks to [Mathias Westerdahl](https://github.com/JCash),
-which offers superior speed and dispersion for 64-bit systems.
-Note however that 32-bit applications will still run faster using the 32-bit version.
-
-SMHasher speed test, compiled using GCC 4.8.2, on Linux Mint 64-bit.
-The reference system uses a Core i5-3340M @2.7GHz
-
-| Version | Speed on 64-bit | Speed on 32-bit |
-|------------|------------------|------------------|
-| XXH64 | 13.8 GB/s | 1.9 GB/s |
-| XXH32 | 6.8 GB/s | 6.0 GB/s |
-
-This project also includes a command line utility, named `xxhsum`, offering similar features to `md5sum`,
-thanks to [Takayuki Matsuoka](https://github.com/t-mat)'s contributions.
-
-
-### License
-
-The library files `xxhash.c` and `xxhash.h` are BSD licensed.
-The utility `xxhsum` is GPL licensed.
-
-
-### New hash algorithms
-
-Starting with `v0.7.0`, the library includes a new algorithm named `XXH3`,
-which is able to generate 64 and 128-bit hashes.
-
-The new algorithm is much faster than its predecessors for both long and small inputs,
-which can be observed in the following graphs:
-
-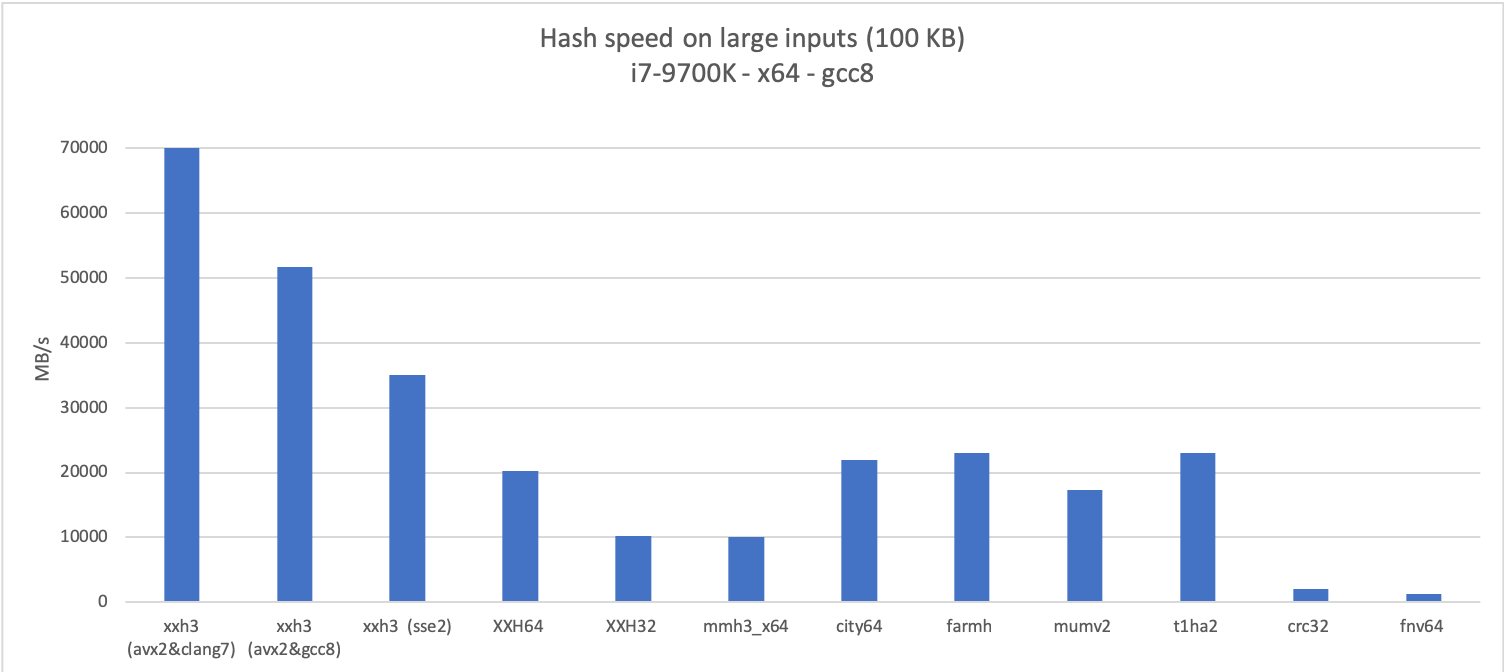
-
-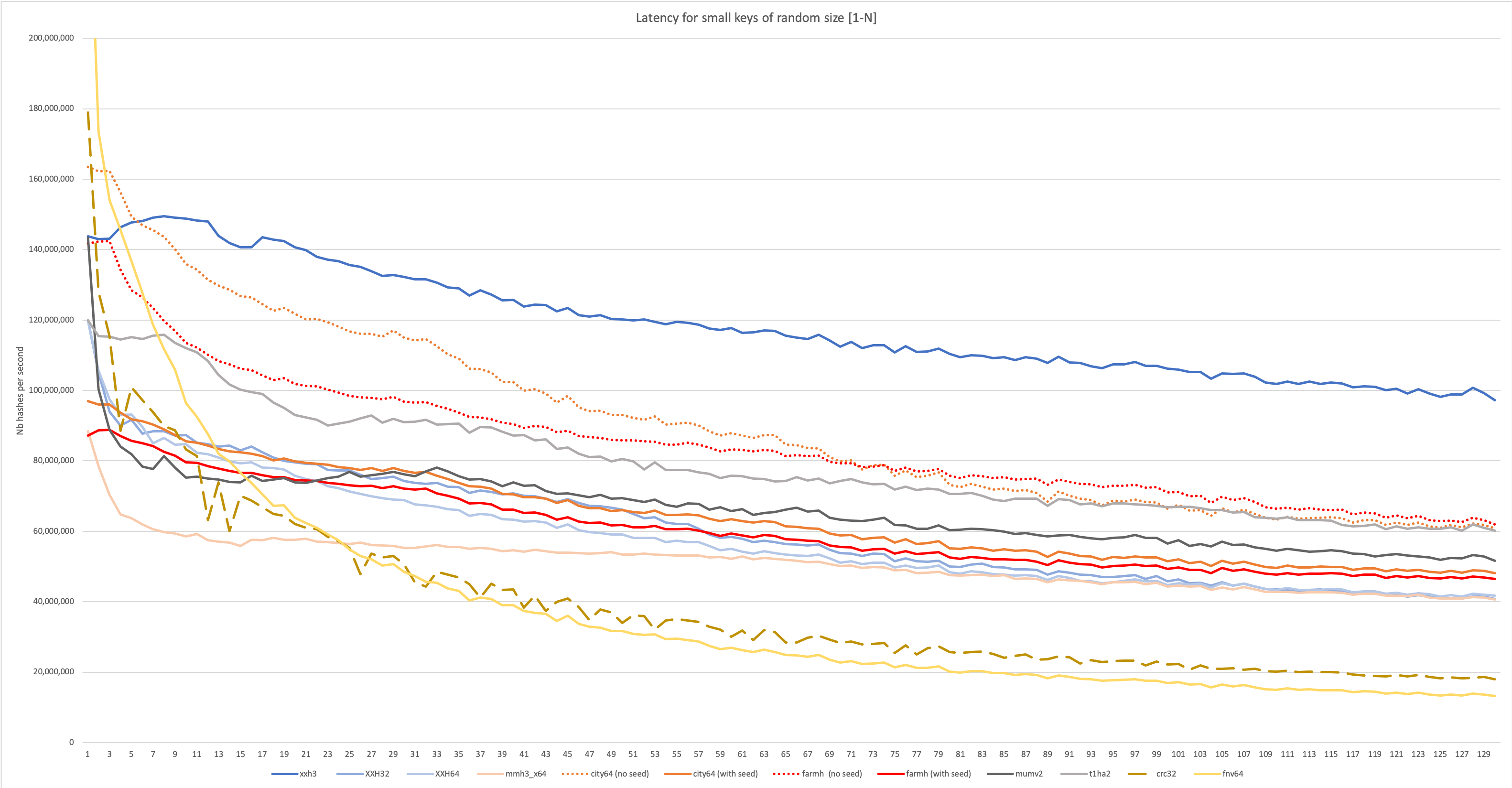
-
-To access these new prototypes, one needs to unlock their declaration, using the build macro `XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY`.
-
-The algorithm is currently in development, meaning its return values might still change in future versions.
-However, the API is stable, and can be used in production, typically for ephemeral
-data (produced and consumed in same session).
-
-`XXH3`'s return values will be finalized upon reaching `v0.8.0`.
-
-
-### Build modifiers
-
-The following macros can be set at compilation time to modify libxxhash's behavior. They are all disabled by default.
-
-- `XXH_INLINE_ALL`: Make all functions `inline`, with implementations being directly included within `xxhash.h`.
- Inlining functions is beneficial for speed on small keys.
- It's _extremely effective_ when key length is expressed as _a compile time constant_,
- with performance improvements being observed in the +200% range .
- See [this article](https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2018/03/xxhash-for-small-keys-impressive-power.html) for details.
- Note: there is no need to compile an `xxhash.o` object file in this case.
-- `XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS`: By default, xxHash uses tricks like `__attribute__((always_inline))` and `__forceinline` to try and improve performance at the cost of code size. Defining this to 1 will mark all internal functions as `static`, allowing the compiler to decide whether to inline a function or not. This is very useful when optimizing for the smallest binary size, and it is automatically defined when compiling with `-O0`, `-Os`, `-Oz`, or `-fno-inline` on GCC and Clang. This may also increase performance depending on the compiler and the architecture.
-- `XXH_REROLL`: Reduces the size of the generated code by not unrolling some loops. Impact on performance may vary, depending on the platform and the algorithm.
-- `XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER`: if set to `1`, when input is a `NULL` pointer,
- xxHash'd result is the same as a zero-length input
- (instead of a dereference segfault).
- Adds one branch at the beginning of the hash.
-- `XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS`: The default method `0` uses a portable `memcpy()` notation.
- Method `1` uses a gcc-specific `packed` attribute, which can provide better performance for some targets.
- Method `2` forces unaligned reads, which is not standards compliant, but might sometimes be the only way to extract better read performance.
- Method `3` uses a byteshift operation, which is best for old compilers which don't inline `memcpy()` or big-endian systems without a byteswap instruction
-- `XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN`: By default, endianess is determined at compile time.
- It's possible to skip auto-detection and force format to little-endian, by setting this macro to 1.
- Setting it to 0 forces big-endian.
-- `XXH_PRIVATE_API`: same impact as `XXH_INLINE_ALL`.
- Name underlines that XXH_* symbols will not be exported.
-- `XXH_NAMESPACE`: Prefixes all symbols with the value of `XXH_NAMESPACE`.
- Useful to evade symbol naming collisions,
- in case of multiple inclusions of xxHash's source code.
- Client applications can still use the regular function name,
- as symbols are automatically translated through `xxhash.h`.
-- `XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY`: gives access to the state declaration for static allocation.
- Incompatible with dynamic linking, due to risks of ABI changes.
-- `XXH_NO_LONG_LONG`: removes support for XXH3 and XXH64 for targets without 64-bit support.
-- `XXH_IMPORT`: MSVC specific: should only be defined for dynamic linking, as it prevents linkage errors.
-
-
-### Building xxHash - Using vcpkg
-
-You can download and install xxHash using the [vcpkg](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) dependency manager:
-
- git clone https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg.git
- cd vcpkg
- ./bootstrap-vcpkg.sh
- ./vcpkg integrate install
- ./vcpkg install xxhash
-
-The xxHash port in vcpkg is kept up to date by Microsoft team members and community contributors. If the version is out of date, please [create an issue or pull request](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) on the vcpkg repository.
-
-
-### Example
-
-Calling xxhash 64-bit variant from a C program:
-
-```C
-#include "xxhash.h"
-
- (...)
- XXH64_hash_t hash = XXH64(buffer, size, seed);
-}
-```
-
-Using streaming variant is more involved, but makes it possible to provide data incrementally:
-```C
-#include "stdlib.h" /* abort() */
-#include "xxhash.h"
-
-
-XXH64_hash_t calcul_hash_streaming(FileHandler fh)
-{
- /* create a hash state */
- XXH64_state_t* const state = XXH64_createState();
- if (state==NULL) abort();
-
- size_t const bufferSize = SOME_SIZE;
- void* const buffer = malloc(bufferSize);
- if (buffer==NULL) abort();
-
- /* Initialize state with selected seed */
- XXH64_hash_t const seed = 0; /* or any other value */
- if (XXH64_reset(state, seed) == XXH_ERROR) abort();
-
- /* Feed the state with input data, any size, any number of times */
- (...)
- while ( /* any condition */ ) {
- size_t const length = get_more_data(buffer, bufferSize, fh);
- if (XXH64_update(state, buffer, length) == XXH_ERROR) abort();
- (...)
- }
- (...)
-
- /* Get the hash */
- XXH64_hash_t const hash = XXH64_digest(state);
-
- /* State can be re-used; in this example, it is simply freed */
- free(buffer);
- XXH64_freeState(state);
-
- return hash;
-}
-```
-
-
-### Other programming languages
-
-Aside from the C reference version,
-xxHash is also available in many different programming languages,
-thanks to many great contributors.
-They are [listed here](https://www.xxhash.com/#other-languages).
-
-
-### Branch Policy
-
-> - The "master" branch is considered stable, at all times.
-> - The "dev" branch is the one where all contributions must be merged
- before being promoted to master.
-> + If you plan to propose a patch, please commit into the "dev" branch,
- or its own feature branch.
- Direct commit to "master" are not permitted.
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/appveyor.yml b/core/deps/xxHash/appveyor.yml
deleted file mode 100644
index 850f48b14d..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/appveyor.yml
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,111 +0,0 @@
-#---------------------------------#
-# general configuration #
-#---------------------------------#
-version: 1.0.{build}
-max_jobs: 2
-
-#---------------------------------#
-# environment configuration #
-#---------------------------------#
-clone_depth: 2
-environment:
- matrix:
- - COMPILER: "visual"
- ARCH: "x64"
- TEST_XXHSUM: "true"
- - COMPILER: "visual"
- ARCH: "x64"
- APPVEYOR_BUILD_WORKER_IMAGE: Visual Studio 2017
- TEST_XXHSUM: "true"
- - COMPILER: "visual"
- ARCH: "Win32"
- TEST_XXHSUM: "true"
- - COMPILER: "visual"
- ARCH: "Win32"
- APPVEYOR_BUILD_WORKER_IMAGE: Visual Studio 2013
- TEST_XXHSUM: "true"
- - COMPILER: "visual"
- ARCH: "ARM"
- - COMPILER: "visual"
- ARCH: "ARM64"
- APPVEYOR_BUILD_WORKER_IMAGE: Visual Studio 2017
- # note: ARM64 is not available with Visual Studio 14 2015, which is default for Appveyor
- - COMPILER: "gcc"
- PLATFORM: "mingw64"
- - COMPILER: "gcc"
- PLATFORM: "mingw32"
- - COMPILER: "gcc"
- PLATFORM: "clang"
-
-install:
- - ECHO Installing %COMPILER% %PLATFORM% %ARCH%
- - MKDIR bin
- - if [%COMPILER%]==[gcc] SET PATH_ORIGINAL=%PATH%
- - if [%COMPILER%]==[gcc] (
- SET "PATH_MINGW32=c:\MinGW\bin;c:\MinGW\usr\bin" &&
- SET "PATH_MINGW64=c:\msys64\mingw64\bin;c:\msys64\usr\bin" &&
- COPY C:\MinGW\bin\mingw32-make.exe C:\MinGW\bin\make.exe &&
- COPY C:\MinGW\bin\gcc.exe C:\MinGW\bin\cc.exe
- )
-
-#---------------------------------#
-# build configuration #
-#---------------------------------#
-build_script:
- - if [%PLATFORM%]==[mingw32] SET PATH=%PATH_MINGW32%;%PATH_ORIGINAL%
- - if [%PLATFORM%]==[mingw64] SET PATH=%PATH_MINGW64%;%PATH_ORIGINAL%
- - if [%PLATFORM%]==[clang] SET PATH=%PATH_MINGW64%;%PATH_ORIGINAL%
- - ECHO ***
- - ECHO Building %COMPILER% %PLATFORM% %ARCH%
- - ECHO ***
-
- - if [%COMPILER%]==[gcc] (
- if [%PLATFORM%]==[clang] (
- clang -v
- ) ELSE (
- gcc -v
- )
- )
- - if [%COMPILER%]==[gcc] (
- echo ----- &&
- make -v &&
- echo ----- &&
- if not [%PLATFORM%]==[clang] (
- if [%PLATFORM%]==[mingw32] ( SET CPPFLAGS=-DPOOL_MT=0 ) &&
- make -B clean test MOREFLAGS=-Werror
- ) ELSE (
- SET CXXFLAGS=--std=c++14 &&
- make -B clean test CC=clang CXX=clang++ MOREFLAGS="--target=x86_64-w64-mingw32 -Werror -Wno-pass-failed" NO_C90_TEST=true
- ) &&
- make -C tests/bench
- )
- # note 1: strict c90 tests with clang fail, due to (erroneous) presence on `inline` keyword in some included system file
- # note 2: multi-threading code doesn't work with mingw32, disabled through POOL_MT=0
- # note 3: clang requires C++14 to compile sort because its own code contains c++14-only code
-
- - if [%COMPILER%]==[visual] (
- cd cmake_unofficial &&
- cmake . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -A %ARCH% -DXXHASH_C_FLAGS="/WX" &&
- cmake --build . --config Release
- )
-
-#---------------------------------#
-# tests configuration #
-#---------------------------------#
-test_script:
- # note: can only run x86 and x64 binaries on Appveyor
- # note: if %COMPILER%==gcc, xxhsum was already tested within `make test`
- - if [%TEST_XXHSUM%]==[true] (
- ECHO *** &&
- ECHO Testing %COMPILER% %PLATFORM% %ARCH% &&
- ECHO *** &&
- cd Release &&
- xxhsum.exe -bi1 &&
- ECHO ------- xxhsum tested -------
- )
-
-
-#---------------------------------#
-# artifacts configuration #
-#---------------------------------#
-# none yet
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/.gitignore b/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/.gitignore
deleted file mode 100644
index 93d9fe4f6d..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/.gitignore
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
-# cmake artifacts
-
-CMakeCache.txt
-CMakeFiles
-Makefile
-cmake_install.cmake
-
-
-# make compilation results
-
-*.dylib
-*.a
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/CMakeLists.txt b/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/CMakeLists.txt
deleted file mode 100644
index d37c5fc846..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/CMakeLists.txt
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,167 +0,0 @@
-# To the extent possible under law, the author(s) have dedicated all
-# copyright and related and neighboring rights to this software to
-# the public domain worldwide. This software is distributed without
-# any warranty.
-#
-# For details, see .
-
-cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 2.8.12 FATAL_ERROR)
-
-set(XXHASH_DIR "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/..")
-
-file(STRINGS "${XXHASH_DIR}/xxhash.h" XXHASH_VERSION_MAJOR REGEX "^#define XXH_VERSION_MAJOR +([0-9]+) *$")
-string(REGEX REPLACE "^#define XXH_VERSION_MAJOR +([0-9]+) *$" "\\1" XXHASH_VERSION_MAJOR "${XXHASH_VERSION_MAJOR}")
-file(STRINGS "${XXHASH_DIR}/xxhash.h" XXHASH_VERSION_MINOR REGEX "^#define XXH_VERSION_MINOR +([0-9]+) *$")
-string(REGEX REPLACE "^#define XXH_VERSION_MINOR +([0-9]+) *$" "\\1" XXHASH_VERSION_MINOR "${XXHASH_VERSION_MINOR}")
-file(STRINGS "${XXHASH_DIR}/xxhash.h" XXHASH_VERSION_RELEASE REGEX "^#define XXH_VERSION_RELEASE +([0-9]+) *$")
-string(REGEX REPLACE "^#define XXH_VERSION_RELEASE +([0-9]+) *$" "\\1" XXHASH_VERSION_RELEASE "${XXHASH_VERSION_RELEASE}")
-set(XXHASH_VERSION_STRING "${XXHASH_VERSION_MAJOR}.${XXHASH_VERSION_MINOR}.${XXHASH_VERSION_RELEASE}")
-set(XXHASH_LIB_VERSION ${XXHASH_VERSION_STRING})
-set(XXHASH_LIB_SOVERSION "${XXHASH_VERSION_MAJOR}")
-mark_as_advanced(XXHASH_VERSION_MAJOR XXHASH_VERSION_MINOR XXHASH_VERSION_RELEASE XXHASH_VERSION_STRING XXHASH_LIB_VERSION XXHASH_LIB_SOVERSION)
-
-if("${CMAKE_VERSION}" VERSION_LESS "3.13")
- #message(WARNING "CMake ${CMAKE_VERSION} has no CMP0077 policy: options will erase uncached/untyped normal vars!")
-else()
- cmake_policy (SET CMP0077 NEW)
-endif()
-if("${CMAKE_VERSION}" VERSION_LESS "3.0")
- project(xxHash C)
-else()
- cmake_policy (SET CMP0048 NEW)
- project(xxHash
- VERSION ${XXHASH_VERSION_STRING}
- LANGUAGES C)
-endif()
-
-if(NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE AND NOT CMAKE_CONFIGURATION_TYPES)
- set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release" CACHE STRING "Project build type" FORCE)
- set_property(CACHE CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE
- PROPERTY STRINGS "Debug" "Release" "RelWithDebInfo" "MinSizeRel")
-endif()
-if(NOT CMAKE_CONFIGURATION_TYPES)
- message(STATUS "xxHash build type: ${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}")
-endif()
-
-option(BUILD_SHARED_LIBS "Build shared library" ON)
-set(XXHASH_BUILD_XXHSUM ON CACHE BOOL "Build the xxhsum binary")
-
-# If XXHASH is being bundled in another project, we don't want to
-# install anything. However, we want to let people override this, so
-# we'll use the XXHASH_BUNDLED_MODE variable to let them do that; just
-# set it to OFF in your project before you add_subdirectory(xxhash/cmake_unofficial).
-if(NOT DEFINED XXHASH_BUNDLED_MODE)
- if("${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}" STREQUAL "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}")
- set(XXHASH_BUNDLED_MODE OFF)
- else()
- set(XXHASH_BUNDLED_MODE ON)
- endif()
-endif()
-set(XXHASH_BUNDLED_MODE ${XXHASH_BUNDLED_MODE} CACHE BOOL "" FORCE)
-mark_as_advanced(XXHASH_BUNDLED_MODE)
-
-# Allow people to choose whether to build shared or static libraries
-# via the BUILD_SHARED_LIBS option unless we are in bundled mode, in
-# which case we always use static libraries.
-include(CMakeDependentOption)
-CMAKE_DEPENDENT_OPTION(BUILD_SHARED_LIBS "Build shared libraries" ON "NOT XXHASH_BUNDLED_MODE" OFF)
-
-# libxxhash
-add_library(xxhash "${XXHASH_DIR}/xxhash.c")
-add_library(${PROJECT_NAME}::xxhash ALIAS xxhash)
-
-target_include_directories(xxhash
- PUBLIC
- $
- $)
-if (BUILD_SHARED_LIBS)
- target_compile_definitions(xxhash PUBLIC XXH_EXPORT)
-endif ()
-set_target_properties(xxhash PROPERTIES
- SOVERSION "${XXHASH_VERSION_STRING}"
- VERSION "${XXHASH_VERSION_STRING}")
-
-if(XXHASH_BUILD_XXHSUM)
- # xxhsum
- add_executable(xxhsum "${XXHASH_DIR}/xxhsum.c")
- add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME}::xxhsum ALIAS xxhsum)
-
- target_link_libraries(xxhsum PRIVATE xxhash)
- target_include_directories(xxhsum PRIVATE "${XXHASH_DIR}")
-endif(XXHASH_BUILD_XXHSUM)
-
-# Extra warning flags
-include (CheckCCompilerFlag)
-if (XXHASH_C_FLAGS)
- set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} ${XXHASH_C_FLAGS}")
-endif()
-foreach (flag
- -Wall -Wextra -Wcast-qual -Wcast-align -Wshadow
- -Wstrict-aliasing=1 -Wswitch-enum -Wdeclaration-after-statement
- -Wstrict-prototypes -Wundef)
- # Because https://gcc.gnu.org/wiki/FAQ#wnowarning
- string(REGEX REPLACE "\\-Wno\\-(.+)" "-W\\1" flag_to_test "${flag}")
- string(REGEX REPLACE "[^a-zA-Z0-9]+" "_" test_name "CFLAG_${flag_to_test}")
-
- check_c_compiler_flag("${ADD_COMPILER_FLAGS_PREPEND} ${flag_to_test}" ${test_name})
-
- if(${test_name})
- set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${flag} ${CMAKE_C_FLAGS}")
- endif()
-
- unset(test_name)
- unset(flag_to_test)
-endforeach (flag)
-
-if(NOT XXHASH_BUNDLED_MODE)
- include(GNUInstallDirs)
-
- install(TARGETS xxhash
- EXPORT xxHashTargets
- LIBRARY DESTINATION "${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}"
- ARCHIVE DESTINATION "${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}")
- install(FILES "${XXHASH_DIR}/xxhash.h"
- DESTINATION "${CMAKE_INSTALL_INCLUDEDIR}")
- install(FILES "${XXHASH_DIR}/xxh3.h"
- DESTINATION "${CMAKE_INSTALL_INCLUDEDIR}")
- if(XXHASH_BUILD_XXHSUM)
- install(TARGETS xxhsum
- EXPORT xxHashTargets
- RUNTIME DESTINATION "${CMAKE_INSTALL_BINDIR}")
- install(FILES "${XXHASH_DIR}/xxhsum.1"
- DESTINATION "${CMAKE_INSTALL_MANDIR}/man1")
- endif(XXHASH_BUILD_XXHSUM)
-
- include(CMakePackageConfigHelpers)
-
- set(xxHash_VERSION_CONFIG "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/xxHashConfigVersion.cmake")
- set(xxHash_PROJECT_CONFIG "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/xxHashConfig.cmake")
- set(xxHash_TARGETS_CONFIG "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/xxHashTargets.cmake")
- set(xxHash_CONFIG_INSTALL_DIR "${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}/cmake/xxHash/")
- write_basic_package_version_file(${xxHash_VERSION_CONFIG}
- VERSION ${XXHASH_VERSION_STRING}
- COMPATIBILITY AnyNewerVersion)
- configure_package_config_file(
- ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/xxHashConfig.cmake.in
- ${xxHash_PROJECT_CONFIG}
- INSTALL_DESTINATION ${xxHash_CONFIG_INSTALL_DIR})
- if("${CMAKE_VERSION}" VERSION_LESS "3.0")
- set(XXHASH_EXPORT_SET xxhash)
- if(XXHASH_BUILD_XXHSUM)
- set(XXHASH_EXPORT_SET ${XXHASH_EXPORT_SET} xxhsum)
- endif()
- export(TARGETS ${XXHASH_EXPORT_SET}
- FILE ${xxHash_TARGETS_CONFIG}
- NAMESPACE ${PROJECT_NAME}::)
- else()
- export(EXPORT xxHashTargets
- FILE ${xxHash_TARGETS_CONFIG}
- NAMESPACE ${PROJECT_NAME}::)
- endif()
-
- install(FILES ${xxHash_PROJECT_CONFIG} ${xxHash_VERSION_CONFIG}
- DESTINATION ${xxHash_CONFIG_INSTALL_DIR})
- install(EXPORT xxHashTargets
- DESTINATION ${xxHash_CONFIG_INSTALL_DIR}
- NAMESPACE ${PROJECT_NAME}::)
-endif(NOT XXHASH_BUNDLED_MODE)
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/README.md b/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 554c55a2ee..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-
-## Usage
-
-### Way 1: import targets
-Build xxHash targets:
-
- cd
- mkdir build
- cd build
- cmake ../cmake_unofficial [options]
- cmake --build .
- cmake --build . --target install #optional
-
-Where possible options are:
-- `-DXXHASH_BUILD_ENABLE_INLINE_API=`: adds xxhash.c for the `-DXXH_INLINE_ALL` api. ON by default.
-- `-DXXHASH_BUILD_XXHSUM=`: build the command line binary. ON by default
-- `-DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=`: build dynamic library. ON by default.
-- `-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=`: use custom install prefix path.
-
-Add lines into downstream CMakeLists.txt:
-
- find_package(xxHash 0.7 CONFIG REQUIRED)
- ...
- target_link_libraries(MyTarget PRIVATE xxHash::xxhash)
-
-### Way 2: Add subdirectory
-Add lines into downstream CMakeLists.txt:
-
- option(BUILD_SHARE_LIBS "Build shared libs" OFF) #optional
- ...
- set(XXHASH_BUILD_ENABLE_INLINE_API OFF) #optional
- set(XXHASH_BUILD_XXHSUM OFF) #optional
- add_subdirectory( EXCLUDE_FROM_ALL)
- ...
- target_link_libraries(MyTarget PRIVATE xxHash::xxhash)
-
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/xxHashConfig.cmake.in b/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/xxHashConfig.cmake.in
deleted file mode 100644
index fd282bee66..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/cmake_unofficial/xxHashConfig.cmake.in
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,4 +0,0 @@
-@PACKAGE_INIT@
-
-include(${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/xxHashTargets.cmake)
-
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/doc/README.md b/core/deps/xxHash/doc/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a73ad72907..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/doc/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
-xxHash Specification
-=======================
-
-This directory contains material defining the xxHash algorithm.
-It's described in [this specification document](xxhash_spec.md).
-
-The algorithm is also be illustrated by a [simple educational library](https://github.com/easyaspi314/xxhash-clean),
-written by @easyaspi314 and designed for readability
-(as opposed to the reference library which is designed for speed).
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/doc/xxhash_spec.md b/core/deps/xxHash/doc/xxhash_spec.md
deleted file mode 100644
index cd593d4eca..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/doc/xxhash_spec.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,317 +0,0 @@
-xxHash fast digest algorithm
-======================
-
-### Notices
-
-Copyright (c) Yann Collet
-
-Permission is granted to copy and distribute this document
-for any purpose and without charge,
-including translations into other languages
-and incorporation into compilations,
-provided that the copyright notice and this notice are preserved,
-and that any substantive changes or deletions from the original
-are clearly marked.
-Distribution of this document is unlimited.
-
-### Version
-
-0.1.1 (10/10/18)
-
-
-Table of Contents
----------------------
-- [Introduction](#introduction)
-- [XXH32 algorithm description](#xxh32-algorithm-description)
-- [XXH64 algorithm description](#xxh64-algorithm-description)
-- [Performance considerations](#performance-considerations)
-- [Reference Implementation](#reference-implementation)
-
-
-Introduction
-----------------
-
-This document describes the xxHash digest algorithm for both 32-bit and 64-bit variants, named `XXH32` and `XXH64`. The algorithm takes an input a message of arbitrary length and an optional seed value, then produces an output of 32 or 64-bit as "fingerprint" or "digest".
-
-xxHash is primarily designed for speed. It is labeled non-cryptographic, and is not meant to avoid intentional collisions (same digest for 2 different messages), or to prevent producing a message with a predefined digest.
-
-XXH32 is designed to be fast on 32-bit machines.
-XXH64 is designed to be fast on 64-bit machines.
-Both variants produce different output.
-However, a given variant shall produce exactly the same output, irrespective of the cpu / os used. In particular, the result remains identical whatever the endianness and width of the cpu is.
-
-### Operation notations
-
-All operations are performed modulo {32,64} bits. Arithmetic overflows are expected.
-`XXH32` uses 32-bit modular operations. `XXH64` uses 64-bit modular operations.
-
-- `+`: denotes modular addition
-- `*`: denotes modular multiplication
-- `X <<< s`: denotes the value obtained by circularly shifting (rotating) `X` left by `s` bit positions.
-- `X >> s`: denotes the value obtained by shifting `X` right by s bit positions. Upper `s` bits become `0`.
-- `X xor Y`: denotes the bit-wise XOR of `X` and `Y` (same width).
-
-
-XXH32 Algorithm Description
--------------------------------------
-
-### Overview
-
-We begin by supposing that we have a message of any length `L` as input, and that we wish to find its digest. Here `L` is an arbitrary nonnegative integer; `L` may be zero. The following steps are performed to compute the digest of the message.
-
-The algorithm collect and transform input in _stripes_ of 16 bytes. The transforms are stored inside 4 "accumulators", each one storing an unsigned 32-bit value. Each accumulator can be processed independently in parallel, speeding up processing for cpu with multiple execution units.
-
-The algorithm uses 32-bits addition, multiplication, rotate, shift and xor operations. Many operations require some 32-bits prime number constants, all defined below:
-
- static const u32 PRIME32_1 = 0x9E3779B1U; // 0b10011110001101110111100110110001
- static const u32 PRIME32_2 = 0x85EBCA77U; // 0b10000101111010111100101001110111
- static const u32 PRIME32_3 = 0xC2B2AE3DU; // 0b11000010101100101010111000111101
- static const u32 PRIME32_4 = 0x27D4EB2FU; // 0b00100111110101001110101100101111
- static const u32 PRIME32_5 = 0x165667B1U; // 0b00010110010101100110011110110001
-
-These constants are prime numbers, and feature a good mix of bits 1 and 0, neither too regular, nor too dissymmetric. These properties help dispersion capabilities.
-
-### Step 1. Initialize internal accumulators
-
-Each accumulator gets an initial value based on optional `seed` input. Since the `seed` is optional, it can be `0`.
-
- u32 acc1 = seed + PRIME32_1 + PRIME32_2;
- u32 acc2 = seed + PRIME32_2;
- u32 acc3 = seed + 0;
- u32 acc4 = seed - PRIME32_1;
-
-#### Special case: input is less than 16 bytes
-
-When the input is too small (< 16 bytes), the algorithm will not process any stripes. Consequently, it will not make use of parallel accumulators.
-
-In this case, a simplified initialization is performed, using a single accumulator:
-
- u32 acc = seed + PRIME32_5;
-
-The algorithm then proceeds directly to step 4.
-
-### Step 2. Process stripes
-
-A stripe is a contiguous segment of 16 bytes.
-It is evenly divided into 4 _lanes_, of 4 bytes each.
-The first lane is used to update accumulator 1, the second lane is used to update accumulator 2, and so on.
-
-Each lane read its associated 32-bit value using __little-endian__ convention.
-
-For each {lane, accumulator}, the update process is called a _round_, and applies the following formula:
-
- accN = accN + (laneN * PRIME32_2);
- accN = accN <<< 13;
- accN = accN * PRIME32_1;
-
-This shuffles the bits so that any bit from input _lane_ impacts several bits in output _accumulator_. All operations are performed modulo 2^32.
-
-Input is consumed one full stripe at a time. Step 2 is looped as many times as necessary to consume the whole input, except for the last remaining bytes which cannot form a stripe (< 16 bytes).
-When that happens, move to step 3.
-
-### Step 3. Accumulator convergence
-
-All 4 lane accumulators from the previous steps are merged to produce a single remaining accumulator of the same width (32-bit). The associated formula is as follows:
-
- acc = (acc1 <<< 1) + (acc2 <<< 7) + (acc3 <<< 12) + (acc4 <<< 18);
-
-### Step 4. Add input length
-
-The input total length is presumed known at this stage. This step is just about adding the length to accumulator, so that it participates to final mixing.
-
- acc = acc + (u32)inputLength;
-
-Note that, if input length is so large that it requires more than 32-bits, only the lower 32-bits are added to the accumulator.
-
-### Step 5. Consume remaining input
-
-There may be up to 15 bytes remaining to consume from the input.
-The final stage will digest them according to following pseudo-code:
-
- while (remainingLength >= 4) {
- lane = read_32bit_little_endian(input_ptr);
- acc = acc + lane * PRIME32_3;
- acc = (acc <<< 17) * PRIME32_4;
- input_ptr += 4; remainingLength -= 4;
- }
-
- while (remainingLength >= 1) {
- lane = read_byte(input_ptr);
- acc = acc + lane * PRIME32_5;
- acc = (acc <<< 11) * PRIME32_1;
- input_ptr += 1; remainingLength -= 1;
- }
-
-This process ensures that all input bytes are present in the final mix.
-
-### Step 6. Final mix (avalanche)
-
-The final mix ensures that all input bits have a chance to impact any bit in the output digest, resulting in an unbiased distribution. This is also called avalanche effect.
-
- acc = acc xor (acc >> 15);
- acc = acc * PRIME32_2;
- acc = acc xor (acc >> 13);
- acc = acc * PRIME32_3;
- acc = acc xor (acc >> 16);
-
-### Step 7. Output
-
-The `XXH32()` function produces an unsigned 32-bit value as output.
-
-For systems which require to store and/or display the result in binary or hexadecimal format, the canonical format is defined to reproduce the same value as the natural decimal format, hence follows __big-endian__ convention (most significant byte first).
-
-
-XXH64 Algorithm Description
--------------------------------------
-
-### Overview
-
-`XXH64`'s algorithm structure is very similar to `XXH32` one. The major difference is that `XXH64` uses 64-bit arithmetic, speeding up memory transfer for 64-bit compliant systems, but also relying on cpu capability to efficiently perform 64-bit operations.
-
-The algorithm collects and transforms input in _stripes_ of 32 bytes. The transforms are stored inside 4 "accumulators", each one storing an unsigned 64-bit value. Each accumulator can be processed independently in parallel, speeding up processing for cpu with multiple execution units.
-
-The algorithm uses 64-bit addition, multiplication, rotate, shift and xor operations. Many operations require some 64-bit prime number constants, all defined below:
-
- static const u64 PRIME64_1 = 0x9E3779B185EBCA87ULL; // 0b1001111000110111011110011011000110000101111010111100101010000111
- static const u64 PRIME64_2 = 0xC2B2AE3D27D4EB4FULL; // 0b1100001010110010101011100011110100100111110101001110101101001111
- static const u64 PRIME64_3 = 0x165667B19E3779F9ULL; // 0b0001011001010110011001111011000110011110001101110111100111111001
- static const u64 PRIME64_4 = 0x85EBCA77C2B2AE63ULL; // 0b1000010111101011110010100111011111000010101100101010111001100011
- static const u64 PRIME64_5 = 0x27D4EB2F165667C5ULL; // 0b0010011111010100111010110010111100010110010101100110011111000101
-
-These constants are prime numbers, and feature a good mix of bits 1 and 0, neither too regular, nor too dissymmetric. These properties help dispersion capabilities.
-
-### Step 1. Initialise internal accumulators
-
-Each accumulator gets an initial value based on optional `seed` input. Since the `seed` is optional, it can be `0`.
-
- u64 acc1 = seed + PRIME64_1 + PRIME64_2;
- u64 acc2 = seed + PRIME64_2;
- u64 acc3 = seed + 0;
- u64 acc4 = seed - PRIME64_1;
-
-#### Special case: input is less than 32 bytes
-
-When the input is too small (< 32 bytes), the algorithm will not process any stripes. Consequently, it will not make use of parallel accumulators.
-
-In this case, a simplified initialization is performed, using a single accumulator:
-
- u64 acc = seed + PRIME64_5;
-
-The algorithm then proceeds directly to step 4.
-
-### Step 2. Process stripes
-
-A stripe is a contiguous segment of 32 bytes.
-It is evenly divided into 4 _lanes_, of 8 bytes each.
-The first lane is used to update accumulator 1, the second lane is used to update accumulator 2, and so on.
-
-Each lane read its associated 64-bit value using __little-endian__ convention.
-
-For each {lane, accumulator}, the update process is called a _round_, and applies the following formula:
-
- round(accN,laneN):
- accN = accN + (laneN * PRIME64_2);
- accN = accN <<< 31;
- return accN * PRIME64_1;
-
-This shuffles the bits so that any bit from input _lane_ impacts several bits in output _accumulator_. All operations are performed modulo 2^64.
-
-Input is consumed one full stripe at a time. Step 2 is looped as many times as necessary to consume the whole input, except for the last remaining bytes which cannot form a stripe (< 32 bytes).
-When that happens, move to step 3.
-
-### Step 3. Accumulator convergence
-
-All 4 lane accumulators from previous steps are merged to produce a single remaining accumulator of same width (64-bit). The associated formula is as follows.
-
-Note that accumulator convergence is more complex than 32-bit variant, and requires to define another function called _mergeAccumulator()_:
-
- mergeAccumulator(acc,accN):
- acc = acc xor round(0, accN);
- acc = acc * PRIME64_1
- return acc + PRIME64_4;
-
-which is then used in the convergence formula:
-
- acc = (acc1 <<< 1) + (acc2 <<< 7) + (acc3 <<< 12) + (acc4 <<< 18);
- acc = mergeAccumulator(acc, acc1);
- acc = mergeAccumulator(acc, acc2);
- acc = mergeAccumulator(acc, acc3);
- acc = mergeAccumulator(acc, acc4);
-
-### Step 4. Add input length
-
-The input total length is presumed known at this stage. This step is just about adding the length to accumulator, so that it participates to final mixing.
-
- acc = acc + inputLength;
-
-### Step 5. Consume remaining input
-
-There may be up to 31 bytes remaining to consume from the input.
-The final stage will digest them according to following pseudo-code:
-
- while (remainingLength >= 8) {
- lane = read_64bit_little_endian(input_ptr);
- acc = acc xor round(0, lane);
- acc = (acc <<< 27) * PRIME64_1;
- acc = acc + PRIME64_4;
- input_ptr += 8; remainingLength -= 8;
- }
-
- if (remainingLength >= 4) {
- lane = read_32bit_little_endian(input_ptr);
- acc = acc xor (lane * PRIME64_1);
- acc = (acc <<< 23) * PRIME64_2;
- acc = acc + PRIME64_3;
- input_ptr += 4; remainingLength -= 4;
- }
-
- while (remainingLength >= 1) {
- lane = read_byte(input_ptr);
- acc = acc xor (lane * PRIME64_5);
- acc = (acc <<< 11) * PRIME64_1;
- input_ptr += 1; remainingLength -= 1;
- }
-
-This process ensures that all input bytes are present in the final mix.
-
-### Step 6. Final mix (avalanche)
-
-The final mix ensures that all input bits have a chance to impact any bit in the output digest, resulting in an unbiased distribution. This is also called avalanche effect.
-
- acc = acc xor (acc >> 33);
- acc = acc * PRIME64_2;
- acc = acc xor (acc >> 29);
- acc = acc * PRIME64_3;
- acc = acc xor (acc >> 32);
-
-### Step 7. Output
-
-The `XXH64()` function produces an unsigned 64-bit value as output.
-
-For systems which require to store and/or display the result in binary or hexadecimal format, the canonical format is defined to reproduce the same value as the natural decimal format, hence follows __big-endian__ convention (most significant byte first).
-
-Performance considerations
-----------------------------------
-
-The xxHash algorithms are simple and compact to implement. They provide a system independent "fingerprint" or digest of a message of arbitrary length.
-
-The algorithm allows input to be streamed and processed in multiple steps. In such case, an internal buffer is needed to ensure data is presented to the algorithm in full stripes.
-
-On 64-bit systems, the 64-bit variant `XXH64` is generally faster to compute, so it is a recommended variant, even when only 32-bit are needed.
-
-On 32-bit systems though, positions are reversed: `XXH64` performance is reduced, due to its usage of 64-bit arithmetic. `XXH32` becomes a faster variant.
-
-
-Reference Implementation
-----------------------------------------
-
-A reference library written in C is available at https://www.xxhash.com.
-The web page also links to multiple other implementations written in many different languages.
-It links to the [github project page](https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash) where an [issue board](https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/issues) can be used for further public discussions on the topic.
-
-
-Version changes
---------------------
-v0.7.3: Minor fixes
-v0.1.1: added a note on rationale for selection of constants
-v0.1.0: initial release
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/libxxhash.pc.in b/core/deps/xxHash/libxxhash.pc.in
deleted file mode 100644
index 3f77f991c5..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/libxxhash.pc.in
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
-# xxHash - Extremely fast hash algorithm
-# BSD 2-Clause License (https://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php)
-
-prefix=@PREFIX@
-exec_prefix=${prefix}
-includedir=${prefix}/include
-libdir=${exec_prefix}/lib
-
-Name: xxhash
-Description: extremely fast hash algorithm
-URL: https://www.xxhash.com/
-Version: @VERSION@
-Libs: -L${libdir} -lxxhash
-Cflags: -I${includedir}
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/Makefile b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/Makefile
deleted file mode 100644
index bf286620db..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/Makefile
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-CFLAGS += -Wall -Wextra -g
-
-NM = nm
-GREP = grep
-
-# Define *.exe as extension for Windows systems
-ifneq (,$(filter Windows%,$(OS)))
-EXT =.exe
-else
-EXT =
-endif
-
-ifneq (,$(filter %UTF-8,$(LANG)))
-ENABLE_UNICODE ?= 1
-else
-ENABLE_UNICODE ?= 0
-endif
-
-.PHONY: default
-default: all
-
-.PHONY: all
-all: test
-
-.PHONY: test
-test: test_multiInclude test_unicode
-
-.PHONY: test_multiInclude
-test_multiInclude:
- @$(MAKE) clean
- # compile without xxhash.o, ensure symbols exist within target
- # Note: built using only default rules
- $(MAKE) multiInclude
- @$(MAKE) clean
- # compile with xxhash.o, to detect duplicated symbols
- $(MAKE) multiInclude_withxxhash
- @$(MAKE) clean
- # Note: XXH_INLINE_ALL with XXH_NAMESPACE is currently disabled
- # compile with XXH_NAMESPACE
- # CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_NAMESPACE=TESTN_ $(MAKE) multiInclude_withxxhash
- # no symbol prefixed TESTN_ should exist
- # ! $(NM) multiInclude_withxxhash | $(GREP) TESTN_
- #$(MAKE) clean
- # compile with XXH_NAMESPACE and without xxhash.o
- # CPPFLAGS=-DXXH_NAMESPACE=TESTN_ $(MAKE) multiInclude
- # no symbol prefixed TESTN_ should exist
- # ! $(NM) multiInclude | $(GREP) TESTN_
- #@$(MAKE) clean
-
-xxhsum$(EXT): ../xxhash.c ../xxhash.h ../xxh3.h ../xxhsum.c
- $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) ../xxhash.c ../xxhsum.c -o $@
-
-# Make sure that Unicode filenames work.
-# https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/issues/293
-.PHONY: test_unicode
-ifeq (0,$(ENABLE_UNICODE))
-test_unicode:
- @echo "Skipping Unicode test, your terminal doesn't appear to support UTF-8."
- @echo "Try with ENABLE_UNICODE=1"
-else
-test_unicode: xxhsum$(EXT) generate_unicode_test.c
- # Generate a Unicode filename test dynamically
- # to keep UTF-8 out of the source tree.
- $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) generate_unicode_test.c -o generate_unicode_test$(EXT)
- ./generate_unicode_test$(EXT)
- $(SHELL) ./unicode_test.sh
-endif
-
-xxhash.o: ../xxhash.c ../xxhash.h
- $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(CPPFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -c -o $@ $<
-
-multiInclude_withxxhash: multiInclude.o xxhash.o
- $(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(CPPFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) -o $@ $^
-
-clean:
- @$(RM) *.o
- @$(RM) multiInclude multiInclude_withxxhash
- @$(RM) *.unicode generate_unicode_test$(EXT) unicode_test.* xxhsum$(EXT)
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/.gitignore b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/.gitignore
deleted file mode 100644
index ede2d5880f..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/.gitignore
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
-# build artifacts
-
-*.o
-benchHash
-benchHash32
-benchHash_avx2
-benchHash_hw
-
-# test files
-
-test*
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/LICENSE b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/LICENSE
deleted file mode 100644
index d159169d10..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/LICENSE
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,339 +0,0 @@
- GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
- Version 2, June 1991
-
- Copyright (C) 1989, 1991 Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
- Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
- of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
-
- Preamble
-
- The licenses for most software are designed to take away your
-freedom to share and change it. By contrast, the GNU General Public
-License is intended to guarantee your freedom to share and change free
-software--to make sure the software is free for all its users. This
-General Public License applies to most of the Free Software
-Foundation's software and to any other program whose authors commit to
-using it. (Some other Free Software Foundation software is covered by
-the GNU Lesser General Public License instead.) You can apply it to
-your programs, too.
-
- When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not
-price. Our General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that you
-have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge for
-this service if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it
-if you want it, that you can change the software or use pieces of it
-in new free programs; and that you know you can do these things.
-
- To protect your rights, we need to make restrictions that forbid
-anyone to deny you these rights or to ask you to surrender the rights.
-These restrictions translate to certain responsibilities for you if you
-distribute copies of the software, or if you modify it.
-
- For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whether
-gratis or for a fee, you must give the recipients all the rights that
-you have. You must make sure that they, too, receive or can get the
-source code. And you must show them these terms so they know their
-rights.
-
- We protect your rights with two steps: (1) copyright the software, and
-(2) offer you this license which gives you legal permission to copy,
-distribute and/or modify the software.
-
- Also, for each author's protection and ours, we want to make certain
-that everyone understands that there is no warranty for this free
-software. If the software is modified by someone else and passed on, we
-want its recipients to know that what they have is not the original, so
-that any problems introduced by others will not reflect on the original
-authors' reputations.
-
- Finally, any free program is threatened constantly by software
-patents. We wish to avoid the danger that redistributors of a free
-program will individually obtain patent licenses, in effect making the
-program proprietary. To prevent this, we have made it clear that any
-patent must be licensed for everyone's free use or not licensed at all.
-
- The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and
-modification follow.
-
- GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
- TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR COPYING, DISTRIBUTION AND MODIFICATION
-
- 0. This License applies to any program or other work which contains
-a notice placed by the copyright holder saying it may be distributed
-under the terms of this General Public License. The "Program", below,
-refers to any such program or work, and a "work based on the Program"
-means either the Program or any derivative work under copyright law:
-that is to say, a work containing the Program or a portion of it,
-either verbatim or with modifications and/or translated into another
-language. (Hereinafter, translation is included without limitation in
-the term "modification".) Each licensee is addressed as "you".
-
-Activities other than copying, distribution and modification are not
-covered by this License; they are outside its scope. The act of
-running the Program is not restricted, and the output from the Program
-is covered only if its contents constitute a work based on the
-Program (independent of having been made by running the Program).
-Whether that is true depends on what the Program does.
-
- 1. You may copy and distribute verbatim copies of the Program's
-source code as you receive it, in any medium, provided that you
-conspicuously and appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate
-copyright notice and disclaimer of warranty; keep intact all the
-notices that refer to this License and to the absence of any warranty;
-and give any other recipients of the Program a copy of this License
-along with the Program.
-
-You may charge a fee for the physical act of transferring a copy, and
-you may at your option offer warranty protection in exchange for a fee.
-
- 2. You may modify your copy or copies of the Program or any portion
-of it, thus forming a work based on the Program, and copy and
-distribute such modifications or work under the terms of Section 1
-above, provided that you also meet all of these conditions:
-
- a) You must cause the modified files to carry prominent notices
- stating that you changed the files and the date of any change.
-
- b) You must cause any work that you distribute or publish, that in
- whole or in part contains or is derived from the Program or any
- part thereof, to be licensed as a whole at no charge to all third
- parties under the terms of this License.
-
- c) If the modified program normally reads commands interactively
- when run, you must cause it, when started running for such
- interactive use in the most ordinary way, to print or display an
- announcement including an appropriate copyright notice and a
- notice that there is no warranty (or else, saying that you provide
- a warranty) and that users may redistribute the program under
- these conditions, and telling the user how to view a copy of this
- License. (Exception: if the Program itself is interactive but
- does not normally print such an announcement, your work based on
- the Program is not required to print an announcement.)
-
-These requirements apply to the modified work as a whole. If
-identifiable sections of that work are not derived from the Program,
-and can be reasonably considered independent and separate works in
-themselves, then this License, and its terms, do not apply to those
-sections when you distribute them as separate works. But when you
-distribute the same sections as part of a whole which is a work based
-on the Program, the distribution of the whole must be on the terms of
-this License, whose permissions for other licensees extend to the
-entire whole, and thus to each and every part regardless of who wrote it.
-
-Thus, it is not the intent of this section to claim rights or contest
-your rights to work written entirely by you; rather, the intent is to
-exercise the right to control the distribution of derivative or
-collective works based on the Program.
-
-In addition, mere aggregation of another work not based on the Program
-with the Program (or with a work based on the Program) on a volume of
-a storage or distribution medium does not bring the other work under
-the scope of this License.
-
- 3. You may copy and distribute the Program (or a work based on it,
-under Section 2) in object code or executable form under the terms of
-Sections 1 and 2 above provided that you also do one of the following:
-
- a) Accompany it with the complete corresponding machine-readable
- source code, which must be distributed under the terms of Sections
- 1 and 2 above on a medium customarily used for software interchange; or,
-
- b) Accompany it with a written offer, valid for at least three
- years, to give any third party, for a charge no more than your
- cost of physically performing source distribution, a complete
- machine-readable copy of the corresponding source code, to be
- distributed under the terms of Sections 1 and 2 above on a medium
- customarily used for software interchange; or,
-
- c) Accompany it with the information you received as to the offer
- to distribute corresponding source code. (This alternative is
- allowed only for noncommercial distribution and only if you
- received the program in object code or executable form with such
- an offer, in accord with Subsection b above.)
-
-The source code for a work means the preferred form of the work for
-making modifications to it. For an executable work, complete source
-code means all the source code for all modules it contains, plus any
-associated interface definition files, plus the scripts used to
-control compilation and installation of the executable. However, as a
-special exception, the source code distributed need not include
-anything that is normally distributed (in either source or binary
-form) with the major components (compiler, kernel, and so on) of the
-operating system on which the executable runs, unless that component
-itself accompanies the executable.
-
-If distribution of executable or object code is made by offering
-access to copy from a designated place, then offering equivalent
-access to copy the source code from the same place counts as
-distribution of the source code, even though third parties are not
-compelled to copy the source along with the object code.
-
- 4. You may not copy, modify, sublicense, or distribute the Program
-except as expressly provided under this License. Any attempt
-otherwise to copy, modify, sublicense or distribute the Program is
-void, and will automatically terminate your rights under this License.
-However, parties who have received copies, or rights, from you under
-this License will not have their licenses terminated so long as such
-parties remain in full compliance.
-
- 5. You are not required to accept this License, since you have not
-signed it. However, nothing else grants you permission to modify or
-distribute the Program or its derivative works. These actions are
-prohibited by law if you do not accept this License. Therefore, by
-modifying or distributing the Program (or any work based on the
-Program), you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so, and
-all its terms and conditions for copying, distributing or modifying
-the Program or works based on it.
-
- 6. Each time you redistribute the Program (or any work based on the
-Program), the recipient automatically receives a license from the
-original licensor to copy, distribute or modify the Program subject to
-these terms and conditions. You may not impose any further
-restrictions on the recipients' exercise of the rights granted herein.
-You are not responsible for enforcing compliance by third parties to
-this License.
-
- 7. If, as a consequence of a court judgment or allegation of patent
-infringement or for any other reason (not limited to patent issues),
-conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or
-otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not
-excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you cannot
-distribute so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this
-License and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you
-may not distribute the Program at all. For example, if a patent
-license would not permit royalty-free redistribution of the Program by
-all those who receive copies directly or indirectly through you, then
-the only way you could satisfy both it and this License would be to
-refrain entirely from distribution of the Program.
-
-If any portion of this section is held invalid or unenforceable under
-any particular circumstance, the balance of the section is intended to
-apply and the section as a whole is intended to apply in other
-circumstances.
-
-It is not the purpose of this section to induce you to infringe any
-patents or other property right claims or to contest validity of any
-such claims; this section has the sole purpose of protecting the
-integrity of the free software distribution system, which is
-implemented by public license practices. Many people have made
-generous contributions to the wide range of software distributed
-through that system in reliance on consistent application of that
-system; it is up to the author/donor to decide if he or she is willing
-to distribute software through any other system and a licensee cannot
-impose that choice.
-
-This section is intended to make thoroughly clear what is believed to
-be a consequence of the rest of this License.
-
- 8. If the distribution and/or use of the Program is restricted in
-certain countries either by patents or by copyrighted interfaces, the
-original copyright holder who places the Program under this License
-may add an explicit geographical distribution limitation excluding
-those countries, so that distribution is permitted only in or among
-countries not thus excluded. In such case, this License incorporates
-the limitation as if written in the body of this License.
-
- 9. The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions
-of the General Public License from time to time. Such new versions will
-be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to
-address new problems or concerns.
-
-Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the Program
-specifies a version number of this License which applies to it and "any
-later version", you have the option of following the terms and conditions
-either of that version or of any later version published by the Free
-Software Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number of
-this License, you may choose any version ever published by the Free Software
-Foundation.
-
- 10. If you wish to incorporate parts of the Program into other free
-programs whose distribution conditions are different, write to the author
-to ask for permission. For software which is copyrighted by the Free
-Software Foundation, write to the Free Software Foundation; we sometimes
-make exceptions for this. Our decision will be guided by the two goals
-of preserving the free status of all derivatives of our free software and
-of promoting the sharing and reuse of software generally.
-
- NO WARRANTY
-
- 11. BECAUSE THE PROGRAM IS LICENSED FREE OF CHARGE, THERE IS NO WARRANTY
-FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN
-OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES
-PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED
-OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
-MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS
-TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE
-PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF ALL NECESSARY SERVICING,
-REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
-
- 12. IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING
-WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MAY MODIFY AND/OR
-REDISTRIBUTE THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES,
-INCLUDING ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING
-OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED
-TO LOSS OF DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY
-YOU OR THIRD PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER
-PROGRAMS), EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE
-POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
-
- END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
-
- How to Apply These Terms to Your New Programs
-
- If you develop a new program, and you want it to be of the greatest
-possible use to the public, the best way to achieve this is to make it
-free software which everyone can redistribute and change under these terms.
-
- To do so, attach the following notices to the program. It is safest
-to attach them to the start of each source file to most effectively
-convey the exclusion of warranty; and each file should have at least
-the "copyright" line and a pointer to where the full notice is found.
-
-
- Copyright (C)
-
- This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
- it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
- the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
- (at your option) any later version.
-
- This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
- MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
- GNU General Public License for more details.
-
- You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
- with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
-
-Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and paper mail.
-
-If the program is interactive, make it output a short notice like this
-when it starts in an interactive mode:
-
- Gnomovision version 69, Copyright (C) year name of author
- Gnomovision comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details type `show w'.
- This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it
- under certain conditions; type `show c' for details.
-
-The hypothetical commands `show w' and `show c' should show the appropriate
-parts of the General Public License. Of course, the commands you use may
-be called something other than `show w' and `show c'; they could even be
-mouse-clicks or menu items--whatever suits your program.
-
-You should also get your employer (if you work as a programmer) or your
-school, if any, to sign a "copyright disclaimer" for the program, if
-necessary. Here is a sample; alter the names:
-
- Yoyodyne, Inc., hereby disclaims all copyright interest in the program
- `Gnomovision' (which makes passes at compilers) written by James Hacker.
-
- , 1 April 1989
- Ty Coon, President of Vice
-
-This General Public License does not permit incorporating your program into
-proprietary programs. If your program is a subroutine library, you may
-consider it more useful to permit linking proprietary applications with the
-library. If this is what you want to do, use the GNU Lesser General
-Public License instead of this License.
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/Makefile b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/Makefile
deleted file mode 100644
index a3ab11e9f7..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/Makefile
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-# ################################################################
-# xxHash Makefile
-# Copyright (C) Yann Collet 2012-present
-#
-# GPL v2 License
-#
-# This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
-# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
-# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
-# (at your option) any later version.
-#
-# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
-# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
-# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
-# GNU General Public License for more details.
-#
-# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
-# with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
-# 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
-#
-# You can contact the author at:
-# - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
-# - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
-# ################################################################
-# benchHash: A generic benchmark for hash algorithms
-# measuring throughput, latency and bandwidth
-# ################################################################
-
-
-CPPFLAGS += -I../.. # directory of xxHash source files
-CFLAGS ?= -O3
-CFLAGS += -std=c99 -Wall -Wextra -Wstrict-aliasing=1
-CFLAGS += $(MOREFLAGS) # custom way to add flags
-CXXFLAGS ?= -O3
-LDFLAGS += $(MOREFLAGS)
-
-
-OBJ_LIST = main.o bhDisplay.o benchHash.o benchfn.o timefn.o
-
-
-default: benchHash
-
-all: benchHash
-
-benchHash32: CFLAGS += -m32
-benchHash32: CXXFLAGS += -m32
-
-benchHash_avx2: CFLAGS += -mavx2
-benchHash_avx2: CXXFLAGS += -mavx2
-
-benchHash_hw: CPPFLAGS += -DHARDWARE_SUPPORT
-benchHash_hw: CFLAGS += -mavx2 -maes
-benchHash_hw: CXXFLAGS += -mavx2 -mpclmul -std=c++14
-
-benchHash benchHash32 benchHash_avx2 benchHash_nosimd benchHash_hw: $(OBJ_LIST)
- $(CXX) $(CPPFLAGS) $(CXXFLAGS) $^ $(LDFLAGS) -o $@
-
-
-main.o: bhDisplay.h hashes.h
-
-bhDisplay.o: bhDisplay.h benchHash.h
-
-benchHash.o: benchHash.h
-
-
-clean:
- $(RM) *.o benchHash benchHash32 benchHash_avx2 benchHash_hw
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchHash.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchHash.c
deleted file mode 100644
index 846c9e7b0b..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchHash.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,164 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* Hash benchmark module
-* Part of the xxHash project
-* Copyright (C) 2019-present, Yann Collet
-*
-* GPL v2 License
-*
-* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
-* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
-* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
-* (at your option) any later version.
-*
-* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
-* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
-* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
-* GNU General Public License for more details.
-*
-* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
-* with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
-* 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
-*
-* You can contact the author at:
-* - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
-* - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
-*/
-
-/* benchmark hash functions */
-
-#include // malloc
-#include
-
-#include "benchHash.h"
-
-
-static void initBuffer(void* buffer, size_t size)
-{
- const unsigned long long k1 = 11400714785074694791ULL; /* 0b1001111000110111011110011011000110000101111010111100101010000111 */
- const unsigned long long k2 = 14029467366897019727ULL; /* 0b1100001010110010101011100011110100100111110101001110101101001111 */
- unsigned long long acc = k2;
- unsigned char* const p = (unsigned char*)buffer;
- for (size_t s = 0; s < size; s++) {
- acc *= k1;
- p[s] = (unsigned char)(acc >> 56);
- }
-}
-
-
-#define MARGIN_FOR_LATENCY 1024
-#define START_MASK (MARGIN_FOR_LATENCY-1)
-
-typedef size_t (*sizeFunction_f)(size_t targetSize);
-
-/*
- * bench_hash_internal():
- * Benchmarks hashfn repeateadly over single input of size `size`
- * return: nb of hashes per second
- */
-static double
-bench_hash_internal(BMK_benchFn_t hashfn, void* payload,
- size_t nbBlocks, sizeFunction_f selectSize, size_t size,
- unsigned total_time_ms, unsigned iter_time_ms)
-{
- BMK_timedFnState_shell shell;
- BMK_timedFnState_t* const txf = BMK_initStatic_timedFnState(&shell, sizeof(shell), total_time_ms, iter_time_ms);
- assert(txf != NULL);
-
- size_t const srcSize = (size_t)size;
- size_t const srcBufferSize = srcSize + MARGIN_FOR_LATENCY;
- void* const srcBuffer = malloc(srcBufferSize);
- assert(srcBuffer != NULL);
- initBuffer(srcBuffer, srcBufferSize);
- #define FAKE_DSTSIZE 32
- size_t const dstSize = FAKE_DSTSIZE;
- char dstBuffer_static[FAKE_DSTSIZE] = {0};
-
- #define NB_BLOCKS_MAX 1024
- const void* srcBuffers[NB_BLOCKS_MAX];
- size_t srcSizes[NB_BLOCKS_MAX];
- void* dstBuffers[NB_BLOCKS_MAX];
- size_t dstCapacities[NB_BLOCKS_MAX];
- assert(nbBlocks < NB_BLOCKS_MAX);
-
- assert(size > 0);
- for (size_t n=0; n < nbBlocks; n++) {
- srcBuffers[n] = srcBuffer;
- srcSizes[n] = selectSize(size);
- dstBuffers[n] = dstBuffer_static;
- dstCapacities[n] = dstSize;
- }
-
-
- BMK_benchParams_t params = {
- .benchFn = hashfn,
- .benchPayload = payload,
- .initFn = NULL,
- .initPayload = NULL,
- .errorFn = NULL,
- .blockCount = nbBlocks,
- .srcBuffers = srcBuffers,
- .srcSizes = srcSizes,
- .dstBuffers = dstBuffers,
- .dstCapacities = dstCapacities,
- .blockResults = NULL
- };
- BMK_runOutcome_t result;
-
- while (!BMK_isCompleted_TimedFn(txf)) {
- result = BMK_benchTimedFn(txf, params);
- assert(BMK_isSuccessful_runOutcome(result));
- }
-
- BMK_runTime_t const runTime = BMK_extract_runTime(result);
-
- free(srcBuffer);
- assert(runTime.nanoSecPerRun != 0);
- return (1000000000U / runTime.nanoSecPerRun) * nbBlocks;
-
-}
-
-
-static size_t rand_1_N(size_t N) { return ((size_t)rand() % N) + 1; }
-
-static size_t identity(size_t s) { return s; }
-
-static size_t
-benchLatency(const void* src, size_t srcSize,
- void* dst, size_t dstCapacity,
- void* customPayload)
-{
- (void)dst; (void)dstCapacity;
- BMK_benchFn_t benchfn = (BMK_benchFn_t)customPayload;
- static size_t hash = 0;
-
- const void* const start = (const char*)src + (hash & START_MASK);
-
- return hash = benchfn(start, srcSize, dst, dstCapacity, NULL);
-}
-
-
-
-#ifndef SIZE_TO_HASH_PER_ROUND
-# define SIZE_TO_HASH_PER_ROUND 200000
-#endif
-
-#ifndef NB_HASH_ROUNDS_MAX
-# define NB_HASH_ROUNDS_MAX 1000
-#endif
-
-double bench_hash(BMK_benchFn_t hashfn,
- BMK_benchMode benchMode,
- size_t size, BMK_sizeMode sizeMode,
- unsigned total_time_ms, unsigned iter_time_ms)
-{
- sizeFunction_f const sizef = (sizeMode == BMK_fixedSize) ? identity : rand_1_N;
- BMK_benchFn_t const benchfn = (benchMode == BMK_throughput) ? hashfn : benchLatency;
- BMK_benchFn_t const payload = (benchMode == BMK_throughput) ? NULL : hashfn;
-
- size_t nbBlocks = (SIZE_TO_HASH_PER_ROUND / size) + 1;
- if (nbBlocks > NB_HASH_ROUNDS_MAX) nbBlocks = NB_HASH_ROUNDS_MAX;
-
- return bench_hash_internal(benchfn, payload,
- nbBlocks, sizef, size,
- total_time_ms, iter_time_ms);
-}
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchHash.h b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchHash.h
deleted file mode 100644
index 5871ff51a2..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchHash.h
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* Hash benchmark module
-* Part of the xxHash project
-* Copyright (C) 2019-present, Yann Collet
-*
-* GPL v2 License
-*
-* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
-* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
-* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
-* (at your option) any later version.
-*
-* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
-* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
-* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
-* GNU General Public License for more details.
-*
-* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
-* with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
-* 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
-*
-* You can contact the author at:
-* - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
-* - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
-*/
-
-
-#ifndef BENCH_HASH_H_983426678
-#define BENCH_HASH_H_983426678
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-extern "C" {
-#endif
-
-
-/* === Dependencies === */
-
-#include "benchfn.h" /* BMK_benchFn_t */
-
-
-/* === Declarations === */
-
-typedef enum { BMK_throughput, BMK_latency } BMK_benchMode;
-
-typedef enum { BMK_fixedSize, /* hash always `size` bytes */
- BMK_randomSize, /* hash a random nb of bytes, between 1 and `size` (inclusive) */
-} BMK_sizeMode;
-
-/*
- * bench_hash():
- * Returns speed expressed as nb hashes per second.
- * total_time_ms: time spent benchmarking the hash function with given parameters
- * iter_time_ms: time spent for one round. If multiple rounds are run,
- * bench_hash() will report the speed of best round.
- */
-double bench_hash(BMK_benchFn_t hashfn,
- BMK_benchMode benchMode,
- size_t size, BMK_sizeMode sizeMode,
- unsigned total_time_ms, unsigned iter_time_ms);
-
-
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-}
-#endif
-
-#endif /* BENCH_HASH_H_983426678 */
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchfn.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchfn.c
deleted file mode 100644
index 06ff6bf485..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchfn.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,252 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * Copyright (c) 2016-present, Yann Collet, Facebook, Inc.
- * All rights reserved.
- *
- * This source code is licensed under both the BSD-style license (found in the
- * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree) and the GPLv2 (found
- * in the COPYING file in the root directory of this source tree).
- * You may select, at your option, one of the above-listed licenses.
- */
-
-
-
-/* *************************************
-* Includes
-***************************************/
-#include /* malloc, free */
-#include /* memset */
-#undef NDEBUG /* assert must not be disabled */
-#include /* assert */
-
-#include "timefn.h" /* UTIL_time_t, UTIL_getTime */
-#include "benchfn.h"
-
-
-/* *************************************
-* Constants
-***************************************/
-#define TIMELOOP_MICROSEC SEC_TO_MICRO /* 1 second */
-#define TIMELOOP_NANOSEC (1*1000000000ULL) /* 1 second */
-
-#define KB *(1 <<10)
-#define MB *(1 <<20)
-#define GB *(1U<<30)
-
-
-/* *************************************
-* Debug errors
-***************************************/
-#if defined(DEBUG) && (DEBUG >= 1)
-# include /* fprintf */
-# define DISPLAY(...) fprintf(stderr, __VA_ARGS__)
-# define DEBUGOUTPUT(...) { if (DEBUG) DISPLAY(__VA_ARGS__); }
-#else
-# define DEBUGOUTPUT(...)
-#endif
-
-
-/* error without displaying */
-#define RETURN_QUIET_ERROR(retValue, ...) { \
- DEBUGOUTPUT("%s: %i: \n", __FILE__, __LINE__); \
- DEBUGOUTPUT("Error : "); \
- DEBUGOUTPUT(__VA_ARGS__); \
- DEBUGOUTPUT(" \n"); \
- return retValue; \
-}
-
-
-/* *************************************
-* Benchmarking an arbitrary function
-***************************************/
-
-int BMK_isSuccessful_runOutcome(BMK_runOutcome_t outcome)
-{
- return outcome.error_tag_never_ever_use_directly == 0;
-}
-
-/* warning : this function will stop program execution if outcome is invalid !
- * check outcome validity first, using BMK_isValid_runResult() */
-BMK_runTime_t BMK_extract_runTime(BMK_runOutcome_t outcome)
-{
- assert(outcome.error_tag_never_ever_use_directly == 0);
- return outcome.internal_never_ever_use_directly;
-}
-
-size_t BMK_extract_errorResult(BMK_runOutcome_t outcome)
-{
- assert(outcome.error_tag_never_ever_use_directly != 0);
- return outcome.error_result_never_ever_use_directly;
-}
-
-static BMK_runOutcome_t BMK_runOutcome_error(size_t errorResult)
-{
- BMK_runOutcome_t b;
- memset(&b, 0, sizeof(b));
- b.error_tag_never_ever_use_directly = 1;
- b.error_result_never_ever_use_directly = errorResult;
- return b;
-}
-
-static BMK_runOutcome_t BMK_setValid_runTime(BMK_runTime_t runTime)
-{
- BMK_runOutcome_t outcome;
- outcome.error_tag_never_ever_use_directly = 0;
- outcome.internal_never_ever_use_directly = runTime;
- return outcome;
-}
-
-
-/* initFn will be measured once, benchFn will be measured `nbLoops` times */
-/* initFn is optional, provide NULL if none */
-/* benchFn must return a size_t value that errorFn can interpret */
-/* takes # of blocks and list of size & stuff for each. */
-/* can report result of benchFn for each block into blockResult. */
-/* blockResult is optional, provide NULL if this information is not required */
-/* note : time per loop can be reported as zero if run time < timer resolution */
-BMK_runOutcome_t BMK_benchFunction(BMK_benchParams_t p,
- unsigned nbLoops)
-{
- /* init */
- { size_t i;
- for (i = 0; i < p.blockCount; i++) {
- memset(p.dstBuffers[i], 0xE5, p.dstCapacities[i]); /* warm up and erase result buffer */
- } }
-
- /* benchmark */
- { UTIL_time_t const clockStart = UTIL_getTime();
- size_t dstSize = 0;
- unsigned loopNb, blockNb;
- nbLoops += !nbLoops; /* minimum nbLoops is 1 */
- if (p.initFn != NULL) p.initFn(p.initPayload);
- for (loopNb = 0; loopNb < nbLoops; loopNb++) {
- for (blockNb = 0; blockNb < p.blockCount; blockNb++) {
- size_t const res = p.benchFn(p.srcBuffers[blockNb], p.srcSizes[blockNb],
- p.dstBuffers[blockNb], p.dstCapacities[blockNb],
- p.benchPayload);
- if (loopNb == 0) {
- if (p.blockResults != NULL) p.blockResults[blockNb] = res;
- if ((p.errorFn != NULL) && (p.errorFn(res))) {
- RETURN_QUIET_ERROR(BMK_runOutcome_error(res),
- "Function benchmark failed on block %u (of size %u) with error %i",
- blockNb, (unsigned)p.srcSizes[blockNb], (int)res);
- }
- dstSize += res;
- } }
- } /* for (loopNb = 0; loopNb < nbLoops; loopNb++) */
-
- { PTime const totalTime = UTIL_clockSpanNano(clockStart);
- BMK_runTime_t rt;
- rt.nanoSecPerRun = (double)totalTime / nbLoops;
- rt.sumOfReturn = dstSize;
- return BMK_setValid_runTime(rt);
- } }
-}
-
-
-/* ==== Benchmarking any function, providing intermediate results ==== */
-
-struct BMK_timedFnState_s {
- PTime timeSpent_ns;
- PTime timeBudget_ns;
- PTime runBudget_ns;
- BMK_runTime_t fastestRun;
- unsigned nbLoops;
- UTIL_time_t coolTime;
-}; /* typedef'd to BMK_timedFnState_t within bench.h */
-
-BMK_timedFnState_t* BMK_createTimedFnState(unsigned total_ms, unsigned run_ms)
-{
- BMK_timedFnState_t* const r = (BMK_timedFnState_t*)malloc(sizeof(*r));
- if (r == NULL) return NULL; /* malloc() error */
- BMK_resetTimedFnState(r, total_ms, run_ms);
- return r;
-}
-
-void BMK_freeTimedFnState(BMK_timedFnState_t* state) { free(state); }
-
-BMK_timedFnState_t*
-BMK_initStatic_timedFnState(void* buffer, size_t size, unsigned total_ms, unsigned run_ms)
-{
- typedef char check_size[ 2 * (sizeof(BMK_timedFnState_shell) >= sizeof(struct BMK_timedFnState_s)) - 1]; /* static assert : a compilation failure indicates that BMK_timedFnState_shell is not large enough */
- typedef struct { check_size c; BMK_timedFnState_t tfs; } tfs_align; /* force tfs to be aligned at its next best position */
- size_t const tfs_alignment = offsetof(tfs_align, tfs); /* provides the minimal alignment restriction for BMK_timedFnState_t */
- BMK_timedFnState_t* const r = (BMK_timedFnState_t*)buffer;
- if (buffer == NULL) return NULL;
- if (size < sizeof(struct BMK_timedFnState_s)) return NULL;
- if ((size_t)buffer % tfs_alignment) return NULL; /* buffer must be properly aligned */
- BMK_resetTimedFnState(r, total_ms, run_ms);
- return r;
-}
-
-void BMK_resetTimedFnState(BMK_timedFnState_t* timedFnState, unsigned total_ms, unsigned run_ms)
-{
- if (!total_ms) total_ms = 1 ;
- if (!run_ms) run_ms = 1;
- if (run_ms > total_ms) run_ms = total_ms;
- timedFnState->timeSpent_ns = 0;
- timedFnState->timeBudget_ns = (PTime)total_ms * TIMELOOP_NANOSEC / 1000;
- timedFnState->runBudget_ns = (PTime)run_ms * TIMELOOP_NANOSEC / 1000;
- timedFnState->fastestRun.nanoSecPerRun = (double)TIMELOOP_NANOSEC * 2000000000; /* hopefully large enough : must be larger than any potential measurement */
- timedFnState->fastestRun.sumOfReturn = (size_t)(-1LL);
- timedFnState->nbLoops = 1;
- timedFnState->coolTime = UTIL_getTime();
-}
-
-/* Tells if nb of seconds set in timedFnState for all runs is spent.
- * note : this function will return 1 if BMK_benchFunctionTimed() has actually errored. */
-int BMK_isCompleted_TimedFn(const BMK_timedFnState_t* timedFnState)
-{
- return (timedFnState->timeSpent_ns >= timedFnState->timeBudget_ns);
-}
-
-
-#undef MIN
-#define MIN(a,b) ( (a) < (b) ? (a) : (b) )
-
-#define MINUSABLETIME (TIMELOOP_NANOSEC / 2) /* 0.5 seconds */
-
-BMK_runOutcome_t BMK_benchTimedFn(BMK_timedFnState_t* cont,
- BMK_benchParams_t p)
-{
- PTime const runBudget_ns = cont->runBudget_ns;
- PTime const runTimeMin_ns = runBudget_ns / 2;
- BMK_runTime_t bestRunTime = cont->fastestRun;
-
- for (;;) {
- BMK_runOutcome_t const runResult = BMK_benchFunction(p, cont->nbLoops);
-
- if (!BMK_isSuccessful_runOutcome(runResult)) { /* error : move out */
- return runResult;
- }
-
- { BMK_runTime_t const newRunTime = BMK_extract_runTime(runResult);
- double const loopDuration_ns = newRunTime.nanoSecPerRun * cont->nbLoops;
-
- cont->timeSpent_ns += (unsigned long long)loopDuration_ns;
-
- /* estimate nbLoops for next run to last approximately 1 second */
- if (loopDuration_ns > (runBudget_ns / 50)) {
- double const fastestRun_ns = MIN(bestRunTime.nanoSecPerRun, newRunTime.nanoSecPerRun);
- cont->nbLoops = (unsigned)(runBudget_ns / fastestRun_ns) + 1;
- } else {
- /* previous run was too short : blindly increase workload by x multiplier */
- const unsigned multiplier = 10;
- assert(cont->nbLoops < ((unsigned)-1) / multiplier); /* avoid overflow */
- cont->nbLoops *= multiplier;
- }
-
- if (loopDuration_ns < runTimeMin_ns) {
- /* When benchmark run time is too small : don't report results.
- * increased risks of rounding errors */
- continue;
- }
-
- if (newRunTime.nanoSecPerRun < bestRunTime.nanoSecPerRun) {
- bestRunTime = newRunTime;
- }
- }
- break;
- } /* while (!completed) */
-
- return BMK_setValid_runTime(bestRunTime);
-}
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchfn.h b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchfn.h
deleted file mode 100644
index 19e056581a..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/benchfn.h
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,183 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * Copyright (c) 2016-present, Yann Collet, Facebook, Inc.
- * All rights reserved.
- *
- * This source code is licensed under both the BSD-style license (found in the
- * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree) and the GPLv2 (found
- * in the COPYING file in the root directory of this source tree).
- * You may select, at your option, one of the above-listed licenses.
- */
-
-
-/* benchfn :
- * benchmark any function on a set of input
- * providing result in nanoSecPerRun
- * or detecting and returning an error
- */
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-extern "C" {
-#endif
-
-#ifndef BENCH_FN_H_23876
-#define BENCH_FN_H_23876
-
-/* === Dependencies === */
-#include /* size_t */
-
-
-/* ==== Benchmark any function, iterated on a set of blocks ==== */
-
-/* BMK_runTime_t: valid result return type */
-
-typedef struct {
- double nanoSecPerRun; /* time per iteration (over all blocks) */
- size_t sumOfReturn; /* sum of return values */
-} BMK_runTime_t;
-
-
-/* BMK_runOutcome_t:
- * type expressing the outcome of a benchmark run by BMK_benchFunction(),
- * which can be either valid or invalid.
- * benchmark outcome can be invalid if errorFn is provided.
- * BMK_runOutcome_t must be considered "opaque" : never access its members directly.
- * Instead, use its assigned methods :
- * BMK_isSuccessful_runOutcome, BMK_extract_runTime, BMK_extract_errorResult.
- * The structure is only described here to allow its allocation on stack. */
-
-typedef struct {
- BMK_runTime_t internal_never_ever_use_directly;
- size_t error_result_never_ever_use_directly;
- int error_tag_never_ever_use_directly;
-} BMK_runOutcome_t;
-
-
-/* prototypes for benchmarked functions */
-typedef size_t (*BMK_benchFn_t)(const void* src, size_t srcSize, void* dst, size_t dstCapacity, void* customPayload);
-typedef size_t (*BMK_initFn_t)(void* initPayload);
-typedef unsigned (*BMK_errorFn_t)(size_t);
-
-
-/* BMK_benchFunction() parameters are provided via the following structure.
- * A structure is preferable for readability,
- * as the number of parameters required is fairly large.
- * No initializer is provided, because it doesn't make sense to provide some "default" :
- * all parameters must be specified by the caller.
- * optional parameters are labelled explicitly, and accept value NULL when not used */
-typedef struct {
- BMK_benchFn_t benchFn; /* the function to benchmark, over the set of blocks */
- void* benchPayload; /* pass custom parameters to benchFn :
- * (*benchFn)(srcBuffers[i], srcSizes[i], dstBuffers[i], dstCapacities[i], benchPayload) */
- BMK_initFn_t initFn; /* (*initFn)(initPayload) is run once per run, at the beginning. */
- void* initPayload; /* Both arguments can be NULL, in which case nothing is run. */
- BMK_errorFn_t errorFn; /* errorFn will check each return value of benchFn over each block, to determine if it failed or not.
- * errorFn can be NULL, in which case no check is performed.
- * errorFn must return 0 when benchFn was successful, and >= 1 if it detects an error.
- * Execution is stopped as soon as an error is detected.
- * the triggering return value can be retrieved using BMK_extract_errorResult(). */
- size_t blockCount; /* number of blocks to operate benchFn on.
- * It's also the size of all array parameters :
- * srcBuffers, srcSizes, dstBuffers, dstCapacities, blockResults */
- const void *const * srcBuffers; /* read-only array of buffers to be operated on by benchFn */
- const size_t* srcSizes; /* read-only array containing sizes of srcBuffers */
- void *const * dstBuffers; /* array of buffers to be written into by benchFn. This array is not optional, it must be provided even if unused by benchfn. */
- const size_t* dstCapacities; /* read-only array containing capacities of dstBuffers. This array must be present. */
- size_t* blockResults; /* Optional: store the return value of benchFn for each block. Use NULL if this result is not requested. */
-} BMK_benchParams_t;
-
-
-/* BMK_benchFunction() :
- * This function benchmarks benchFn and initFn, providing a result.
- *
- * params : see description of BMK_benchParams_t above.
- * nbLoops: defines number of times benchFn is run over the full set of blocks.
- * Minimum value is 1. A 0 is interpreted as a 1.
- *
- * @return: can express either an error or a successful result.
- * Use BMK_isSuccessful_runOutcome() to check if benchmark was successful.
- * If yes, extract the result with BMK_extract_runTime(),
- * it will contain :
- * .sumOfReturn : the sum of all return values of benchFn through all of blocks
- * .nanoSecPerRun : time per run of benchFn + (time for initFn / nbLoops)
- * .sumOfReturn is generally intended for functions which return a # of bytes written into dstBuffer,
- * in which case, this value will be the total amount of bytes written into dstBuffer.
- *
- * blockResults : when provided (!= NULL), and when benchmark is successful,
- * params.blockResults contains all return values of `benchFn` over all blocks.
- * when provided (!= NULL), and when benchmark failed,
- * params.blockResults contains return values of `benchFn` over all blocks preceding and including the failed block.
- */
-BMK_runOutcome_t BMK_benchFunction(BMK_benchParams_t params, unsigned nbLoops);
-
-
-
-/* check first if the benchmark was successful or not */
-int BMK_isSuccessful_runOutcome(BMK_runOutcome_t outcome);
-
-/* If the benchmark was successful, extract the result.
- * note : this function will abort() program execution if benchmark failed !
- * always check if benchmark was successful first !
- */
-BMK_runTime_t BMK_extract_runTime(BMK_runOutcome_t outcome);
-
-/* when benchmark failed, it means one invocation of `benchFn` failed.
- * The failure was detected by `errorFn`, operating on return values of `benchFn`.
- * Returns the faulty return value.
- * note : this function will abort() program execution if benchmark did not failed.
- * always check if benchmark failed first !
- */
-size_t BMK_extract_errorResult(BMK_runOutcome_t outcome);
-
-
-
-/* ==== Benchmark any function, returning intermediate results ==== */
-
-/* state information tracking benchmark session */
-typedef struct BMK_timedFnState_s BMK_timedFnState_t;
-
-/* BMK_benchTimedFn() :
- * Similar to BMK_benchFunction(), most arguments being identical.
- * Automatically determines `nbLoops` so that each result is regularly produced at interval of about run_ms.
- * Note : minimum `nbLoops` is 1, therefore a run may last more than run_ms, and possibly even more than total_ms.
- * Usage - initialize timedFnState, select benchmark duration (total_ms) and each measurement duration (run_ms)
- * call BMK_benchTimedFn() repetitively, each measurement is supposed to last about run_ms
- * Check if total time budget is spent or exceeded, using BMK_isCompleted_TimedFn()
- */
-BMK_runOutcome_t BMK_benchTimedFn(BMK_timedFnState_t* timedFnState,
- BMK_benchParams_t params);
-
-/* Tells if duration of all benchmark runs has exceeded total_ms
- */
-int BMK_isCompleted_TimedFn(const BMK_timedFnState_t* timedFnState);
-
-/* BMK_createTimedFnState() and BMK_resetTimedFnState() :
- * Create/Set BMK_timedFnState_t for next benchmark session,
- * which shall last a minimum of total_ms milliseconds,
- * producing intermediate results, paced at interval of (approximately) run_ms.
- */
-BMK_timedFnState_t* BMK_createTimedFnState(unsigned total_ms, unsigned run_ms);
-void BMK_resetTimedFnState(BMK_timedFnState_t* timedFnState, unsigned total_ms, unsigned run_ms);
-void BMK_freeTimedFnState(BMK_timedFnState_t* state);
-
-
-/* BMK_timedFnState_shell and BMK_initStatic_timedFnState() :
- * Makes it possible to statically allocate a BMK_timedFnState_t on stack.
- * BMK_timedFnState_shell is only there to allocate space,
- * never ever access its members.
- * BMK_timedFnState_t() actually accepts any buffer.
- * It will check if provided buffer is large enough and is correctly aligned,
- * and will return NULL if conditions are not respected.
- */
-#define BMK_TIMEDFNSTATE_SIZE 64
-typedef union {
- char never_access_space[BMK_TIMEDFNSTATE_SIZE];
- long long alignment_enforcer; /* must be aligned on 8-bytes boundaries */
-} BMK_timedFnState_shell;
-BMK_timedFnState_t* BMK_initStatic_timedFnState(void* buffer, size_t size, unsigned total_ms, unsigned run_ms);
-
-
-#endif /* BENCH_FN_H_23876 */
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-}
-#endif
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/bhDisplay.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/bhDisplay.c
deleted file mode 100644
index eabec1a523..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/bhDisplay.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,159 +0,0 @@
-/*
-* CSV Display module for the hash benchmark program
-* Part of the xxHash project
-* Copyright (C) 2019-present, Yann Collet
-*
-* GPL v2 License
-*
-* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
-* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
-* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
-* (at your option) any later version.
-*
-* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
-* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
-* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
-* GNU General Public License for more details.
-*
-* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
-* with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
-* 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
-*
-* You can contact the author at :
-* - xxHash homepage : https://www.xxhash.com
-* - xxHash source repository : https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
-*/
-
-
-/* === Dependencies === */
-
-#include /* rand */
-#include /* printf */
-#include
-
-#include "benchHash.h"
-#include "bhDisplay.h"
-
-
-/* === benchmark large input === */
-
-#define MB_UNIT 1000000
-#define BENCH_LARGE_ITER_MS 490
-#define BENCH_LARGE_TOTAL_MS 1010
-static void bench_oneHash_largeInput(Bench_Entry hashDesc, int minlog, int maxlog)
-{
- printf("%-7s", hashDesc.name);
- for (int sizelog=minlog; sizelog<=maxlog; sizelog++) {
- size_t const inputSize = (size_t)1 << sizelog;
- double const nbhps = bench_hash(hashDesc.hash, BMK_throughput,
- inputSize, BMK_fixedSize,
- BENCH_LARGE_TOTAL_MS, BENCH_LARGE_ITER_MS);
- printf(",%9.1f", nbhps * inputSize / MB_UNIT); fflush(NULL);
- }
- printf("\n");
-}
-
-void bench_largeInput(Bench_Entry const* hashDescTable, int nbHashes, int minlog, int maxlog)
-{
- assert(maxlog < 31);
- assert(minlog >= 0);
- printf("benchmarking large inputs : from %u bytes (log%i) to %u MB (log%i) \n",
- 1U << minlog, minlog,
- (1U << maxlog) >> 20, maxlog);
- for (int i=0; i /* size_t */
-
-
-/* ==================================================
- * Non-portable hash algorithms
- * =============================================== */
-
-
-#ifdef HARDWARE_SUPPORT
-
-/*
- * List any hash algorithms that depend on specific hardware support,
- * including for example:
- * - Hardware crc32c
- * - Hardware AES support
- * - Carryless Multipliers (clmul)
- * - AVX2
- */
-
-#endif
-
-
-
-/* ==================================================
- * List of hashes
- * ==================================================
- * Each hash must be wrapped in a thin redirector conformant with the BMK_benchfn_t.
- * BMK_benchfn_t is generic, not specifically designed for hashes.
- * For hashes, the following parameters are expected to be useless:
- * dst, dstCapacity, customPayload.
- *
- * The result of each hash is assumed to be provided as function return value.
- * This condition is important for latency measurements.
- */
-
- /* === xxHash === */
-
-#include "xxh3.h"
-
-size_t XXH32_wrapper(const void* src, size_t srcSize, void* dst, size_t dstCapacity, void* customPayload)
-{
- (void)dst; (void)dstCapacity; (void)customPayload;
- return (size_t) XXH32(src, srcSize, 0);
-}
-
-
-size_t XXH64_wrapper(const void* src, size_t srcSize, void* dst, size_t dstCapacity, void* customPayload)
-{
- (void)dst; (void)dstCapacity; (void)customPayload;
- return (size_t) XXH64(src, srcSize, 0);
-}
-
-
-size_t xxh3_wrapper(const void* src, size_t srcSize, void* dst, size_t dstCapacity, void* customPayload)
-{
- (void)dst; (void)dstCapacity; (void)customPayload;
- return (size_t) XXH3_64bits(src, srcSize);
-}
-
-
-size_t XXH128_wrapper(const void* src, size_t srcSize, void* dst, size_t dstCapacity, void* customPayload)
-{
- (void)dst; (void)dstCapacity; (void)customPayload;
- return (size_t) XXH3_128bits(src, srcSize).low64;
-}
-
-
-
-/* ==================================================
- * Table of hashes
- * =============================================== */
-
-#include "bhDisplay.h" /* Bench_Entry */
-
-#ifndef HARDWARE_SUPPORT
-# define NB_HASHES 4
-#else
-# define NB_HASHES 4
-#endif
-
-Bench_Entry const hashCandidates[NB_HASHES] = {
- { "xxh3" , xxh3_wrapper },
- { "XXH32" , XXH32_wrapper },
- { "XXH64" , XXH64_wrapper },
- { "XXH128", XXH128_wrapper },
-#ifdef HARDWARE_SUPPORT
- /* list here codecs which require specific hardware support, such SSE4.1, PCLMUL, AVX2, etc. */
-#endif
-};
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/main.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/main.c
deleted file mode 100644
index 47c956c70b..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/main.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,220 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * Main program to benchmark hash functions
- * Part of the xxHash project
- * Copyright (C) 2019-present, Yann Collet
- * GPL v2 License
- *
- * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
- * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
- * the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
- * (at your option) any later version.
- *
- * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
- * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
- * GNU General Public License for more details.
- *
- * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
- * with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- * 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
- * - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
- */
-
-
-/* === dependencies === */
-
-#include /* printf */
-#include /* INT_MAX */
-#include "bhDisplay.h" /* bench_x */
-
-
-/* === defines list of hashes `hashCandidates` and NB_HASHES *** */
-
-#include "hashes.h"
-
-
-/* === parse command line === */
-
-#undef NDEBUG
-#include
-
-
-/*!
- * readIntFromChar():
- * Allows and interprets K, KB, KiB, M, MB and MiB suffix.
- * Will also modify `*stringPtr`, advancing it to position where it stopped reading.
- */
-static int readIntFromChar(const char** stringPtr)
-{
- static int const max = (INT_MAX / 10) - 1;
- int result = 0;
- while ((**stringPtr >='0') && (**stringPtr <='9')) {
- assert(result < max);
- result *= 10;
- result += (unsigned)(**stringPtr - '0');
- (*stringPtr)++ ;
- }
- if ((**stringPtr=='K') || (**stringPtr=='M')) {
- int const maxK = INT_MAX >> 10;
- assert(result < maxK);
- result <<= 10;
- if (**stringPtr=='M') {
- assert(result < maxK);
- result <<= 10;
- }
- (*stringPtr)++; /* skip `K` or `M` */
- if (**stringPtr=='i') (*stringPtr)++;
- if (**stringPtr=='B') (*stringPtr)++;
- }
- return result;
-}
-
-
-/**
- * longCommand():
- * Checks if string is the same as longCommand.
- * If yes, @return 1, otherwise @return 0
- */
-static int isCommand(const char* string, const char* longCommand)
-{
- assert(string);
- assert(longCommand);
- size_t const comSize = strlen(longCommand);
- return !strncmp(string, longCommand, comSize);
-}
-
-/*
- * longCommandWArg():
- * Checks if *stringPtr is the same as longCommand.
- * If yes, @return 1 and advances *stringPtr to the position which immediately
- * follows longCommand.
- * @return 0 and doesn't modify *stringPtr otherwise.
- */
-static int longCommandWArg(const char** stringPtr, const char* longCommand)
-{
- assert(stringPtr);
- assert(longCommand);
- size_t const comSize = strlen(longCommand);
- int const result = isCommand(*stringPtr, longCommand);
- if (result) *stringPtr += comSize;
- return result;
-}
-
-
-/* === default values - can be redefined at compilation time === */
-
-#ifndef SMALL_SIZE_MIN_DEFAULT
-# define SMALL_SIZE_MIN_DEFAULT 1
-#endif
-#ifndef SMALL_SIZE_MAX_DEFAULT
-# define SMALL_SIZE_MAX_DEFAULT 127
-#endif
-#ifndef LARGE_SIZELOG_MIN_DEFAULT
-# define LARGE_SIZELOG_MIN_DEFAULT 9
-#endif
-#ifndef LARGE_SIZELOG_MAX_DEFAULT
-# define LARGE_SIZELOG_MAX_DEFAULT 27
-#endif
-
-
-static int display_hash_names(void)
-{
- int i;
- printf("available hashes : \n");
- for (i=0; i= 1); return help(exename); }
- if (isCommand(*arg, "--list")) { return display_hash_names(); }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--n=")) { nb_h_test = readIntFromChar(arg); continue; } /* hidden command */
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--minl=")) { largeTest_log_min = readIntFromChar(arg); continue; }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--maxl=")) { largeTest_log_max = readIntFromChar(arg); continue; }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--mins=")) { smallTest_size_min = (size_t)readIntFromChar(arg); continue; }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--maxs=")) { smallTest_size_max = (size_t)readIntFromChar(arg); continue; }
- /* not a command: must be a hash name */
- hashNb = hashID(*arg);
- if (hashNb >= 0) {
- nb_h_test = 1;
- } else {
- /* not a hash name: error */
- return badusage(exename);
- }
- }
-
- /* border case (requires (mis)using hidden command `--n=#`) */
- if (hashNb + nb_h_test > NB_HASHES) {
- printf("wrong hash selection \n");
- return 1;
- }
-
- printf(" === benchmarking %i hash functions === \n", nb_h_test);
- if (largeTest_log_max >= largeTest_log_min) {
- bench_largeInput(hashCandidates+hashNb, nb_h_test, largeTest_log_min, largeTest_log_max);
- }
- if (smallTest_size_max >= smallTest_size_min) {
- bench_throughput_smallInputs(hashCandidates+hashNb, nb_h_test, smallTest_size_min, smallTest_size_max);
- bench_throughput_randomInputLength(hashCandidates+hashNb, nb_h_test, smallTest_size_min, smallTest_size_max);
- bench_latency_smallInputs(hashCandidates+hashNb, nb_h_test, smallTest_size_min, smallTest_size_max);
- bench_latency_randomInputLength(hashCandidates+hashNb, nb_h_test, smallTest_size_min, smallTest_size_max);
- }
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/timefn.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/timefn.c
deleted file mode 100644
index 096e1910bf..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/timefn.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,168 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * Copyright (c) 2019-present, Yann Collet, Facebook, Inc.
- * All rights reserved.
- *
- * This source code is licensed under both the BSD-style license (found in the
- * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree) and the GPLv2 (found
- * in the COPYING file in the root directory of this source tree).
- * You may select, at your option, one of the above-listed licenses.
- */
-
-
-/* === Dependencies === */
-
-#include "timefn.h"
-
-
-/*-****************************************
-* Time functions
-******************************************/
-
-#if defined(_WIN32) /* Windows */
-
-#include /* abort */
-#include /* perror */
-
-UTIL_time_t UTIL_getTime(void) { UTIL_time_t x; QueryPerformanceCounter(&x); return x; }
-
-PTime UTIL_getSpanTimeMicro(UTIL_time_t clockStart, UTIL_time_t clockEnd)
-{
- static LARGE_INTEGER ticksPerSecond;
- static int init = 0;
- if (!init) {
- if (!QueryPerformanceFrequency(&ticksPerSecond)) {
- perror("timefn::QueryPerformanceFrequency");
- abort();
- }
- init = 1;
- }
- return 1000000ULL*(clockEnd.QuadPart - clockStart.QuadPart)/ticksPerSecond.QuadPart;
-}
-
-PTime UTIL_getSpanTimeNano(UTIL_time_t clockStart, UTIL_time_t clockEnd)
-{
- static LARGE_INTEGER ticksPerSecond;
- static int init = 0;
- if (!init) {
- if (!QueryPerformanceFrequency(&ticksPerSecond)) {
- perror("timefn::QueryPerformanceFrequency");
- abort();
- }
- init = 1;
- }
- return 1000000000ULL*(clockEnd.QuadPart - clockStart.QuadPart)/ticksPerSecond.QuadPart;
-}
-
-
-
-#elif defined(__APPLE__) && defined(__MACH__)
-
-UTIL_time_t UTIL_getTime(void) { return mach_absolute_time(); }
-
-PTime UTIL_getSpanTimeMicro(UTIL_time_t clockStart, UTIL_time_t clockEnd)
-{
- static mach_timebase_info_data_t rate;
- static int init = 0;
- if (!init) {
- mach_timebase_info(&rate);
- init = 1;
- }
- return (((clockEnd - clockStart) * (PTime)rate.numer) / ((PTime)rate.denom))/1000ULL;
-}
-
-PTime UTIL_getSpanTimeNano(UTIL_time_t clockStart, UTIL_time_t clockEnd)
-{
- static mach_timebase_info_data_t rate;
- static int init = 0;
- if (!init) {
- mach_timebase_info(&rate);
- init = 1;
- }
- return ((clockEnd - clockStart) * (PTime)rate.numer) / ((PTime)rate.denom);
-}
-
-
-
-#elif (defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 201112L) /* C11 */) \
- && defined(TIME_UTC) /* C11 requires timespec_get, but FreeBSD 11 lacks it, while still claiming C11 compliance */
-
-#include /* abort */
-#include /* perror */
-
-UTIL_time_t UTIL_getTime(void)
-{
- /* time must be initialized, othersize it may fail msan test.
- * No good reason, likely a limitation of timespec_get() for some target */
- UTIL_time_t time = UTIL_TIME_INITIALIZER;
- if (timespec_get(&time, TIME_UTC) != TIME_UTC) {
- perror("timefn::timespec_get");
- abort();
- }
- return time;
-}
-
-static UTIL_time_t UTIL_getSpanTime(UTIL_time_t begin, UTIL_time_t end)
-{
- UTIL_time_t diff;
- if (end.tv_nsec < begin.tv_nsec) {
- diff.tv_sec = (end.tv_sec - 1) - begin.tv_sec;
- diff.tv_nsec = (end.tv_nsec + 1000000000ULL) - begin.tv_nsec;
- } else {
- diff.tv_sec = end.tv_sec - begin.tv_sec;
- diff.tv_nsec = end.tv_nsec - begin.tv_nsec;
- }
- return diff;
-}
-
-PTime UTIL_getSpanTimeMicro(UTIL_time_t begin, UTIL_time_t end)
-{
- UTIL_time_t const diff = UTIL_getSpanTime(begin, end);
- PTime micro = 0;
- micro += 1000000ULL * diff.tv_sec;
- micro += diff.tv_nsec / 1000ULL;
- return micro;
-}
-
-PTime UTIL_getSpanTimeNano(UTIL_time_t begin, UTIL_time_t end)
-{
- UTIL_time_t const diff = UTIL_getSpanTime(begin, end);
- PTime nano = 0;
- nano += 1000000000ULL * diff.tv_sec;
- nano += diff.tv_nsec;
- return nano;
-}
-
-
-
-#else /* relies on standard C90 (note : clock_t measurements can be wrong when using multi-threading) */
-
-UTIL_time_t UTIL_getTime(void) { return clock(); }
-PTime UTIL_getSpanTimeMicro(UTIL_time_t clockStart, UTIL_time_t clockEnd) { return 1000000ULL * (clockEnd - clockStart) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; }
-PTime UTIL_getSpanTimeNano(UTIL_time_t clockStart, UTIL_time_t clockEnd) { return 1000000000ULL * (clockEnd - clockStart) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; }
-
-#endif
-
-
-
-/* returns time span in microseconds */
-PTime UTIL_clockSpanMicro(UTIL_time_t clockStart )
-{
- UTIL_time_t const clockEnd = UTIL_getTime();
- return UTIL_getSpanTimeMicro(clockStart, clockEnd);
-}
-
-/* returns time span in microseconds */
-PTime UTIL_clockSpanNano(UTIL_time_t clockStart )
-{
- UTIL_time_t const clockEnd = UTIL_getTime();
- return UTIL_getSpanTimeNano(clockStart, clockEnd);
-}
-
-void UTIL_waitForNextTick(void)
-{
- UTIL_time_t const clockStart = UTIL_getTime();
- UTIL_time_t clockEnd;
- do {
- clockEnd = UTIL_getTime();
- } while (UTIL_getSpanTimeNano(clockStart, clockEnd) == 0);
-}
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/timefn.h b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/timefn.h
deleted file mode 100644
index d1ddd31b1c..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/bench/timefn.h
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * Copyright (c) 2016-present, Yann Collet, Facebook, Inc.
- * All rights reserved.
- *
- * This source code is licensed under both the BSD-style license (found in the
- * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree) and the GPLv2 (found
- * in the COPYING file in the root directory of this source tree).
- * You may select, at your option, one of the above-listed licenses.
- */
-
-#ifndef TIME_FN_H_MODULE_287987
-#define TIME_FN_H_MODULE_287987
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-extern "C" {
-#endif
-
-
-/*-****************************************
-* Dependencies
-******************************************/
-#include /* utime */
-#if defined(_MSC_VER)
-# include /* utime */
-#else
-# include /* utime */
-#endif
-#include /* clock_t, clock, CLOCKS_PER_SEC */
-
-
-
-/*-****************************************
-* Local Types
-******************************************/
-
-#if !defined (__VMS) && (defined (__cplusplus) || (defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L) /* C99 */) )
-# include
- typedef uint64_t PTime; /* Precise Time */
-#else
- typedef unsigned long long PTime; /* does not support compilers without long long support */
-#endif
-
-
-
-/*-****************************************
-* Time functions
-******************************************/
-#if defined(_WIN32) /* Windows */
-
- #include /* LARGE_INTEGER */
- typedef LARGE_INTEGER UTIL_time_t;
- #define UTIL_TIME_INITIALIZER { { 0, 0 } }
-
-#elif defined(__APPLE__) && defined(__MACH__)
-
- #include
- typedef PTime UTIL_time_t;
- #define UTIL_TIME_INITIALIZER 0
-
-#elif (defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 201112L) /* C11 */) \
- && defined(TIME_UTC) /* C11 requires timespec_get, but FreeBSD 11 lacks it, while still claiming C11 compliance */
-
- typedef struct timespec UTIL_time_t;
- #define UTIL_TIME_INITIALIZER { 0, 0 }
-
-#else /* relies on standard C90 (note : clock_t measurements can be wrong when using multi-threading) */
-
- typedef clock_t UTIL_time_t;
- #define UTIL_TIME_INITIALIZER 0
-
-#endif
-
-
-UTIL_time_t UTIL_getTime(void);
-PTime UTIL_getSpanTimeMicro(UTIL_time_t clockStart, UTIL_time_t clockEnd);
-PTime UTIL_getSpanTimeNano(UTIL_time_t clockStart, UTIL_time_t clockEnd);
-
-#define SEC_TO_MICRO ((PTime)1000000)
-PTime UTIL_clockSpanMicro(UTIL_time_t clockStart);
-PTime UTIL_clockSpanNano(UTIL_time_t clockStart);
-
-void UTIL_waitForNextTick(void);
-
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-}
-#endif
-
-#endif /* TIME_FN_H_MODULE_287987 */
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/.gitignore b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/.gitignore
deleted file mode 100644
index f85592639b..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/.gitignore
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
-#build artefacts
-collisionsTest
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/LICENSE b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/LICENSE
deleted file mode 100644
index d159169d10..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/LICENSE
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,339 +0,0 @@
- GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
- Version 2, June 1991
-
- Copyright (C) 1989, 1991 Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
- Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
- of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
-
- Preamble
-
- The licenses for most software are designed to take away your
-freedom to share and change it. By contrast, the GNU General Public
-License is intended to guarantee your freedom to share and change free
-software--to make sure the software is free for all its users. This
-General Public License applies to most of the Free Software
-Foundation's software and to any other program whose authors commit to
-using it. (Some other Free Software Foundation software is covered by
-the GNU Lesser General Public License instead.) You can apply it to
-your programs, too.
-
- When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not
-price. Our General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that you
-have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge for
-this service if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it
-if you want it, that you can change the software or use pieces of it
-in new free programs; and that you know you can do these things.
-
- To protect your rights, we need to make restrictions that forbid
-anyone to deny you these rights or to ask you to surrender the rights.
-These restrictions translate to certain responsibilities for you if you
-distribute copies of the software, or if you modify it.
-
- For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whether
-gratis or for a fee, you must give the recipients all the rights that
-you have. You must make sure that they, too, receive or can get the
-source code. And you must show them these terms so they know their
-rights.
-
- We protect your rights with two steps: (1) copyright the software, and
-(2) offer you this license which gives you legal permission to copy,
-distribute and/or modify the software.
-
- Also, for each author's protection and ours, we want to make certain
-that everyone understands that there is no warranty for this free
-software. If the software is modified by someone else and passed on, we
-want its recipients to know that what they have is not the original, so
-that any problems introduced by others will not reflect on the original
-authors' reputations.
-
- Finally, any free program is threatened constantly by software
-patents. We wish to avoid the danger that redistributors of a free
-program will individually obtain patent licenses, in effect making the
-program proprietary. To prevent this, we have made it clear that any
-patent must be licensed for everyone's free use or not licensed at all.
-
- The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and
-modification follow.
-
- GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
- TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR COPYING, DISTRIBUTION AND MODIFICATION
-
- 0. This License applies to any program or other work which contains
-a notice placed by the copyright holder saying it may be distributed
-under the terms of this General Public License. The "Program", below,
-refers to any such program or work, and a "work based on the Program"
-means either the Program or any derivative work under copyright law:
-that is to say, a work containing the Program or a portion of it,
-either verbatim or with modifications and/or translated into another
-language. (Hereinafter, translation is included without limitation in
-the term "modification".) Each licensee is addressed as "you".
-
-Activities other than copying, distribution and modification are not
-covered by this License; they are outside its scope. The act of
-running the Program is not restricted, and the output from the Program
-is covered only if its contents constitute a work based on the
-Program (independent of having been made by running the Program).
-Whether that is true depends on what the Program does.
-
- 1. You may copy and distribute verbatim copies of the Program's
-source code as you receive it, in any medium, provided that you
-conspicuously and appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate
-copyright notice and disclaimer of warranty; keep intact all the
-notices that refer to this License and to the absence of any warranty;
-and give any other recipients of the Program a copy of this License
-along with the Program.
-
-You may charge a fee for the physical act of transferring a copy, and
-you may at your option offer warranty protection in exchange for a fee.
-
- 2. You may modify your copy or copies of the Program or any portion
-of it, thus forming a work based on the Program, and copy and
-distribute such modifications or work under the terms of Section 1
-above, provided that you also meet all of these conditions:
-
- a) You must cause the modified files to carry prominent notices
- stating that you changed the files and the date of any change.
-
- b) You must cause any work that you distribute or publish, that in
- whole or in part contains or is derived from the Program or any
- part thereof, to be licensed as a whole at no charge to all third
- parties under the terms of this License.
-
- c) If the modified program normally reads commands interactively
- when run, you must cause it, when started running for such
- interactive use in the most ordinary way, to print or display an
- announcement including an appropriate copyright notice and a
- notice that there is no warranty (or else, saying that you provide
- a warranty) and that users may redistribute the program under
- these conditions, and telling the user how to view a copy of this
- License. (Exception: if the Program itself is interactive but
- does not normally print such an announcement, your work based on
- the Program is not required to print an announcement.)
-
-These requirements apply to the modified work as a whole. If
-identifiable sections of that work are not derived from the Program,
-and can be reasonably considered independent and separate works in
-themselves, then this License, and its terms, do not apply to those
-sections when you distribute them as separate works. But when you
-distribute the same sections as part of a whole which is a work based
-on the Program, the distribution of the whole must be on the terms of
-this License, whose permissions for other licensees extend to the
-entire whole, and thus to each and every part regardless of who wrote it.
-
-Thus, it is not the intent of this section to claim rights or contest
-your rights to work written entirely by you; rather, the intent is to
-exercise the right to control the distribution of derivative or
-collective works based on the Program.
-
-In addition, mere aggregation of another work not based on the Program
-with the Program (or with a work based on the Program) on a volume of
-a storage or distribution medium does not bring the other work under
-the scope of this License.
-
- 3. You may copy and distribute the Program (or a work based on it,
-under Section 2) in object code or executable form under the terms of
-Sections 1 and 2 above provided that you also do one of the following:
-
- a) Accompany it with the complete corresponding machine-readable
- source code, which must be distributed under the terms of Sections
- 1 and 2 above on a medium customarily used for software interchange; or,
-
- b) Accompany it with a written offer, valid for at least three
- years, to give any third party, for a charge no more than your
- cost of physically performing source distribution, a complete
- machine-readable copy of the corresponding source code, to be
- distributed under the terms of Sections 1 and 2 above on a medium
- customarily used for software interchange; or,
-
- c) Accompany it with the information you received as to the offer
- to distribute corresponding source code. (This alternative is
- allowed only for noncommercial distribution and only if you
- received the program in object code or executable form with such
- an offer, in accord with Subsection b above.)
-
-The source code for a work means the preferred form of the work for
-making modifications to it. For an executable work, complete source
-code means all the source code for all modules it contains, plus any
-associated interface definition files, plus the scripts used to
-control compilation and installation of the executable. However, as a
-special exception, the source code distributed need not include
-anything that is normally distributed (in either source or binary
-form) with the major components (compiler, kernel, and so on) of the
-operating system on which the executable runs, unless that component
-itself accompanies the executable.
-
-If distribution of executable or object code is made by offering
-access to copy from a designated place, then offering equivalent
-access to copy the source code from the same place counts as
-distribution of the source code, even though third parties are not
-compelled to copy the source along with the object code.
-
- 4. You may not copy, modify, sublicense, or distribute the Program
-except as expressly provided under this License. Any attempt
-otherwise to copy, modify, sublicense or distribute the Program is
-void, and will automatically terminate your rights under this License.
-However, parties who have received copies, or rights, from you under
-this License will not have their licenses terminated so long as such
-parties remain in full compliance.
-
- 5. You are not required to accept this License, since you have not
-signed it. However, nothing else grants you permission to modify or
-distribute the Program or its derivative works. These actions are
-prohibited by law if you do not accept this License. Therefore, by
-modifying or distributing the Program (or any work based on the
-Program), you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so, and
-all its terms and conditions for copying, distributing or modifying
-the Program or works based on it.
-
- 6. Each time you redistribute the Program (or any work based on the
-Program), the recipient automatically receives a license from the
-original licensor to copy, distribute or modify the Program subject to
-these terms and conditions. You may not impose any further
-restrictions on the recipients' exercise of the rights granted herein.
-You are not responsible for enforcing compliance by third parties to
-this License.
-
- 7. If, as a consequence of a court judgment or allegation of patent
-infringement or for any other reason (not limited to patent issues),
-conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or
-otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not
-excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you cannot
-distribute so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this
-License and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you
-may not distribute the Program at all. For example, if a patent
-license would not permit royalty-free redistribution of the Program by
-all those who receive copies directly or indirectly through you, then
-the only way you could satisfy both it and this License would be to
-refrain entirely from distribution of the Program.
-
-If any portion of this section is held invalid or unenforceable under
-any particular circumstance, the balance of the section is intended to
-apply and the section as a whole is intended to apply in other
-circumstances.
-
-It is not the purpose of this section to induce you to infringe any
-patents or other property right claims or to contest validity of any
-such claims; this section has the sole purpose of protecting the
-integrity of the free software distribution system, which is
-implemented by public license practices. Many people have made
-generous contributions to the wide range of software distributed
-through that system in reliance on consistent application of that
-system; it is up to the author/donor to decide if he or she is willing
-to distribute software through any other system and a licensee cannot
-impose that choice.
-
-This section is intended to make thoroughly clear what is believed to
-be a consequence of the rest of this License.
-
- 8. If the distribution and/or use of the Program is restricted in
-certain countries either by patents or by copyrighted interfaces, the
-original copyright holder who places the Program under this License
-may add an explicit geographical distribution limitation excluding
-those countries, so that distribution is permitted only in or among
-countries not thus excluded. In such case, this License incorporates
-the limitation as if written in the body of this License.
-
- 9. The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions
-of the General Public License from time to time. Such new versions will
-be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to
-address new problems or concerns.
-
-Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the Program
-specifies a version number of this License which applies to it and "any
-later version", you have the option of following the terms and conditions
-either of that version or of any later version published by the Free
-Software Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number of
-this License, you may choose any version ever published by the Free Software
-Foundation.
-
- 10. If you wish to incorporate parts of the Program into other free
-programs whose distribution conditions are different, write to the author
-to ask for permission. For software which is copyrighted by the Free
-Software Foundation, write to the Free Software Foundation; we sometimes
-make exceptions for this. Our decision will be guided by the two goals
-of preserving the free status of all derivatives of our free software and
-of promoting the sharing and reuse of software generally.
-
- NO WARRANTY
-
- 11. BECAUSE THE PROGRAM IS LICENSED FREE OF CHARGE, THERE IS NO WARRANTY
-FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN
-OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES
-PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED
-OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
-MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS
-TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE
-PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF ALL NECESSARY SERVICING,
-REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
-
- 12. IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING
-WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MAY MODIFY AND/OR
-REDISTRIBUTE THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES,
-INCLUDING ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING
-OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED
-TO LOSS OF DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY
-YOU OR THIRD PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER
-PROGRAMS), EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE
-POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
-
- END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
-
- How to Apply These Terms to Your New Programs
-
- If you develop a new program, and you want it to be of the greatest
-possible use to the public, the best way to achieve this is to make it
-free software which everyone can redistribute and change under these terms.
-
- To do so, attach the following notices to the program. It is safest
-to attach them to the start of each source file to most effectively
-convey the exclusion of warranty; and each file should have at least
-the "copyright" line and a pointer to where the full notice is found.
-
-
- Copyright (C)
-
- This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
- it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
- the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
- (at your option) any later version.
-
- This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
- MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
- GNU General Public License for more details.
-
- You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
- with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
-
-Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and paper mail.
-
-If the program is interactive, make it output a short notice like this
-when it starts in an interactive mode:
-
- Gnomovision version 69, Copyright (C) year name of author
- Gnomovision comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details type `show w'.
- This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it
- under certain conditions; type `show c' for details.
-
-The hypothetical commands `show w' and `show c' should show the appropriate
-parts of the General Public License. Of course, the commands you use may
-be called something other than `show w' and `show c'; they could even be
-mouse-clicks or menu items--whatever suits your program.
-
-You should also get your employer (if you work as a programmer) or your
-school, if any, to sign a "copyright disclaimer" for the program, if
-necessary. Here is a sample; alter the names:
-
- Yoyodyne, Inc., hereby disclaims all copyright interest in the program
- `Gnomovision' (which makes passes at compilers) written by James Hacker.
-
- , 1 April 1989
- Ty Coon, President of Vice
-
-This General Public License does not permit incorporating your program into
-proprietary programs. If your program is a subroutine library, you may
-consider it more useful to permit linking proprietary applications with the
-library. If this is what you want to do, use the GNU Lesser General
-Public License instead of this License.
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/Makefile b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/Makefile
deleted file mode 100644
index df81a22502..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/Makefile
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
-# Brute force collision tester for 64-bit hashes
-# Part of xxHash project
-# Copyright (C) 2012-present, Yann Collet
-#
-# GPL v2 License
-#
-# This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
-# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
-# the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
-# (at your option) any later version.
-#
-# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
-# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
-# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
-# GNU General Public License for more details.
-#
-# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
-# with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
-# 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
-#
-# You can contact the author at :
-# - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
-# - xxHash source repository : https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
-#
-
-SRC_DIRS = ./ ../../ allcodecs/
-VPATH = $(SRC_DIRS)
-CPPFLAGS += $(addprefix -I ,$(SRC_DIRS))
-CFLAGS ?= -std=c99 \
- -Wall -Wextra -Wconversion
-CFLAGS += -maes -mavx2
-CXXFLAGS ?= -Wall -Wextra -Wconversion --std=c++11
-LDFLAGS += -pthread
-LDFLAGS += -maes -mavx2
-TESTHASHES = 110000000
-
-HASH_SRC := $(sort $(wildcard allcodecs/*.c allcodecs/*.cc))
-HASH_OBJ := $(patsubst %.c,%.o,$(HASH_SRC))
-
-
-.PHONY: default
-default: release
-
-.PHONY: all
-all: release
-
-collisionsTest: main.o pool.o threading.o sort.o $(HASH_OBJ)
- $(CXX) $(CPPFLAGS) $(CXXFLAGS) $^ $(LDFLAGS) -o $@
-
-main.o: hashes.h xxh3.h xxhash.h
-
-release: CXXFLAGS += -O3
-release: CFLAGS += -O3
-release: collisionsTest
-
-debug: CXXFLAGS += -g3 -O0 -DDEBUG
-debug: CFLAGS += -g3 -O0 -DDEBUG
-debug: collisionsTest
-
-.PHONY: check
-check: test
-
-.PHONY: test
-test: debug
- @echo ""
- @echo "## $(TESTHASHES) hashes with original and 0 threads"
- @time ./collisionsTest --nbh=$(TESTHASHES)
- @echo ""
- @echo "## $(TESTHASHES) hashes with original and 4 threads"
- @time ./collisionsTest --nbh=$(TESTHASHES) --threadlog=2
- @echo ""
-
-.PHONY: clean
-clean:
- $(RM) *.o allcodecs/*.o
- $(RM) collisionsTest
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/README.md b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 683b115186..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,122 +0,0 @@
-
-__collisionsTest__ is a brute force hash analyzer
-which will measure a 64-bit hash algorithm's collision rate
-by generating billions of hashes,
-and comparing the result to an "ideal" target.
-
-The test requires a very large amount of memory.
-By default, it will generate 24 billion of 64-bit hashes,
-requiring __192 GB of RAM__ for their storage.
-The number of hashes can be modified using command `--nbh=`.
-Be aware that testing the collision ratio of 64-bit hashes
-requires a very large amount of hashes (several billion) for meaningful measurements.
-
-To reduce RAM usage, an optional filter can be requested, with `--filter`.
-It reduces the nb of candidates to analyze, hence associated RAM budget.
-Note that the filter itself requires a lot of RAM
-(32 GB by default, can be modified using `--filterlog=`,
-a too small filter will not be efficient, aim at ~2 bytes per hash),
-and reading and writing into filter cost a significant CPU budget,
-so this method is slower.
-It also doesn't allow advanced analysis of partial bitfields,
-since most hashes will be discarded and not stored.
-
-When using the filter, the RAM budget consists of the filter and a list of candidates,
-which will be a fraction of the original hash list.
-Using default settings (24 billion hashes, 32 GB filter),
-the number of potential candidates should be reduced to less than 2 billion,
-requiring ~14 GB for their storage.
-Such a result also depends on hash algorithm's efficiency.
-The number of effective candidates is likely to be lower, at ~ 1 billion,
-but storage must allocate an upper bound.
-
-For the default test, the expected "optimal" collision rate for a 64-bit hash function is ~18 collisions.
-
-#### How to build
-```
-make
-```
-
-Note: the code is a mix of C99 and C++14,
-it's not compatible with a C90-only compiler.
-
-#### Build modifier
-
-- `SLAB5`: use alternative pattern generator, friendlier for weak hash algorithms
-- `POOL_MT`: if `=0`, disable multi-threading code (enabled by default)
-
-#### How to integrate any hash in the tester
-
-The build script will compile files found in `./allcodecs`.
-Put the source code here.
-This also works if the hash is a single `*.h` file.
-
-The glue happens in `hashes.h`.
-In this file, there are 2 sections:
-- Adds the required `#include "header.h"`, and creates a wrapper
-to respect the format expected by the function pointer.
-- Adds the wrapper, along with the name and an indication of the output width,
-to the table, at the end of `hashes.h`
-
-Build with `make`. Locate your new hash with `./collisionsTest -h`,
-it should be listed.
-
-
-#### Usage
-
-```
-usage: ./collisionsTest [hashName] [opt]
-
-list of hashNames: (...)
-
-Optional parameters:
- --nbh=NB Select nb of hashes to generate (25769803776 by default)
- --filter Enable the filter. Slower, but reduces memory usage for same nb of hashes.
- --threadlog=NB Use 2^NB threads
- --len=NB Select length of input (255 bytes by default)
-```
-
-#### Some advises on how to setup a collisions test
-
-Most tests are primarily driven by the amount of RAM available.
-Here's a method to decide the size of the test.
-
-Presuming that RAM budget is not plentiful, for this example 32 GB,
-the `--filter` mode is actually compulsory to measure anything meaningful.
-Let's plan 50% of memory for the filter, that's 16 GB.
-This will be good enough to filter about 10% less hashes than this size.
-Let's round down to 14 G.
-
-By requesting 14G, the expectation is that the program will automatically
-size the filter to 16 GB, and expect to store ~1G candidates,
-leaving enough room to breeze for the system.
-
-The command line becomes:
-```
-./collisionsTest --nbh=14G --filter NameOfHash
-```
-
-#### Examples:
-
-Here are a few results produced with this tester:
-
-| Algorithm | Input Len | Nb Hashes | Expected | Nb Collisions | Notes |
-| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
-| __XXH3__ | 255 | 100 Gi | 312.5 | 326 | |
-| __XXH64__ | 255 | 100 Gi | 312.5 | 294 | |
-| __XXH128__ low64 | 512 | 100 Gi | 312.5 | 321 | |
-| __XXH128__ high64| 512 | 100 Gi | 312.5 | 325 | |
-| __XXH128__ | 255 | 100 Gi | 0.0 | 0 | a 128-bit hash is expected to generate 0 collisions |
-
-Test on small inputs:
-
-| Algorithm | Input Len | Nb Hashes | Expected | Nb Collisions | Notes |
-| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
-| __XXH64__ | 8 | 100 Gi | 312.5 | __0__ | `XXH64` is bijective for `len==8` |
-| __XXH3__ | 8 | 100 Gi | 312.5 | __0__ | `XXH3` is also bijective for `len==8` |
-| __XXH3__ | 16 | 100 Gi | 312.5 | 332 | |
-| __XXH3__ | 32 | 14 Gi | 6.1 | 3 | |
-| __XXH128__ | 16 | 25 Gi | 0.0 | 0 | test range 9-16 |
-| __XXH128__ | 32 | 25 Gi | 0.0 | 0 | test range 17-128 |
-| __XXH128__ | 100 | 13 Gi | 0.0 | 0 | test range 17-128 |
-| __XXH128__ | 200 | 13 Gi | 0.0 | 0 | test range 129-240 |
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/allcodecs/README.md b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/allcodecs/README.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d41fc2dbbf..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/allcodecs/README.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1 +0,0 @@
-Put in this directory all hash algorithms to test
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/allcodecs/dummy.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/allcodecs/dummy.c
deleted file mode 100644
index c6dfd474b6..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/allcodecs/dummy.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * dummy.c, a fake hash algorithm, just to test integration capabilities.
- * Part of the xxHash project
- * Copyright (C) 2020-present, Yann Collet
- *
- * GPL v2 License
- *
- * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
- * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
- * the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
- * (at your option) any later version.
- *
- * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
- * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
- * GNU General Public License for more details.
- *
- * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
- * with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- * 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
- * - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
- */
-
-
-#include
-
-unsigned badsum32(const void* input, size_t len, unsigned seed)
-{
- unsigned sum = seed;
- const unsigned char* in8 = input;
- size_t c;
- for (c=0; c /* size_t */
-
-unsigned badsum32(const void* input, size_t len, unsigned seed);
-
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-}
-#endif
-
-#endif /* DUMMY_H_987987 */
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/hashes.h b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/hashes.h
deleted file mode 100644
index cbca35de77..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/hashes.h
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,127 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * List of hashes for the brute force collision tester
- * Part of xxHash project
- * Copyright (C) 2019-present, Yann Collet
- *
- * GPL v2 License
- *
- * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
- * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
- * the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
- * (at your option) any later version.
- *
- * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
- * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
- * GNU General Public License for more details.
- *
- * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
- * with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- * 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
- * - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
- */
-
-#ifndef HASHES_H_1235465
-#define HASHES_H_1235465
-
-#include /* size_t */
-#include /* uint64_t */
-#define XXH_INLINE_ALL /* XXH128_hash_t */
-#include "xxhash.h"
-
-
-/* return type */
-
-typedef union {
- uint64_t h64;
- XXH128_hash_t h128;
-} UniHash;
-
-UniHash uniHash32(uint64_t v32)
-{ UniHash unih;
- unih.h64 = v32;
- return unih;
-}
-
-UniHash uniHash64(uint64_t v64)
-{ UniHash unih;
- unih.h64 = v64;
- return unih;
-}
-
-UniHash uniHash128(XXH128_hash_t v128)
-{ UniHash unih;
- unih.h128 = v128;
- return unih;
-}
-
-
-/* === xxHash === */
-
-UniHash XXH3_wrapper (const void* data, size_t size)
-{
- return uniHash64( XXH3_64bits(data, size) );
-}
-
-UniHash XXH128_wrapper (const void* data, size_t size)
-{
- return uniHash128( XXH3_128bits(data, size) );
-}
-
-UniHash XXH128l_wrapper (const void* data, size_t size)
-{
- return uniHash64( XXH3_128bits(data, size).low64 );
-}
-
-UniHash XXH128h_wrapper (const void* data, size_t size)
-{
- return uniHash64( XXH3_128bits(data, size).high64 );
-}
-
-UniHash XXH64_wrapper (const void* data, size_t size)
-{
- return uniHash64 ( XXH64(data, size, 0) );
-}
-
-UniHash XXH32_wrapper (const void* data, size_t size)
-{
- return uniHash32( XXH32(data, size, 0) );
-}
-
-/* === Dummy integration example === */
-
-#include "dummy.h"
-
-UniHash badsum32_wrapper (const void* data, size_t size)
-{
- return uniHash32( badsum32(data, size, 0) );
-}
-
-
-
-/* === Table === */
-
-typedef UniHash (*hashfn) (const void* data, size_t size);
-
-typedef struct {
- const char* name;
- hashfn fn;
- int bits;
-} hashDescription;
-
-#define HASH_FN_TOTAL 7
-
-hashDescription hashfnTable[HASH_FN_TOTAL] = {
- { "xxh3" , XXH3_wrapper, 64 },
- { "xxh64" , XXH64_wrapper, 64 },
- { "xxh128", XXH128_wrapper, 128 },
- { "xxh128l", XXH128l_wrapper, 64 },
- { "xxh128h", XXH128h_wrapper, 64 },
- { "xxh32" , XXH32_wrapper, 32 },
- { "badsum32",badsum32_wrapper, 32 },
-};
-
-#endif /* HASHES_H_1235465 */
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/main.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/main.c
deleted file mode 100644
index 22b14da997..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/main.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,1124 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * Brute force collision tester for 64-bit hashes
- * Part of the xxHash project
- * Copyright (C) 2019-present, Yann Collet
- *
- * GPL v2 License
- *
- * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
- * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
- * the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
- * (at your option) any later version.
- *
- * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
- * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
- * GNU General Public License for more details.
- *
- * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
- * with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- * 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
- * - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
- */
-
-/*
- * The collision tester will generate 24 billion hashes (by default),
- * and count how many collisions were produced by the 64-bit hash algorithm.
- * The optimal amount of collisions for 64-bit is ~18 collisions.
- * A good hash should be close to this figure.
- *
- * This program requires a lot of memory:
- * - Either store hash values directly => 192 GB
- * - Or use a filter:
- * - 32 GB (by default) for the filter itself
- * - + ~14 GB for the list of hashes (depending on the filter's outcome)
- * Due to these memory constraints, it requires a 64-bit system.
- */
-
-
- /* === Dependencies === */
-
-#include /* uint64_t */
-#include /* malloc, free, qsort, exit */
-#include /* memset */
-#include /* printf, fflush */
-
-#undef NDEBUG /* ensure assert is _not_ disabled */
-#include
-
-#include "hashes.h" /* UniHash, hashfn, hashfnTable */
-
-#include "sort.hh" /* sort64 */
-
-
-
-typedef enum { ht32, ht64, ht128 } Htype_e;
-
-/* === Debug === */
-
-#define EXIT(...) { printf(__VA_ARGS__); printf("\n"); exit(1); }
-
-static void hexRaw(const void* buffer, size_t size)
-{
- const unsigned char* p = (const unsigned char*)buffer;
- for (size_t i=0; i> 33;
- h64 *= prime64_2;
- h64 ^= h64 >> 29;
- h64 *= prime64_3;
- h64 ^= h64 >> 32;
- return h64;
-}
-
-static unsigned char randomByte(size_t n)
-{
- uint64_t n64 = avalanche64(n+1);
- n64 *= prime64_1;
- return (unsigned char)(n64 >> 56);
-}
-
-typedef enum { sf_slab5, sf_sparse } sf_genMode;
-
-
-#ifdef SLAB5
-
-/*
- * Slab5 sample generation.
- * This algorithm generates unique inputs flipping on average 16 bits per candidate.
- * It is generally much more friendly for most hash algorithms, especially
- * weaker ones, as it shuffles more the input.
- * The algorithm also avoids overfitting the per4 or per8 ingestion patterns.
- */
-
-#define SLAB_SIZE 5
-
-typedef struct {
- void* buffer;
- size_t size;
- sf_genMode mode;
- size_t prngSeed;
- uint64_t hnb;
-} sampleFactory;
-
-static void init_sampleFactory(sampleFactory* sf, uint64_t htotal)
-{
- uint64_t const minNbSlabs = ((htotal-1) >> 32) + 1;
- uint64_t const minSize = minNbSlabs * SLAB_SIZE;
- if (sf->size < minSize)
- EXIT("sample size must be >= %i bytes for this amount of hashes",
- (int)minSize);
-
- unsigned char* const p = (unsigned char*)sf->buffer;
- for (size_t n=0; n < sf->size; n++)
- p[n] = randomByte(n);
- sf->hnb = 0;
-}
-
-static sampleFactory*
-create_sampleFactory(size_t size, uint64_t htotal, uint64_t seed)
-{
- sampleFactory* const sf = malloc(sizeof(sampleFactory));
- if (!sf) EXIT("not enough memory");
- void* const buffer = malloc(size);
- if (!buffer) EXIT("not enough memory");
- sf->buffer = buffer;
- sf->size = size;
- sf->mode = sf_slab5;
- sf->prngSeed = seed;
- init_sampleFactory(sf, htotal);
- return sf;
-}
-
-static void free_sampleFactory(sampleFactory* sf)
-{
- if (!sf) return;
- free(sf->buffer);
- free(sf);
-}
-
-static inline void update_sampleFactory(sampleFactory* sf)
-{
- size_t const nbSlabs = sf->size / SLAB_SIZE;
- size_t const SlabNb = sf->hnb % nbSlabs;
- sf->hnb++;
-
- char* const ptr = (char*)sf->buffer;
- size_t const start = (SlabNb * SLAB_SIZE) + 1;
- uint32_t val32;
- memcpy(&val32, ptr+start, sizeof(val32));
- static const uint32_t prime32_5 = 374761393U;
- val32 += prime32_5;
- memcpy(ptr+start, &val32, sizeof(val32));
-}
-
-#else
-
-/*
- * Sparse sample generation.
- * This is the default pattern generator.
- * It only flips one bit at a time (mostly).
- * Low hamming distance scenario is more difficult for weak hash algorithms.
- * Note that CRC is immune to this scenario, since they are specifically
- * designed to detect low hamming distances.
- * Prefer the Slab5 pattern generator for collisions on CRC algorithms.
- */
-
-#define SPARSE_LEVEL_MAX 15
-
-/* Nb of combinations of m bits in a register of n bits */
-static double Cnm(int n, int m)
-{
- assert(n > 0);
- assert(m > 0);
- assert(m <= m);
- double acc = 1;
- for (int i=0; i= SPARSE_LEVEL_MAX) return 0;
- acc += (uint64_t)Cnm((int)srcBits, nbBitsSet);
- }
- return 1;
-}
-
-typedef struct {
- void* buffer;
- size_t size;
- sf_genMode mode;
- /* sparse */
- size_t bitIdx[SPARSE_LEVEL_MAX];
- int level;
- size_t maxBitIdx;
- /* slab5 */
- size_t nbSlabs;
- size_t current;
- size_t prngSeed;
-} sampleFactory;
-
-static void init_sampleFactory(sampleFactory* sf, uint64_t htotal)
-{
- if (!enoughCombos(sf->size, htotal)) {
- EXIT("sample size must be larger for this amount of hashes");
- }
-
- memset(sf->bitIdx, 0, sizeof(sf->bitIdx));
- sf->level = 0;
-
- unsigned char* const p = (unsigned char*)sf->buffer;
- for (size_t n=0; nsize; n++)
- p[n] = randomByte(sf->prngSeed + n);
-}
-
-static sampleFactory*
-create_sampleFactory(size_t size, uint64_t htotal, uint64_t seed)
-{
- sampleFactory* const sf = malloc(sizeof(sampleFactory));
- if (!sf) EXIT("not enough memory");
- void* const buffer = malloc(size);
- if (!buffer) EXIT("not enough memory");
- sf->buffer = buffer;
- sf->size = size;
- sf->mode = sf_sparse;
- sf->maxBitIdx = size * 8;
- sf->prngSeed = seed;
- init_sampleFactory(sf, htotal);
- return sf;
-}
-
-static void free_sampleFactory(sampleFactory* sf)
-{
- if (!sf) return;
- free(sf->buffer);
- free(sf);
-}
-
-static void flipbit(void* buffer, uint64_t bitID)
-{
- size_t const pos = bitID >> 3;
- unsigned char const mask = (unsigned char)(1 << (bitID & 7));
- unsigned char* const p = (unsigned char*)buffer;
- p[pos] ^= mask;
-}
-
-static int updateBit(void* buffer, size_t* bitIdx, int level, size_t max)
-{
- if (level==0) return 0; /* can't progress further */
-
- flipbit(buffer, bitIdx[level]); /* erase previous bits */
-
- if (bitIdx[level] < max-1) { /* simple case: go to next bit */
- bitIdx[level]++;
- flipbit(buffer, bitIdx[level]); /* set new bit */
- return 1;
- }
-
- /* reached last bit: need to update a bit from lower level */
- if (!updateBit(buffer, bitIdx, level-1, max-1)) return 0;
- bitIdx[level] = bitIdx[level-1] + 1;
- flipbit(buffer, bitIdx[level]); /* set new bit */
- return 1;
-}
-
-static inline void update_sampleFactory(sampleFactory* sf)
-{
- if (!updateBit(sf->buffer, sf->bitIdx, sf->level, sf->maxBitIdx)) {
- /* no more room => move to next level */
- sf->level++;
- assert(sf->level < SPARSE_LEVEL_MAX);
-
- /* set new bits */
- for (int i=1; i <= sf->level; i++) {
- sf->bitIdx[i] = (size_t)(i-1);
- flipbit(sf->buffer, sf->bitIdx[i]);
- }
- }
-}
-
-#endif /* pattern generator selection */
-
-
-/* === Candidate Filter === */
-
-typedef unsigned char Filter;
-
-Filter* create_Filter(int bflog)
-{
- assert(bflog < 64 && bflog > 1);
- size_t bfsize = (size_t)1 << bflog;
- Filter* bf = malloc(bfsize);
- assert(((void)"Filter creation failed", bf));
- memset(bf, 0, bfsize);
- return bf;
-}
-
-void free_Filter(Filter* bf)
-{
- free(bf);
-}
-
-#ifdef FILTER_1_PROBE
-
-/*
- * Attach hash to a slot
- * return: Nb of potential collision candidates detected
- * 0: position not yet occupied
- * 2: position previously occupied by a single candidate
- * 1: position already occupied by multiple candidates
- */
-inline int Filter_insert(Filter* bf, int bflog, uint64_t hash)
-{
- int const slotNb = hash & 3;
- int const shift = slotNb * 2 ;
-
- size_t const bfmask = ((size_t)1 << bflog) - 1;
- size_t const pos = (hash >> 2) & bfmask;
-
- int const existingCandidates = ((((unsigned char*)bf)[pos]) >> shift) & 3;
-
- static const int addCandidates[4] = { 0, 2, 1, 1 };
- static const int nextValue[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 3 };
-
- ((unsigned char*)bf)[pos] |= (unsigned char)(nextValue[existingCandidates] << shift);
- return addCandidates[existingCandidates];
-}
-
-/*
- * Check if provided 64-bit hash is a collision candidate
- * Requires the slot to be occupied by at least 2 candidates.
- * return >0 if hash is a collision candidate
- * 0 otherwise (slot unoccupied, or only one candidate)
- * note: unoccupied slots should not happen in this algorithm,
- * since all hashes are supposed to have been inserted at least once.
- */
-inline int Filter_check(const Filter* bf, int bflog, uint64_t hash)
-{
- int const slotNb = hash & 3;
- int const shift = slotNb * 2;
-
- size_t const bfmask = ((size_t)1 << bflog) - 1;
- size_t const pos = (hash >> 2) & bfmask;
-
- return (((const unsigned char*)bf)[pos]) >> (shift+1) & 1;
-}
-
-#else
-
-/*
- * 2-probes strategy,
- * more efficient at filtering candidates,
- * requires filter size to be > nb of hashes
- */
-
-#define MIN(a,b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b))
-#define MAX(a,b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
-
-/*
- * Attach hash to 2 slots
- * return: Nb of potential candidates detected
- * 0: position not yet occupied
- * 2: position previously occupied by a single candidate (at most)
- * 1: position already occupied by multiple candidates
- */
-static inline int Filter_insert(Filter* bf, int bflog, uint64_t hash)
- {
- hash = avalanche64(hash);
- unsigned const slot1 = hash & 255;
- hash >>= 8;
- unsigned const slot2 = hash & 255;
- hash >>= 8;
-
- size_t const fclmask = ((size_t)1 << (bflog-6)) - 1;
- size_t const cacheLineNb = hash & fclmask;
-
- size_t const pos1 = (cacheLineNb << 6) + (slot1 >> 2);
- unsigned const shift1 = (slot1 & 3) * 2;
- unsigned const ex1 = (bf[pos1] >> shift1) & 3;
-
- size_t const pos2 = (cacheLineNb << 6) + (slot2 >> 2);
- unsigned const shift2 = (slot2 & 3) * 2;
- unsigned const ex2 = (bf[pos2] >> shift2) & 3;
-
- unsigned const existing = MIN(ex1, ex2);
-
- static const int addCandidates[4] = { 0, 2, 1, 1 };
- static const unsigned nextValue[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 3 };
-
- bf[pos1] &= (Filter)(~(3 << shift1)); /* erase previous value */
- bf[pos1] |= (Filter)(MAX(ex1, nextValue[existing]) << shift1);
- bf[pos2] |= (Filter)(MAX(ex2, nextValue[existing]) << shift2);
-
- return addCandidates[existing];
- }
-
-
-/*
- * Check if provided 64-bit hash is a collision candidate
- * Requires the slot to be occupied by at least 2 candidates.
- * return >0 if hash is a collision candidate
- * 0 otherwise (slot unoccupied, or only one candidate)
- * note: unoccupied slots should not happen in this algorithm,
- * since all hashes are supposed to have been inserted at least once.
- */
-static inline int Filter_check(const Filter* bf, int bflog, uint64_t hash)
- {
- hash = avalanche64(hash);
- unsigned const slot1 = hash & 255;
- hash >>= 8;
- unsigned const slot2 = hash & 255;
- hash >>= 8;
-
- size_t const fclmask = ((size_t)1 << (bflog-6)) - 1;
- size_t const cacheLineNb = hash & fclmask;
-
- size_t const pos1 = (cacheLineNb << 6) + (slot1 >> 2);
- unsigned const shift1 = (slot1 & 3) * 2;
- unsigned const ex1 = (bf[pos1] >> shift1) & 3;
-
- size_t const pos2 = (cacheLineNb << 6) + (slot2 >> 2);
- unsigned const shift2 = (slot2 & 3) * 2;
- unsigned const ex2 = (bf[pos2] >> shift2) & 3;
-
- return (ex1 >= 2) && (ex2 >= 2);
- }
-
-#endif // FILTER_1_PROBE
-
-
-/* === Display === */
-
-#include /* clock_t, clock, time_t, time, difftime */
-
-void update_indicator(uint64_t v, uint64_t total)
-{
- static clock_t start = 0;
- if (start==0) start = clock();
- clock_t const updateRate = CLOCKS_PER_SEC / 2;
-
- clock_t const clockSpan = (clock_t)(clock() - start);
- if (clockSpan > updateRate) {
- start = clock();
- assert(v <= total);
- assert(total > 0);
- double share = ((double)v / (double)total) * 100;
- printf("%6.2f%% (%llu) \r", share, (unsigned long long)v);
- fflush(NULL);
- }
-}
-
-/* note: not thread safe */
-const char* displayDelay(double delay_s)
-{
- static char delayString[50];
- memset(delayString, 0, sizeof(delayString));
-
- int const mn = ((int)delay_s / 60) % 60;
- int const h = (int)delay_s / 3600;
- int const sec = (int)delay_s % 60;
-
- char* p = delayString;
- if (h) sprintf(p, "%i h ", h);
- if (mn || h) {
- p = delayString + strlen(delayString);
- sprintf(p, "%i mn ", mn);
- }
- p = delayString + strlen(delayString);
- sprintf(p, "%is ", sec);
-
- return delayString;
-}
-
-
-/* === Math === */
-
-static double power(uint64_t base, int p)
-{
- double value = 1;
- assert(p>=0);
- for (int i=0; i>= 1) bitId++;
- return bitId;
-}
-
-
-/* === Filter and search collisions === */
-
-#undef NDEBUG /* ensure assert is not disabled */
-#include
-
-/* will recommend 24 billion samples for 64-bit hashes,
- * expecting 18 collisions for a good 64-bit hash */
-#define NB_BITS_MAX 64 /* can't store nor analyze hash wider than 64-bits for the time being */
-uint64_t select_nbh(int nbBits)
-{
- assert(nbBits > 0);
- if (nbBits > NB_BITS_MAX) nbBits = NB_BITS_MAX;
- double targetColls = (double)((128 + 17) - (nbBits * 2));
- uint64_t nbH = 24;
- while (estimateNbCollisions(nbH, nbBits) < targetColls) nbH *= 2;
- return nbH;
-}
-
-
-typedef struct {
- uint64_t nbCollisions;
-} searchCollisions_results;
-
-typedef struct {
- uint64_t nbH;
- uint64_t mask;
- uint64_t maskSelector;
- size_t sampleSize;
- uint64_t prngSeed;
- int filterLog; /* <0 = disable filter; 0 = auto-size; */
- int hashID;
- int display;
- int nbThreads;
- searchCollisions_results* resultPtr;
-} searchCollisions_parameters;
-
-#define DISPLAY(...) { if (display) printf(__VA_ARGS__); }
-
-static int isEqual(void* hTablePtr, size_t index1, size_t index2, Htype_e htype)
-{
- if ((htype == ht64) || (htype == ht32)) {
- uint64_t const h1 = ((const uint64_t*)hTablePtr)[index1];
- uint64_t const h2 = ((const uint64_t*)hTablePtr)[index2];
- return (h1 == h2);
- } else {
- assert(htype == ht128);
- XXH128_hash_t const h1 = ((const XXH128_hash_t*)hTablePtr)[index1];
- XXH128_hash_t const h2 = ((const XXH128_hash_t*)hTablePtr)[index2];
- return XXH128_isEqual(h1, h2);
- }
-}
-
-static int isHighEqual(void* hTablePtr, size_t index1, size_t index2, Htype_e htype, int rShift)
-{
- uint64_t h1, h2;
- if ((htype == ht64) || (htype == ht32)) {
- h1 = ((const uint64_t*)hTablePtr)[index1];
- h2 = ((const uint64_t*)hTablePtr)[index2];
- } else {
- assert(htype == ht128);
- h1 = ((const XXH128_hash_t*)hTablePtr)[index1].high64;
- h2 = ((const XXH128_hash_t*)hTablePtr)[index2].high64;
- assert(rShift >= 64);
- rShift -= 64;
- }
- assert(0 <= rShift && rShift < 64);
- return (h1 >> rShift) == (h2 >> rShift);
-}
-
-/* assumption: (htype*)hTablePtr[index] is valid */
-static void addHashCandidate(void* hTablePtr, UniHash h, Htype_e htype, size_t index)
-{
- if ((htype == ht64) || (htype == ht32)) {
- ((uint64_t*)hTablePtr)[index] = h.h64;
- } else {
- assert(htype == ht128);
- ((XXH128_hash_t*)hTablePtr)[index] = h.h128;
- }
-}
-
-static int getNbBits_fromHtype(Htype_e htype) {
- switch(htype) {
- case ht32: return 32;
- case ht64: return 64;
- case ht128:return 128;
- default: EXIT("hash size not supported");
- }
-}
-
-static Htype_e getHtype_fromHbits(int nbBits) {
- switch(nbBits) {
- case 32 : return ht32;
- case 64 : return ht64;
- case 128: return ht128;
- default: EXIT("hash size not supported");
- }
-}
-
-static size_t search_collisions(
- searchCollisions_parameters param)
-{
- uint64_t totalH = param.nbH;
- const uint64_t hMask = param.mask;
- const uint64_t hSelector = param.maskSelector;
- int bflog = param.filterLog;
- const int filter = (param.filterLog >= 0);
- const size_t sampleSize = param.sampleSize;
- const int hashID = param.hashID;
- const Htype_e htype = getHtype_fromHbits(hashfnTable[hashID].bits);
- const int display = param.display;
- /* init */
- sampleFactory* const sf = create_sampleFactory(sampleSize, totalH, param.prngSeed);
- if (!sf) EXIT("not enough memory");
-
- //const char* const hname = hashfnTable[hashID].name;
- hashfn const hfunction = hashfnTable[hashID].fn;
- int const hwidth = hashfnTable[hashID].bits;
- if (totalH == 0) totalH = select_nbh(hwidth);
- if (bflog == 0) bflog = highestBitSet(totalH) + 1; /* auto-size filter */
- uint64_t const bfsize = (1ULL << bflog);
-
-
- /* === filter hashes (optional) === */
-
- Filter* bf = NULL;
- uint64_t nbPresents = totalH;
-
- if (filter) {
- time_t const filterTBegin = time(NULL);
- DISPLAY(" Creating filter (%i GB) \n", (int)(bfsize >> 30));
- bf = create_Filter(bflog);
- if (!bf) EXIT("not enough memory for filter");
-
-
- DISPLAY(" Generate %llu hashes from samples of %u bytes \n",
- (unsigned long long)totalH, (unsigned)sampleSize);
- nbPresents = 0;
-
- for (uint64_t n=0; n < totalH; n++) {
- if (display && ((n&0xFFFFF) == 1) )
- update_indicator(n, totalH);
- update_sampleFactory(sf);
-
- UniHash const h = hfunction(sf->buffer, sampleSize);
- if ((h.h64 & hMask) != hSelector) continue;
-
- nbPresents += (uint64_t)Filter_insert(bf, bflog, h.h64);
- }
-
- if (nbPresents==0) {
- DISPLAY(" Analysis completed: No collision detected \n");
- if (param.resultPtr) param.resultPtr->nbCollisions = 0;
- free_Filter(bf);
- free_sampleFactory(sf);
- return 0;
- }
-
- { double const filterDelay = difftime(time(NULL), filterTBegin);
- DISPLAY(" Generation and filter completed in %s, detected up to %llu candidates \n",
- displayDelay(filterDelay), (unsigned long long) nbPresents);
- } }
-
-
- /* === store hash candidates: duplicates will be present here === */
-
- time_t const storeTBegin = time(NULL);
- size_t const hashByteSize = (htype == ht128) ? 16 : 8;
- size_t const tableSize = (nbPresents+1) * hashByteSize;
- assert(tableSize > nbPresents); /* check tableSize calculation overflow */
- DISPLAY(" Storing hash candidates (%i MB) \n", (int)(tableSize >> 20));
-
- /* Generate and store hashes */
- void* const hashCandidates = malloc(tableSize);
- if (!hashCandidates) EXIT("not enough memory to store candidates");
- init_sampleFactory(sf, totalH);
- size_t nbCandidates = 0;
- for (uint64_t n=0; n < totalH; n++) {
- if (display && ((n&0xFFFFF) == 1) ) update_indicator(n, totalH);
- update_sampleFactory(sf);
-
- UniHash const h = hfunction(sf->buffer, sampleSize);
- if ((h.h64 & hMask) != hSelector) continue;
-
- if (filter) {
- if (Filter_check(bf, bflog, h.h64)) {
- assert(nbCandidates < nbPresents);
- addHashCandidate(hashCandidates, h, htype, nbCandidates++);
- }
- } else {
- assert(nbCandidates < nbPresents);
- addHashCandidate(hashCandidates, h, htype, nbCandidates++);
- }
- }
- if (nbCandidates < nbPresents) {
- /* Try to mitigate gnuc_quicksort behavior, by reducing allocated memory,
- * since gnuc_quicksort uses a lot of additional memory for mergesort */
- void* const checkPtr = realloc(hashCandidates, nbCandidates * hashByteSize);
- assert(checkPtr != NULL);
- assert(checkPtr == hashCandidates); /* simplification: since we are reducing the size,
- * we hope to keep the same ptr position.
- * Otherwise, hashCandidates must be mutable. */
- DISPLAY(" List of hashes reduced to %u MB from %u MB (saved %u MB) \n",
- (unsigned)((nbCandidates * hashByteSize) >> 20),
- (unsigned)(tableSize >> 20),
- (unsigned)((tableSize - (nbCandidates * hashByteSize)) >> 20) );
- }
- double const storeTDelay = difftime(time(NULL), storeTBegin);
- DISPLAY(" Stored %llu hash candidates in %s \n",
- (unsigned long long) nbCandidates, displayDelay(storeTDelay));
- free_Filter(bf);
- free_sampleFactory(sf);
-
-
- /* === step 3: look for duplicates === */
- time_t const sortTBegin = time(NULL);
- DISPLAY(" Sorting candidates... ");
- fflush(NULL);
- if ((htype == ht64) || (htype == ht32)) {
- /*
- * Use C++'s std::sort, as it's faster than C stdlib's qsort, and
- * doesn't suffer from gnuc_libsort's memory expansion
- */
- sort64(hashCandidates, nbCandidates);
- } else {
- assert(htype == ht128);
- sort128(hashCandidates, nbCandidates); /* sort with custom comparator */
- }
- double const sortTDelay = difftime(time(NULL), sortTBegin);
- DISPLAY(" Completed in %s \n", displayDelay(sortTDelay));
-
- /* scan and count duplicates */
- time_t const countBegin = time(NULL);
- DISPLAY(" Looking for duplicates: ");
- fflush(NULL);
- size_t collisions = 0;
- for (size_t n=1; n nbCandidates * 100) /* within range for meaningfull collision analysis results */
- && (expectedCollisions > 18.0) ) {
- int const rShift = hashBits - nbHBits;
- size_t HBits_collisions = 0;
- for (size_t n=1; n 2.0) DISPLAY("WARNING !!! ===> ");
- DISPLAY(" high %i bits: %zu collision (%.1f expected): x%.2f \n",
- nbHBits, HBits_collisions, expectedCollisions, collisionRatio);
- if (collisionRatio > worstRatio) {
- worstNbHBits = nbHBits;
- worstRatio = collisionRatio;
- } } }
- DISPLAY("Worst collision ratio at %i high bits: x%.2f \n",
- worstNbHBits, worstRatio);
- }
- double const countDelay = difftime(time(NULL), countBegin);
- DISPLAY(" Completed in %s \n", displayDelay(countDelay));
-
- /* clean and exit */
- free (hashCandidates);
-
-#if 0 /* debug */
- for (size_t n=0; nnbCollisions = collisions;
- return collisions;
-}
-
-
-
-#if defined(__MACH__) || defined(__linux__)
-#include
-static size_t getProcessMemUsage(int children)
-{
- struct rusage stats;
- if (getrusage(children ? RUSAGE_CHILDREN : RUSAGE_SELF, &stats) == 0)
- return (size_t)stats.ru_maxrss;
- return 0;
-}
-#else
-static size_t getProcessMemUsage(int ignore) { return 0; }
-#endif
-
-void time_collisions(searchCollisions_parameters param)
-{
- uint64_t totalH = param.nbH;
- int hashID = param.hashID;
- int display = param.display;
-
- /* init */
- assert(0 <= hashID && hashID < HASH_FN_TOTAL);
- //const char* const hname = hashfnTable[hashID].name;
- int const hwidth = hashfnTable[hashID].bits;
- if (totalH == 0) totalH = select_nbh(hwidth);
- double const targetColls = estimateNbCollisions(totalH, hwidth);
-
- /* Start the timer to measure start/end of hashing + collision detection. */
- time_t const programTBegin = time(NULL);
-
- /* Generate hashes, and count collisions */
- size_t const collisions = search_collisions(param);
-
- /* display results */
- double const programTDelay = difftime(time(NULL), programTBegin);
- size_t const programBytesSelf = getProcessMemUsage(0);
- size_t const programBytesChildren = getProcessMemUsage(1);
- DISPLAY("\n\n");
- DISPLAY("===> Found %llu collisions (x%.2f, %.1f expected) in %s\n",
- (unsigned long long)collisions,
- (double)collisions / targetColls,
- targetColls,
- displayDelay(programTDelay));
- if (programBytesSelf)
- DISPLAY("===> MaxRSS(self) %zuMB, MaxRSS(children) %zuMB\n",
- programBytesSelf>>20,
- programBytesChildren>>20);
- DISPLAY("------------------------------------------ \n");
-}
-
-// wrapper for pthread interface
-void MT_searchCollisions(void* payload)
-{
- search_collisions(*(searchCollisions_parameters*)payload);
-}
-
-/* === Command Line === */
-
-/*!
- * readU64FromChar():
- * Allows and interprets K, KB, KiB, M, MB and MiB suffix.
- * Will also modify `*stringPtr`, advancing it to the position where it stopped reading.
- */
-static uint64_t readU64FromChar(const char** stringPtr)
-{
- static uint64_t const max = (((uint64_t)(-1)) / 10) - 1;
- uint64_t result = 0;
- while ((**stringPtr >='0') && (**stringPtr <='9')) {
- assert(result < max);
- result *= 10;
- result += (unsigned)(**stringPtr - '0');
- (*stringPtr)++ ;
- }
- if ((**stringPtr=='K') || (**stringPtr=='M') || (**stringPtr=='G')) {
- uint64_t const maxK = ((uint64_t)(-1)) >> 10;
- assert(result < maxK);
- result <<= 10;
- if ((**stringPtr=='M') || (**stringPtr=='G')) {
- assert(result < maxK);
- result <<= 10;
- if (**stringPtr=='G') {
- assert(result < maxK);
- result <<= 10;
- }
- }
- (*stringPtr)++; /* skip `K` or `M` */
- if (**stringPtr=='i') (*stringPtr)++;
- if (**stringPtr=='B') (*stringPtr)++;
- }
- return result;
-}
-
-
-/**
- * longCommandWArg():
- * Checks if *stringPtr is the same as longCommand.
- * If yes, @return 1 and advances *stringPtr to the position which immediately follows longCommand.
- * @return 0 and doesn't modify *stringPtr otherwise.
- */
-static int longCommandWArg(const char** stringPtr, const char* longCommand)
-{
- assert(longCommand); assert(stringPtr); assert(*stringPtr);
- size_t const comSize = strlen(longCommand);
- int const result = !strncmp(*stringPtr, longCommand, comSize);
- if (result) *stringPtr += comSize;
- return result;
-}
-
-
-#include "pool.h"
-
-/*
- * As some hashes use different algorithms depending on input size,
- * it can be necessary to test multiple input sizes
- * to paint an accurate picture of collision performance
- */
-#define SAMPLE_SIZE_DEFAULT 255
-#define HASHFN_ID_DEFAULT 0
-
-void help(const char* exeName)
-{
- printf("usage: %s [hashName] [opt] \n\n", exeName);
- printf("list of hashNames:");
- printf("%s ", hashfnTable[0].name);
- for (int i=1; i < HASH_FN_TOTAL; i++) {
- printf(", %s ", hashfnTable[i].name);
- }
- printf(" \n");
- printf("Default hashName is %s\n", hashfnTable[HASHFN_ID_DEFAULT].name);
-
- printf(" \n");
- printf("Optional parameters: \n");
- printf(" --nbh=NB Select nb of hashes to generate (%llu by default) \n", (unsigned long long)select_nbh(64));
- printf(" --filter Activates the filter. Slower, but reduces memory usage for the same nb of hashes.\n");
- printf(" --threadlog=NB Use 2^NB threads.\n");
- printf(" --len=MB Set length of the input (%i bytes by default) \n", SAMPLE_SIZE_DEFAULT);
-}
-
-int bad_argument(const char* exeName)
-{
- printf("incorrect command: \n");
- help(exeName);
- return 1;
-}
-
-
-int main(int argc, const char** argv)
-{
- if (sizeof(size_t) < 8) return 1; // cannot work on systems without ability to allocate objects >= 4 GB
-
- assert(argc > 0);
- const char* const exeName = argv[0];
- uint64_t totalH = 0; /* auto, based on nbBits */
- int bflog = 0; /* auto */
- int filter = 0; /* disabled */
- size_t sampleSize = SAMPLE_SIZE_DEFAULT;
- int hashID = HASHFN_ID_DEFAULT;
- int threadlog = 0;
- uint64_t prngSeed = 0;
-
- int arg_nb;
- for (arg_nb = 1; arg_nb < argc; arg_nb++) {
- const char** arg = argv + arg_nb;
-
- if (!strcmp(*arg, "-h")) { help(exeName); return 0; }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "-T")) { threadlog = (int)readU64FromChar(arg); continue; }
-
- if (!strcmp(*arg, "--filter")) { filter=1; continue; }
- if (!strcmp(*arg, "--no-filter")) { filter=0; continue; }
-
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--seed")) { prngSeed = readU64FromChar(arg); continue; }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--nbh=")) { totalH = readU64FromChar(arg); continue; }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--filter=")) { filter=1; bflog = (int)readU64FromChar(arg); assert(bflog < 64); continue; }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--filterlog=")) { filter=1; bflog = (int)readU64FromChar(arg); assert(bflog < 64); continue; }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--size=")) { sampleSize = (size_t)readU64FromChar(arg); continue; }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--len=")) { sampleSize = (size_t)readU64FromChar(arg); continue; }
- if (longCommandWArg(arg, "--threadlog=")) { threadlog = (int)readU64FromChar(arg); continue; }
-
- /* argument understood as hash name (must be correct) */
- int hnb;
- for (hnb=0; hnb < HASH_FN_TOTAL; hnb++) {
- if (!strcmp(*arg, hashfnTable[hnb].name)) { hashID = hnb; break; }
- }
- if (hnb == HASH_FN_TOTAL) return bad_argument(exeName);
- }
-
- /* init */
- const char* const hname = hashfnTable[hashID].name;
- int const hwidth = hashfnTable[hashID].bits;
- if (totalH == 0) totalH = select_nbh(hwidth);
- double const targetColls = estimateNbCollisions(totalH, hwidth);
- if (bflog == 0) bflog = highestBitSet(totalH) + 1; /* auto-size filter */
- if (!filter) bflog = -1; // disable filter
-
- if (sizeof(size_t) < 8)
- EXIT("This program has not been validated on architectures other than "
- "64bit \n");
-
- printf(" *** Collision tester for 64+ bit hashes *** \n\n");
- printf("Testing %s algorithm (%i-bit) \n", hname, hwidth);
- printf("This program will allocate a lot of memory,\n");
- printf("generate %llu %i-bit hashes from samples of %u bytes, \n",
- (unsigned long long)totalH, hwidth, (unsigned)sampleSize);
- printf("and attempt to produce %.0f collisions. \n\n", targetColls);
-
- int const nbThreads = 1 << threadlog;
- if (nbThreads <= 0) EXIT("Invalid --threadlog value.");
-
- if (nbThreads == 1) {
-
- searchCollisions_parameters params;
- params.nbH = totalH;
- params.mask = 0;
- params.maskSelector = 0;
- params.sampleSize = sampleSize;
- params.filterLog = bflog;
- params.hashID = hashID;
- params.display = 1;
- params.resultPtr = NULL;
- params.prngSeed = prngSeed;
- params.nbThreads = 1;
- time_collisions(params);
-
- } else { /* nbThreads > 1 */
-
- /* use multithreading */
- if (threadlog >= 30) EXIT("too many threads requested");
- if ((uint64_t)nbThreads > (totalH >> 16))
- EXIT("too many threads requested");
- if (bflog > 0 && threadlog > (bflog-10))
- EXIT("too many threads requested");
- printf("using %i threads ... \n", nbThreads);
-
- /* allocation */
- time_t const programTBegin = time(NULL);
- POOL_ctx* const pt = POOL_create((size_t)nbThreads, 1);
- if (!pt) EXIT("not enough memory for threads");
- searchCollisions_results* const MTresults = calloc (sizeof(searchCollisions_results), (size_t)nbThreads);
- if (!MTresults) EXIT("not enough memory");
- searchCollisions_parameters* const MTparams = calloc (sizeof(searchCollisions_parameters), (size_t)nbThreads);
- if (!MTparams) EXIT("not enough memory");
-
- /* distribute jobs */
- for (int tnb=0; tnb Found %llu collisions (x%.2f, %.1f expected) in %s\n",
- (unsigned long long)nbCollisions,
- (double)nbCollisions / targetColls,
- targetColls,
- displayDelay(programTDelay));
- if (programBytesSelf)
- printf("===> MaxRSS(self) %zuMB, MaxRSS(children) %zuMB\n",
- programBytesSelf>>20,
- programBytesChildren>>20);
- printf("------------------------------------------ \n");
-
- /* Clean up */
- free(MTparams);
- free(MTresults);
- }
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/pool.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/pool.c
deleted file mode 100644
index 27d1fb318d..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/pool.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,344 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * Copyright (c) 2016-present, Yann Collet, Facebook, Inc.
- * All rights reserved.
- *
- * This source code is licensed under both the BSD-style license (found in the
- * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree) and the GPLv2 (found
- * in the COPYING file in the root directory of this source tree).
- * You may select, at your option, one of the above-listed licenses.
- */
-
-
-/* ====== Dependencies ======= */
-#include /* size_t */
-#include /* malloc, calloc, free */
-#include /* memcpy */
-#include
-
-#include "pool.h"
-
-
-/* ====== Compiler specifics ====== */
-#if defined(_MSC_VER)
-# pragma warning(disable : 4204) /* disable: C4204: non-constant aggregate initializer */
-#endif
-
-
-/* === Build Macro === */
-
-#ifndef POOL_MT // can be defined on command line
-# define POOL_MT 1
-#endif
-
-
-/* === Implementation === */
-
-#if POOL_MT
-
-#include "threading.h" /* pthread adaptation */
-
-/* A job is a function and an opaque argument */
-typedef struct POOL_job_s {
- POOL_function function;
- void *opaque;
-} POOL_job;
-
-struct POOL_ctx_s {
- /* Keep track of the threads */
- ZSTD_pthread_t* threads;
- size_t threadCapacity;
- size_t threadLimit;
-
- /* The queue is a circular buffer */
- POOL_job *queue;
- size_t queueHead;
- size_t queueTail;
- size_t queueSize;
-
- /* The number of threads working on jobs */
- size_t numThreadsBusy;
- /* Indicates if the queue is empty */
- int queueEmpty;
-
- /* The mutex protects the queue */
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_t queueMutex;
- /* Condition variable for pushers to wait on when the queue is full */
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_t queuePushCond;
- /* Condition variables for poppers to wait on when the queue is empty */
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_t queuePopCond;
- /* Indicates if the queue is shutting down */
- int shutdown;
-};
-
-/* POOL_thread() :
- * Work thread for the thread pool.
- * Waits for jobs and executes them.
- * @returns : NULL on failure else non-null.
- */
-static void* POOL_thread(void* opaque)
-{
- POOL_ctx* const ctx = (POOL_ctx*)opaque;
- if (!ctx) { return NULL; }
- for (;;) {
- /* Lock the mutex and wait for a non-empty queue or until shutdown */
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_lock(&ctx->queueMutex);
-
- while ( ctx->queueEmpty
- || (ctx->numThreadsBusy >= ctx->threadLimit) ) {
- if (ctx->shutdown) {
- /* even if !queueEmpty, (possible if numThreadsBusy >= threadLimit),
- * a few threads will be shutdown while !queueEmpty,
- * but enough threads will remain active to finish the queue */
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(&ctx->queueMutex);
- return opaque;
- }
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_wait(&ctx->queuePopCond, &ctx->queueMutex);
- }
- /* Pop a job off the queue */
- { POOL_job const job = ctx->queue[ctx->queueHead];
- ctx->queueHead = (ctx->queueHead + 1) % ctx->queueSize;
- ctx->numThreadsBusy++;
- ctx->queueEmpty = ctx->queueHead == ctx->queueTail;
- /* Unlock the mutex, signal a pusher, and run the job */
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_signal(&ctx->queuePushCond);
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(&ctx->queueMutex);
-
- job.function(job.opaque);
-
- /* If the intended queue size was 0, signal after finishing job */
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_lock(&ctx->queueMutex);
- ctx->numThreadsBusy--;
- if (ctx->queueSize == 1) {
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_signal(&ctx->queuePushCond);
- }
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(&ctx->queueMutex);
- }
- } /* for (;;) */
- assert(0); /* Unreachable */
-}
-
-POOL_ctx* POOL_create(size_t numThreads, size_t queueSize)
-{
- POOL_ctx* ctx;
- /* Check parameters */
- if (!numThreads) { return NULL; }
- /* Allocate the context and zero initialize */
- ctx = (POOL_ctx*)calloc(1, sizeof(POOL_ctx));
- if (!ctx) { return NULL; }
- /* Initialize the job queue.
- * It needs one extra space since one space is wasted to differentiate
- * empty and full queues.
- */
- ctx->queueSize = queueSize + 1;
- ctx->queue = (POOL_job*)malloc(ctx->queueSize * sizeof(POOL_job));
- ctx->queueHead = 0;
- ctx->queueTail = 0;
- ctx->numThreadsBusy = 0;
- ctx->queueEmpty = 1;
- (void)ZSTD_pthread_mutex_init(&ctx->queueMutex, NULL);
- (void)ZSTD_pthread_cond_init(&ctx->queuePushCond, NULL);
- (void)ZSTD_pthread_cond_init(&ctx->queuePopCond, NULL);
- ctx->shutdown = 0;
- /* Allocate space for the thread handles */
- ctx->threads = (ZSTD_pthread_t*)malloc(numThreads * sizeof(ZSTD_pthread_t));
- ctx->threadCapacity = 0;
- /* Check for errors */
- if (!ctx->threads || !ctx->queue) { POOL_free(ctx); return NULL; }
- /* Initialize the threads */
- { size_t i;
- for (i = 0; i < numThreads; ++i) {
- if (ZSTD_pthread_create(&ctx->threads[i], NULL, &POOL_thread, ctx)) {
- ctx->threadCapacity = i;
- POOL_free(ctx);
- return NULL;
- } }
- ctx->threadCapacity = numThreads;
- ctx->threadLimit = numThreads;
- }
- return ctx;
-}
-
-/*! POOL_join() :
- Shutdown the queue, wake any sleeping threads, and join all of the threads.
-*/
-static void POOL_join(POOL_ctx* ctx) {
- /* Shut down the queue */
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_lock(&ctx->queueMutex);
- ctx->shutdown = 1;
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(&ctx->queueMutex);
-
- /* Wake up sleeping threads */
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_broadcast(&ctx->queuePushCond);
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_broadcast(&ctx->queuePopCond);
-
- /* Join all of the threads */
- { size_t i;
- for (i = 0; i < ctx->threadCapacity; ++i) {
- ZSTD_pthread_join(ctx->threads[i], NULL); /* note : could fail */
- } }
-}
-
-void POOL_free(POOL_ctx *ctx) {
- if (!ctx) { return; }
- POOL_join(ctx);
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_destroy(&ctx->queueMutex);
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_destroy(&ctx->queuePushCond);
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_destroy(&ctx->queuePopCond);
- free(ctx->queue);
- free(ctx->threads);
- free(ctx);
-}
-
-
-
-size_t POOL_sizeof(POOL_ctx *ctx) {
- if (ctx==NULL) return 0; /* supports sizeof NULL */
- return sizeof(*ctx)
- + ctx->queueSize * sizeof(POOL_job)
- + ctx->threadCapacity * sizeof(ZSTD_pthread_t);
-}
-
-
-/* @return : 0 on success, 1 on error */
-static int POOL_resize_internal(POOL_ctx* ctx, size_t numThreads)
-{
- if (numThreads <= ctx->threadCapacity) {
- if (!numThreads) return 1;
- ctx->threadLimit = numThreads;
- return 0;
- }
- /* numThreads > threadCapacity */
- { ZSTD_pthread_t* const threadPool = (ZSTD_pthread_t*)malloc(numThreads * sizeof(ZSTD_pthread_t));
- if (!threadPool) return 1;
- /* replace existing thread pool */
- memcpy(threadPool, ctx->threads, ctx->threadCapacity * sizeof(*threadPool));
- free(ctx->threads);
- ctx->threads = threadPool;
- /* Initialize additional threads */
- { size_t threadId;
- for (threadId = ctx->threadCapacity; threadId < numThreads; ++threadId) {
- if (ZSTD_pthread_create(&threadPool[threadId], NULL, &POOL_thread, ctx)) {
- ctx->threadCapacity = threadId;
- return 1;
- } }
- } }
- /* successfully expanded */
- ctx->threadCapacity = numThreads;
- ctx->threadLimit = numThreads;
- return 0;
-}
-
-/* @return : 0 on success, 1 on error */
-int POOL_resize(POOL_ctx* ctx, size_t numThreads)
-{
- int result;
- if (ctx==NULL) return 1;
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_lock(&ctx->queueMutex);
- result = POOL_resize_internal(ctx, numThreads);
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_broadcast(&ctx->queuePopCond);
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(&ctx->queueMutex);
- return result;
-}
-
-/**
- * Returns 1 if the queue is full and 0 otherwise.
- *
- * When queueSize is 1 (pool was created with an intended queueSize of 0),
- * then a queue is empty if there is a thread free _and_ no job is waiting.
- */
-static int isQueueFull(POOL_ctx const* ctx) {
- if (ctx->queueSize > 1) {
- return ctx->queueHead == ((ctx->queueTail + 1) % ctx->queueSize);
- } else {
- return (ctx->numThreadsBusy == ctx->threadLimit) ||
- !ctx->queueEmpty;
- }
-}
-
-
-static void POOL_add_internal(POOL_ctx* ctx, POOL_function function, void *opaque)
-{
- POOL_job const job = {function, opaque};
- assert(ctx != NULL);
- if (ctx->shutdown) return;
-
- ctx->queueEmpty = 0;
- ctx->queue[ctx->queueTail] = job;
- ctx->queueTail = (ctx->queueTail + 1) % ctx->queueSize;
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_signal(&ctx->queuePopCond);
-}
-
-void POOL_add(POOL_ctx* ctx, POOL_function function, void* opaque)
-{
- assert(ctx != NULL);
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_lock(&ctx->queueMutex);
- /* Wait until there is space in the queue for the new job */
- while (isQueueFull(ctx) && (!ctx->shutdown)) {
- ZSTD_pthread_cond_wait(&ctx->queuePushCond, &ctx->queueMutex);
- }
- POOL_add_internal(ctx, function, opaque);
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(&ctx->queueMutex);
-}
-
-
-int POOL_tryAdd(POOL_ctx* ctx, POOL_function function, void* opaque)
-{
- assert(ctx != NULL);
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_lock(&ctx->queueMutex);
- if (isQueueFull(ctx)) {
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(&ctx->queueMutex);
- return 0;
- }
- POOL_add_internal(ctx, function, opaque);
- ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(&ctx->queueMutex);
- return 1;
-}
-
-
-#else /* POOL_MT not defined */
-
-/* ========================== */
-/* No multi-threading support */
-/* ========================== */
-
-
-/* We don't need any data, but if it is empty, malloc() might return NULL. */
-struct POOL_ctx_s {
- int dummy;
-};
-static POOL_ctx g_ctx;
-
-POOL_ctx* POOL_create(size_t numThreads, size_t queueSize) {
- (void)numThreads;
- (void)queueSize;
- return &g_ctx;
-}
-
-void POOL_free(POOL_ctx* ctx) {
- assert(!ctx || ctx == &g_ctx);
- (void)ctx;
-}
-
-int POOL_resize(POOL_ctx* ctx, size_t numThreads) {
- (void)ctx; (void)numThreads;
- return 0;
-}
-
-void POOL_add(POOL_ctx* ctx, POOL_function function, void* opaque) {
- (void)ctx;
- function(opaque);
-}
-
-int POOL_tryAdd(POOL_ctx* ctx, POOL_function function, void* opaque) {
- (void)ctx;
- function(opaque);
- return 1;
-}
-
-size_t POOL_sizeof(POOL_ctx* ctx) {
- if (ctx==NULL) return 0; /* supports sizeof NULL */
- assert(ctx == &g_ctx);
- return sizeof(*ctx);
-}
-
-#endif /* ZSTD_MULTITHREAD */
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/pool.h b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/pool.h
deleted file mode 100644
index 069022bea4..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/pool.h
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * Copyright (c) 2016-present, Yann Collet, Facebook, Inc.
- * All rights reserved.
- *
- * This source code is licensed under both the BSD-style license (found in the
- * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree) and the GPLv2 (found
- * in the COPYING file in the root directory of this source tree).
- * You may select, at your option, one of the above-listed licenses.
- */
-
-#ifndef POOL_H
-#define POOL_H
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-extern "C" {
-#endif
-
-
-#include /* size_t */
-
-typedef struct POOL_ctx_s POOL_ctx;
-
-/*! POOL_create() :
- * Create a thread pool with at most `numThreads` threads.
- * `numThreads` must be at least 1.
- * The maximum number of queued jobs before blocking is `queueSize`.
- * @return : POOL_ctx pointer on success, else NULL.
-*/
-POOL_ctx* POOL_create(size_t numThreads, size_t queueSize);
-
-/*! POOL_free() :
- * Free a thread pool returned by POOL_create().
- */
-void POOL_free(POOL_ctx* ctx);
-
-/*! POOL_resize() :
- * Expands or shrinks pool's number of threads.
- * This is more efficient than releasing + creating a new context,
- * since it tries to preserve and re-use existing threads.
- * `numThreads` must be at least 1.
- * @return : 0 when resize was successful,
- * !0 (typically 1) if there is an error.
- * note : only numThreads can be resized, queueSize remains unchanged.
- */
-int POOL_resize(POOL_ctx* ctx, size_t numThreads);
-
-/*! POOL_sizeof() :
- * @return threadpool memory usage
- * note : compatible with NULL (returns 0 in this case)
- */
-size_t POOL_sizeof(POOL_ctx* ctx);
-
-/*! POOL_function :
- * The function type that can be added to a thread pool.
- */
-typedef void (*POOL_function)(void*);
-
-/*! POOL_add() :
- * Add the job `function(opaque)` to the thread pool. `ctx` must be valid.
- * Possibly blocks until there is room in the queue.
- * Note : The function may be executed asynchronously,
- * therefore, `opaque` must live until function has been completed.
- */
-void POOL_add(POOL_ctx* ctx, POOL_function function, void* opaque);
-
-
-/*! POOL_tryAdd() :
- * Add the job `function(opaque)` to thread pool _if_ a worker is available.
- * Returns immediately even if not (does not block).
- * @return : 1 if successful, 0 if not.
- */
-int POOL_tryAdd(POOL_ctx* ctx, POOL_function function, void* opaque);
-
-
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-}
-#endif
-
-#endif
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/sort.cc b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/sort.cc
deleted file mode 100644
index c48f8456e6..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/sort.cc
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * sort.cc - C++ sort functions
- * Copyright (C) 2019-present, Yann Collet
- * GPL v2 License
- *
- * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
- * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
- * the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
- * (at your option) any later version.
- *
- * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
- * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
- * GNU General Public License for more details.
- *
- * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
- * with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- * 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
- * - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
- */
-
-/*
- * C++ sort functions tend to run faster than C ones due to templates allowing
- * inline optimizations.
- * Also, glibc's qsort() seems to inflate memory usage, resulting in OOM
- * crashes on the test server.
- */
-
-#include // std::sort
-#define XXH_INLINE_ALL // XXH128_cmp
-#include
-
-#include "sort.hh"
-
-void sort64(uint64_t* table, size_t size)
-{
- std::sort(table, table + size);
-}
-
-#include // qsort
-
-void sort128(XXH128_hash_t* table, size_t size)
-{
-#if 0
- // C++ sort using a custom function object
- struct {
- bool operator()(XXH128_hash_t a, XXH128_hash_t b) const
- {
- return XXH128_cmp(&a, &b);
- }
- } customLess;
- std::sort(table, table + size, customLess);
-#else
- qsort(table, size, sizeof(*table), XXH128_cmp);
-#endif
-}
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/sort.hh b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/sort.hh
deleted file mode 100644
index 6b17b6a3a9..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/sort.hh
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * sort.hh - headers for C++ sort functions
- * Copyright (C) 2019-present, Yann Collet
- * GPL v2 License
- *
- * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
- * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
- * the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
- * (at your option) any later version.
- *
- * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
- * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
- * GNU General Public License for more details.
- *
- * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
- * with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- * 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
- *
- * You can contact the author at :
- * - xxHash homepage : https://www.xxhash.com
- * - xxHash source repository : https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
- */
-
-#ifdef __cplusplus
-extern "C" {
-#endif
-
-#include // size
-#include // uint64_t
-#define XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY // XXH128_hash_t
-#include "xxhash.h"
-
-void sort64(uint64_t* table, size_t size);
-
-void sort128(XXH128_hash_t* table, size_t size);
-
-#ifdef __cplusplus
-} // extern C
-#endif
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/threading.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/threading.c
deleted file mode 100644
index 5164667192..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/threading.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
-/**
- * Copyright (c) 2016 Tino Reichardt
- * All rights reserved.
- *
- * This source code is licensed under both the BSD-style license (found in the
- * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree) and the GPLv2 (found
- * in the COPYING file in the root directory of this source tree).
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - zstdmt source repository: https://github.com/mcmilk/zstdmt
- */
-
-/**
- * This file will hold wrapper for systems, which do not support pthreads
- */
-
-
- /* === Build Macro === */
-
- #ifndef POOL_MT // can be defined on command line
- # define POOL_MT 1
- #endif
-
-
-/* create fake symbol to avoid empty translation unit warning */
-int g_ZSTD_threading_useles_symbol;
-
-#if POOL_MT && defined(_WIN32)
-
-/**
- * Windows minimalist Pthread Wrapper
- */
-
-
-/* === Dependencies === */
-#include
-#include
-#include "threading.h"
-
-
-/* === Implementation === */
-
-static unsigned __stdcall worker(void *arg)
-{
- ZSTD_pthread_t* const thread = (ZSTD_pthread_t*) arg;
- thread->arg = thread->start_routine(thread->arg);
- return 0;
-}
-
-int ZSTD_pthread_create(ZSTD_pthread_t* thread, const void* unused,
- void* (*start_routine) (void*), void* arg)
-{
- (void)unused;
- thread->arg = arg;
- thread->start_routine = start_routine;
- thread->handle = (HANDLE) _beginthreadex(NULL, 0, worker, thread, 0, NULL);
-
- if (!thread->handle)
- return errno;
- else
- return 0;
-}
-
-int ZSTD_pthread_join(ZSTD_pthread_t thread, void **value_ptr)
-{
- DWORD result;
-
- if (!thread.handle) return 0;
-
- result = WaitForSingleObject(thread.handle, INFINITE);
- switch (result) {
- case WAIT_OBJECT_0:
- if (value_ptr) *value_ptr = thread.arg;
- return 0;
- case WAIT_ABANDONED:
- return EINVAL;
- default:
- return (int)GetLastError();
- }
-}
-
-#endif /* POOL_MT */
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/threading.h b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/threading.h
deleted file mode 100644
index 700bf44269..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/collisions/threading.h
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,124 +0,0 @@
-/**
- * Copyright (c) 2016 Tino Reichardt
- * All rights reserved.
- *
- * This source code is licensed under both the BSD-style license (found in the
- * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree) and the GPLv2 (found
- * in the COPYING file in the root directory of this source tree).
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - zstdmt source repository: https://github.com/mcmilk/zstdmt
- */
-
-#ifndef THREADING_H_938743
-#define THREADING_H_938743
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-extern "C" {
-#endif
-
-/* === Build Macro === */
-
-#ifndef POOL_MT // can be defined on command line
-# define POOL_MT 1
-#endif
-
-
-/* === Implementation === */
-
-#if POOL_MT && defined(_WIN32)
-
-/**
- * Define windows version before include
- */
-#undef WINVER
-#define WINVER 0x0600
-
-#undef _WIN32_WINNT
-#define _WIN32_WINNT 0x0600
-
-#ifndef WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
-# define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
-#endif
-
-#include
-#include
-
-/* mutex */
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_t CRITICAL_SECTION
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_init(a, b) ((void)(b), InitializeCriticalSection((a)), 0)
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_destroy(a) DeleteCriticalSection((a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_lock(a) EnterCriticalSection((a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(a) LeaveCriticalSection((a))
-
-/* condition variable */
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_t CONDITION_VARIABLE
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_init(a, b) ((void)(b), InitializeConditionVariable((a)), 0)
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_destroy(a) ((void)(a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_wait(a, b) SleepConditionVariableCS((a), (b), INFINITE)
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_signal(a) WakeConditionVariable((a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_broadcast(a) WakeAllConditionVariable((a))
-
-/* ZSTD_pthread_create() and ZSTD_pthread_join() */
-typedef struct {
- HANDLE handle;
- void* (*start_routine)(void*);
- void* arg;
-} ZSTD_pthread_t;
-
-int ZSTD_pthread_create(ZSTD_pthread_t* thread, const void* unused,
- void* (*start_routine) (void*), void* arg);
-
-int ZSTD_pthread_join(ZSTD_pthread_t thread, void** value_ptr);
-
-/**
- * add here more wrappers as required
- */
-
-
-#elif POOL_MT /* posix assumed ; need a better detection method */
-/* === POSIX Systems === */
-# include
-
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_t pthread_mutex_t
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_init(a, b) pthread_mutex_init((a), (b))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_destroy(a) pthread_mutex_destroy((a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_lock(a) pthread_mutex_lock((a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(a) pthread_mutex_unlock((a))
-
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_t pthread_cond_t
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_init(a, b) pthread_cond_init((a), (b))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_destroy(a) pthread_cond_destroy((a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_wait(a, b) pthread_cond_wait((a), (b))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_signal(a) pthread_cond_signal((a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_broadcast(a) pthread_cond_broadcast((a))
-
-#define ZSTD_pthread_t pthread_t
-#define ZSTD_pthread_create(a, b, c, d) pthread_create((a), (b), (c), (d))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_join(a, b) pthread_join((a),(b))
-
-#else /* POOL_MT == 0 */
-/* No multithreading support */
-
-typedef int ZSTD_pthread_mutex_t;
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_init(a, b) ((void)(a), (void)(b), 0)
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_destroy(a) ((void)(a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_lock(a) ((void)(a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_mutex_unlock(a) ((void)(a))
-
-typedef int ZSTD_pthread_cond_t;
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_init(a, b) ((void)(a), (void)(b), 0)
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_destroy(a) ((void)(a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_wait(a, b) ((void)(a), (void)(b))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_signal(a) ((void)(a))
-#define ZSTD_pthread_cond_broadcast(a) ((void)(a))
-
-/* do not use ZSTD_pthread_t */
-
-#endif /* POOL_MT */
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-}
-#endif
-
-#endif /* THREADING_H_938743 */
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/generate_unicode_test.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/generate_unicode_test.c
deleted file mode 100644
index eed6ac01a5..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/generate_unicode_test.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,154 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * Generates a Unicode test for xxhsum without using Unicode in the source files.
- *
- * Copyright (C) 2020 Devin Hussey (easyaspi314)
- *
- * BSD 2-Clause License (https://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php)
- *
- * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
- * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
- * met:
- *
- * * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
- * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
- * * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
- * copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
- * in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
- * distribution.
- *
- * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
- * "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
- * LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
- * A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
- * OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
- * SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
- * LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
- * DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
- * THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
- * (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
- * OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
- */
-
-/*
- * Certain terminals don't properly handle UTF-8 (i.e. rxvt and command prompt
- * in the default codepage), and that can cause issues when editing text.
- *
- * We use this C file to generate a file with a Unicode filename, a file with
- * a checksum of said file, and both a Windows batch script and a Unix shell
- * script to test the file.
- */
-
-#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS /* Silence warnings on MSVC */
-#include
-
-/* Use a Japanese filename, something that can't be cheated with ANSI.
- * yuniko-do.unicode (literally unicode.unicode) */
-
-/* Use raw hex values to ensure that the output is well-formed UTF-8. It is also more C90 compliant. */
-static const char FILENAME[] = {
- (char)0xe3, (char)0x83, (char)0xa6, /* U+30e6: Katakana letter yu */
- (char)0xe3, (char)0x83, (char)0x8b, /* U+30cb: Katakana letter ni */
- (char)0xe3, (char)0x82, (char)0xb3, /* U+30b3: Katakana letter ko */
- (char)0xe3, (char)0x83, (char)0xbc, /* U+30fc: Katakana-Hiragana prolonged sound mark (dash) */
- (char)0xe3, (char)0x83, (char)0x89, /* U+30c9: Katakana letter do */
- '.','u','n','i','c','o','d','e','\0' /* ".unicode" (so we can glob in make clean and .gitignore) */
-};
-
-#ifdef _WIN32
-/* The same text as above, but encoded in Windows UTF-16. */
-static const wchar_t WFILENAME[] = { 0x30e6, 0x30cb, 0x30b3, 0x30fc, 0x30c9, L'.', L'u', L'n', L'i', L'c', L'o', L'd', L'e', L'\0' };
-#endif
-
-int main(void)
-{
- FILE *f, *script, *checksum;
-
- /* Create our Unicode file. Use _wfopen on Windows as fopen doesn't support Unicode filenames. */
-#ifdef _WIN32
- if (!(f = _wfopen(WFILENAME, L"wb"))) return 1;
-#else
- if (!(f = fopen(FILENAME, "wb"))) return 1;
-#endif
- fprintf(f, "test\n");
- fclose(f);
-
- /* XXH64 checksum file with the precalculated checksum for said file. */
- if (!(checksum = fopen("unicode_test.xxh64", "wb")))
- return 1;
- fprintf(checksum, "2d7f1808da1fa63c %s\n", FILENAME);
- fclose(checksum);
-
-
- /* Create two scripts for both Windows and Unix. */
-
- /* Generate a Windows batch script. Always insert CRLF manually. */
- if (!(script = fopen("unicode_test.bat", "wb")))
- return 1;
-
- /* Disable echoing the commands. We do that ourselves the naive way. */
- fprintf(script, "@echo off\r\n");
-
- /* Change to codepage 65001 to enable UTF-8 support. */
- fprintf(script, "chcp 65001 >NUL 2>&1\r\n");
-
- /* First test a Unicode filename */
- fprintf(script, "echo Testing filename provided on command line...\r\n");
- fprintf(script, "echo xxhsum.exe \"%s\"\r\n", FILENAME);
- fprintf(script, "xxhsum.exe \"%s\"\r\n", FILENAME);
-
- /* Bail on error */
- fprintf(script, "if %%ERRORLEVEL%% neq 0 (\r\n");
- fprintf(script, " exit /B %%ERRORLEVEL%%\r\n");
- fprintf(script, ")\r\n");
-
- /* Then test a checksum file. */
- fprintf(script, "echo Testing a checksum file...\r\n");
- fprintf(script, "echo xxhsum.exe -c unicode_test.xxh64\r\n");
- fprintf(script, "xxhsum.exe -c unicode_test.xxh64\r\n");
-
- fprintf(script, "exit /B %%ERRORLEVEL%%\r\n");
-
- fclose(script);
-
- /* Generate a Unix shell script */
- if (!(script = fopen("unicode_test.sh", "wb")))
- return 1;
-
- fprintf(script, "#!/bin/sh\n");
- /*
- * Some versions of MSYS, MinGW and Cygwin do not support UTF-8, and the ones that
- * don't may error with something like this:
- *
- * Error: Could not open '.unicode': No such file or directory.
- *
- * which is an internal error that happens when it tries to convert MinGW/Cygwin
- * paths to Windows paths.
- *
- * In that case, we bail to cmd.exe and the batch script, which supports UTF-8
- * on Windows 7 and later.
- */
- fprintf(script, "case $(uname) in\n");
- /* MinGW/MSYS converts /c to C:\ unless you have a double slash,
- * Cygwin does not. */
- fprintf(script, " *CYGWIN*)\n");
- fprintf(script, " exec cmd.exe /c unicode_test.bat\n");
- fprintf(script, " ;;\n");
- fprintf(script, " *MINGW*|*MSYS*)\n");
- fprintf(script, " exec cmd.exe //c unicode_test.bat\n");
- fprintf(script, " ;;\n");
- fprintf(script, "esac\n");
-
- /* First test a Unicode filename */
- fprintf(script, "echo Testing filename provided on command line...\n");
- fprintf(script, "echo './xxhsum \"%s\" || exit $?'\n", FILENAME);
- fprintf(script, "./xxhsum \"%s\" || exit $?\n", FILENAME);
-
- /* Then test a checksum file. */
- fprintf(script, "echo Testing a checksum file...\n");
- fprintf(script, "echo './xxhsum -c unicode_test.xxh64 || exit $?'\n");
- fprintf(script, "./xxhsum -c unicode_test.xxh64 || exit $?\n");
-
- fclose(script);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/multiInclude.c b/core/deps/xxHash/tests/multiInclude.c
deleted file mode 100644
index fd82f17d3f..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/tests/multiInclude.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * Multi-include test program
- * Validates that xxhash.h can be included multiple times and in any order
- *
- * Copyright (C) Yann Collet 2020-present
- *
- * GPL v2 License
- *
- * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
- * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
- * the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
- * (at your option) any later version.
- *
- * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
- * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
- * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
- * GNU General Public License for more details.
- *
- * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
- * with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
- * 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
- * - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
- */
-
-#include /* printf */
-
-/* Normal include, gives access to public symbols */
-#include "../xxhash.h"
-
-/*
- * Advanced include, gives access to experimental symbols
- * This test ensure that xxhash.h can be included multiple times and in any
- * order. This order is more difficult: Without care, the declaration of
- * experimental symbols could be skipped.
- */
-#define XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY
-#include "../xxhash.h"
-
-/*
- * Inlining: Re-define all identifiers, keep them private to the unit.
- * Note: Without specific efforts, the identifier names would collide.
- *
- * To be linked with and without xxhash.o to test the symbol's presence and
- * naming collisions.
- */
-#define XXH_INLINE_ALL
-#include "../xxhash.h"
-
-
-int main(void)
-{
- XXH3_state_t state; /* part of experimental API */
-
- XXH3_64bits_reset(&state);
- const char input[] = "Hello World !";
-
- XXH3_64bits_update(&state, input, sizeof(input));
-
- XXH64_hash_t const h = XXH3_64bits_digest(&state);
- printf("hash '%s': %08x%08x \n", input, (unsigned)(h >> 32), (unsigned)h);
-
- return 0;
-}
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/xxh3.h b/core/deps/xxHash/xxh3.h
deleted file mode 100644
index 9e3e88ad61..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/xxh3.h
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,2112 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * xxHash - Extremely Fast Hash algorithm
- * Development source file for `xxh3`
- * Copyright (C) 2019-present, Yann Collet
- *
- * BSD 2-Clause License (https://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php)
- *
- * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
- * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
- * met:
- *
- * * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
- * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
- * * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
- * copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
- * in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
- * distribution.
- *
- * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
- * "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
- * LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
- * A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
- * OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
- * SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
- * LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
- * DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
- * THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
- * (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
- * OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
- * - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
- */
-
-/*
- * Note: This file is separated for development purposes.
- * It will be integrated into `xxhash.h` when development stage is completed.
- *
- * Credit: most of the work on vectorial and asm variants comes from @easyaspi314
- */
-
-#ifndef XXH3_H_1397135465
-#define XXH3_H_1397135465
-
-/* === Dependencies === */
-#ifndef XXHASH_H_5627135585666179
-/* special: when including `xxh3.h` directly, turn on XXH_INLINE_ALL */
-# undef XXH_INLINE_ALL /* avoid redefinition */
-# define XXH_INLINE_ALL
-#endif
-#include "xxhash.h"
-
-
-/* === Compiler specifics === */
-
-#if defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L /* >= C99 */
-# define XXH_RESTRICT restrict
-#else
-/* Note: it might be useful to define __restrict or __restrict__ for some C++ compilers */
-# define XXH_RESTRICT /* disable */
-#endif
-
-#if (defined(__GNUC__) && (__GNUC__ >= 3)) \
- || (defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) && (__INTEL_COMPILER >= 800)) \
- || defined(__clang__)
-# define XXH_likely(x) __builtin_expect(x, 1)
-# define XXH_unlikely(x) __builtin_expect(x, 0)
-#else
-# define XXH_likely(x) (x)
-# define XXH_unlikely(x) (x)
-#endif
-
-#if defined(__GNUC__)
-# if defined(__AVX2__)
-# include
-# elif defined(__SSE2__)
-# include
-# elif defined(__ARM_NEON__) || defined(__ARM_NEON)
-# define inline __inline__ /* clang bug */
-# include
-# undef inline
-# endif
-#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
-# include
-#endif
-
-/*
- * One goal of XXH3 is to make it fast on both 32-bit and 64-bit, while
- * remaining a true 64-bit/128-bit hash function.
- *
- * This is done by prioritizing a subset of 64-bit operations that can be
- * emulated without too many steps on the average 32-bit machine.
- *
- * For example, these two lines seem similar, and run equally fast on 64-bit:
- *
- * xxh_u64 x;
- * x ^= (x >> 47); // good
- * x ^= (x >> 13); // bad
- *
- * However, to a 32-bit machine, there is a major difference.
- *
- * x ^= (x >> 47) looks like this:
- *
- * x.lo ^= (x.hi >> (47 - 32));
- *
- * while x ^= (x >> 13) looks like this:
- *
- * // note: funnel shifts are not usually cheap.
- * x.lo ^= (x.lo >> 13) | (x.hi << (32 - 13));
- * x.hi ^= (x.hi >> 13);
- *
- * The first one is significantly faster than the second, simply because the
- * shift is larger than 32. This means:
- * - All the bits we need are in the upper 32 bits, so we can ignore the lower
- * 32 bits in the shift.
- * - The shift result will always fit in the lower 32 bits, and therefore,
- * we can ignore the upper 32 bits in the xor.
- *
- * Thanks to this optimization, XXH3 only requires these features to be efficient:
- *
- * - Usable unaligned access
- * - A 32-bit or 64-bit ALU
- * - If 32-bit, a decent ADC instruction
- * - A 32 or 64-bit multiply with a 64-bit result
- * - For the 128-bit variant, a decent byteswap helps short inputs.
- *
- * The first two are already required by XXH32, and almost all 32-bit and 64-bit
- * platforms which can run XXH32 can run XXH3 efficiently.
- *
- * Thumb-1, the classic 16-bit only subset of ARM's instruction set, is one
- * notable exception.
- *
- * First of all, Thumb-1 lacks support for the UMULL instruction which
- * performs the important long multiply. This means numerous __aeabi_lmul
- * calls.
- *
- * Second of all, the 8 functional registers are just not enough.
- * Setup for __aeabi_lmul, byteshift loads, pointers, and all arithmetic need
- * Lo registers, and this shuffling results in thousands more MOVs than A32.
- *
- * A32 and T32 don't have this limitation. They can access all 14 registers,
- * do a 32->64 multiply with UMULL, and the flexible operand allowing free
- * shifts is helpful, too.
- *
- * Therefore, we do a quick sanity check.
- *
- * If compiling Thumb-1 for a target which supports ARM instructions, we will
- * emit a warning, as it is not a "sane" platform to compile for.
- *
- * Usually, if this happens, it is because of an accident and you probably need
- * to specify -march, as you likely meant to compile for a newer architecture.
- */
-#if defined(__thumb__) && !defined(__thumb2__) && defined(__ARM_ARCH_ISA_ARM)
-# warning "XXH3 is highly inefficient without ARM or Thumb-2."
-#endif
-
-/* ==========================================
- * Vectorization detection
- * ========================================== */
-#define XXH_SCALAR 0 /* Portable scalar version */
-#define XXH_SSE2 1 /* SSE2 for Pentium 4 and all x86_64 */
-#define XXH_AVX2 2 /* AVX2 for Haswell and Bulldozer */
-#define XXH_NEON 3 /* NEON for most ARMv7-A and all AArch64 */
-#define XXH_VSX 4 /* VSX and ZVector for POWER8/z13 */
-
-#ifndef XXH_VECTOR /* can be defined on command line */
-# if defined(__AVX2__)
-# define XXH_VECTOR XXH_AVX2
-# elif defined(__SSE2__) || defined(_M_AMD64) || defined(_M_X64) || (defined(_M_IX86_FP) && (_M_IX86_FP == 2))
-# define XXH_VECTOR XXH_SSE2
-# elif defined(__GNUC__) /* msvc support maybe later */ \
- && (defined(__ARM_NEON__) || defined(__ARM_NEON)) \
- && (defined(__LITTLE_ENDIAN__) /* We only support little endian NEON */ \
- || (defined(__BYTE_ORDER__) && __BYTE_ORDER__ == __ORDER_LITTLE_ENDIAN__))
-# define XXH_VECTOR XXH_NEON
-# elif (defined(__PPC64__) && defined(__POWER8_VECTOR__)) \
- || (defined(__s390x__) && defined(__VEC__)) \
- && defined(__GNUC__) /* TODO: IBM XL */
-# define XXH_VECTOR XXH_VSX
-# else
-# define XXH_VECTOR XXH_SCALAR
-# endif
-#endif
-
-/*
- * Controls the alignment of the accumulator.
- * This is for compatibility with aligned vector loads, which are usually faster.
- */
-#ifndef XXH_ACC_ALIGN
-# if XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SCALAR /* scalar */
-# define XXH_ACC_ALIGN 8
-# elif XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SSE2 /* sse2 */
-# define XXH_ACC_ALIGN 16
-# elif XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2 /* avx2 */
-# define XXH_ACC_ALIGN 32
-# elif XXH_VECTOR == XXH_NEON /* neon */
-# define XXH_ACC_ALIGN 16
-# elif XXH_VECTOR == XXH_VSX /* vsx */
-# define XXH_ACC_ALIGN 16
-# endif
-#endif
-
-/*
- * UGLY HACK:
- * GCC usually generates the best code with -O3 for xxHash.
- *
- * However, when targeting AVX2, it is overzealous in its unrolling resulting
- * in code roughly 3/4 the speed of Clang.
- *
- * There are other issues, such as GCC splitting _mm256_loadu_si256 into
- * _mm_loadu_si128 + _mm256_inserti128_si256. This is an optimization which
- * only applies to Sandy and Ivy Bridge... which don't even support AVX2.
- *
- * That is why when compiling the AVX2 version, it is recommended to use either
- * -O2 -mavx2 -march=haswell
- * or
- * -O2 -mavx2 -mno-avx256-split-unaligned-load
- * for decent performance, or to use Clang instead.
- *
- * Fortunately, we can control the first one with a pragma that forces GCC into
- * -O2, but the other one we can't control without "failed to inline always
- * inline function due to target mismatch" warnings.
- */
-#if XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2 /* AVX2 */ \
- && defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) /* GCC, not Clang */ \
- && defined(__OPTIMIZE__) && !defined(__OPTIMIZE_SIZE__) /* respect -O0 and -Os */
-# pragma GCC push_options
-# pragma GCC optimize("-O2")
-#endif
-
-
-#if XXH_VECTOR == XXH_NEON
-/*
- * NEON's setup for vmlal_u32 is a little more complicated than it is on
- * SSE2, AVX2, and VSX.
- *
- * While PMULUDQ and VMULEUW both perform a mask, VMLAL.U32 performs an upcast.
- *
- * To do the same operation, the 128-bit 'Q' register needs to be split into
- * two 64-bit 'D' registers, performing this operation::
- *
- * [ a | b ]
- * | '---------. .--------' |
- * | x |
- * | .---------' '--------. |
- * [ a & 0xFFFFFFFF | b & 0xFFFFFFFF ],[ a >> 32 | b >> 32 ]
- *
- * Due to significant changes in aarch64, the fastest method for aarch64 is
- * completely different than the fastest method for ARMv7-A.
- *
- * ARMv7-A treats D registers as unions overlaying Q registers, so modifying
- * D11 will modify the high half of Q5. This is similar to how modifying AH
- * will only affect bits 8-15 of AX on x86.
- *
- * VZIP takes two registers, and puts even lanes in one register and odd lanes
- * in the other.
- *
- * On ARMv7-A, this strangely modifies both parameters in place instead of
- * taking the usual 3-operand form.
- *
- * Therefore, if we want to do this, we can simply use a D-form VZIP.32 on the
- * lower and upper halves of the Q register to end up with the high and low
- * halves where we want - all in one instruction.
- *
- * vzip.32 d10, d11 @ d10 = { d10[0], d11[0] }; d11 = { d10[1], d11[1] }
- *
- * Unfortunately we need inline assembly for this: Instructions modifying two
- * registers at once is not possible in GCC or Clang's IR, and they have to
- * create a copy.
- *
- * aarch64 requires a different approach.
- *
- * In order to make it easier to write a decent compiler for aarch64, many
- * quirks were removed, such as conditional execution.
- *
- * NEON was also affected by this.
- *
- * aarch64 cannot access the high bits of a Q-form register, and writes to a
- * D-form register zero the high bits, similar to how writes to W-form scalar
- * registers (or DWORD registers on x86_64) work.
- *
- * The formerly free vget_high intrinsics now require a vext (with a few
- * exceptions)
- *
- * Additionally, VZIP was replaced by ZIP1 and ZIP2, which are the equivalent
- * of PUNPCKL* and PUNPCKH* in SSE, respectively, in order to only modify one
- * operand.
- *
- * The equivalent of the VZIP.32 on the lower and upper halves would be this
- * mess:
- *
- * ext v2.4s, v0.4s, v0.4s, #2 // v2 = { v0[2], v0[3], v0[0], v0[1] }
- * zip1 v1.2s, v0.2s, v2.2s // v1 = { v0[0], v2[0] }
- * zip2 v0.2s, v0.2s, v1.2s // v0 = { v0[1], v2[1] }
- *
- * Instead, we use a literal downcast, vmovn_u64 (XTN), and vshrn_n_u64 (SHRN):
- *
- * shrn v1.2s, v0.2d, #32 // v1 = (uint32x2_t)(v0 >> 32);
- * xtn v0.2s, v0.2d // v0 = (uint32x2_t)(v0 & 0xFFFFFFFF);
- *
- * This is available on ARMv7-A, but is less efficient than a single VZIP.32.
- */
-
-/*
- * Function-like macro:
- * void XXH_SPLIT_IN_PLACE(uint64x2_t &in, uint32x2_t &outLo, uint32x2_t &outHi)
- * {
- * outLo = (uint32x2_t)(in & 0xFFFFFFFF);
- * outHi = (uint32x2_t)(in >> 32);
- * in = UNDEFINED;
- * }
- */
-# if !defined(XXH_NO_VZIP_HACK) /* define to disable */ \
- && defined(__GNUC__) \
- && !defined(__aarch64__) && !defined(__arm64__)
-# define XXH_SPLIT_IN_PLACE(in, outLo, outHi) \
- do { \
- /* Undocumented GCC/Clang operand modifier: %e0 = lower D half, %f0 = upper D half */ \
- /* https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/blob/38cf91e5/gcc/config/arm/arm.c#L22486 */ \
- /* https://github.com/llvm-mirror/llvm/blob/2c4ca683/lib/Target/ARM/ARMAsmPrinter.cpp#L399 */ \
- __asm__("vzip.32 %e0, %f0" : "+w" (in)); \
- (outLo) = vget_low_u32 (vreinterpretq_u32_u64(in)); \
- (outHi) = vget_high_u32(vreinterpretq_u32_u64(in)); \
- } while (0)
-# else
-# define XXH_SPLIT_IN_PLACE(in, outLo, outHi) \
- do { \
- (outLo) = vmovn_u64 (in); \
- (outHi) = vshrn_n_u64 ((in), 32); \
- } while (0)
-# endif
-#endif /* XXH_VECTOR == XXH_NEON */
-
-/*
- * VSX and Z Vector helpers.
- *
- * This is very messy, and any pull requests to clean this up are welcome.
- *
- * There are a lot of problems with supporting VSX and s390x, due to
- * inconsistent intrinsics, spotty coverage, and multiple endiannesses.
- */
-#if XXH_VECTOR == XXH_VSX
-# if defined(__s390x__)
-# include
-# else
-# include
-# endif
-
-# undef vector /* Undo the pollution */
-
-typedef __vector unsigned long long xxh_u64x2;
-typedef __vector unsigned char xxh_u8x16;
-typedef __vector unsigned xxh_u32x4;
-
-# ifndef XXH_VSX_BE
-# if defined(__BIG_ENDIAN__) \
- || (defined(__BYTE_ORDER__) && __BYTE_ORDER__ == __ORDER_BIG_ENDIAN__)
-# define XXH_VSX_BE 1
-# elif defined(__VEC_ELEMENT_REG_ORDER__) && __VEC_ELEMENT_REG_ORDER__ == __ORDER_BIG_ENDIAN__
-# warning "-maltivec=be is not recommended. Please use native endianness."
-# define XXH_VSX_BE 1
-# else
-# define XXH_VSX_BE 0
-# endif
-# endif /* !defined(XXH_VSX_BE) */
-
-# if XXH_VSX_BE
-/* A wrapper for POWER9's vec_revb. */
-# if defined(__POWER9_VECTOR__) || (defined(__clang__) && defined(__s390x__))
-# define XXH_vec_revb vec_revb
-# else
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64x2 XXH_vec_revb(xxh_u64x2 val)
-{
- xxh_u8x16 const vByteSwap = { 0x07, 0x06, 0x05, 0x04, 0x03, 0x02, 0x01, 0x00,
- 0x0F, 0x0E, 0x0D, 0x0C, 0x0B, 0x0A, 0x09, 0x08 };
- return vec_perm(val, val, vByteSwap);
-}
-# endif
-# endif /* XXH_VSX_BE */
-
-/*
- * Performs an unaligned load and byte swaps it on big endian.
- */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64x2 XXH_vec_loadu(const void *ptr)
-{
- xxh_u64x2 ret;
- memcpy(&ret, ptr, sizeof(xxh_u64x2));
-# if XXH_VSX_BE
- ret = XXH_vec_revb(ret);
-# endif
- return ret;
-}
-
-/*
- * vec_mulo and vec_mule are very problematic intrinsics on PowerPC
- *
- * These intrinsics weren't added until GCC 8, despite existing for a while,
- * and they are endian dependent. Also, their meaning swap depending on version.
- * */
-# if defined(__s390x__)
- /* s390x is always big endian, no issue on this platform */
-# define XXH_vec_mulo vec_mulo
-# define XXH_vec_mule vec_mule
-# elif defined(__clang__) && __has_builtin(__builtin_altivec_vmuleuw)
-/* Clang has a better way to control this, we can just use the builtin which doesn't swap. */
-# define XXH_vec_mulo __builtin_altivec_vmulouw
-# define XXH_vec_mule __builtin_altivec_vmuleuw
-# else
-/* gcc needs inline assembly */
-/* Adapted from https://github.com/google/highwayhash/blob/master/highwayhash/hh_vsx.h. */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64x2 XXH_vec_mulo(xxh_u32x4 a, xxh_u32x4 b)
-{
- xxh_u64x2 result;
- __asm__("vmulouw %0, %1, %2" : "=v" (result) : "v" (a), "v" (b));
- return result;
-}
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64x2 XXH_vec_mule(xxh_u32x4 a, xxh_u32x4 b)
-{
- xxh_u64x2 result;
- __asm__("vmuleuw %0, %1, %2" : "=v" (result) : "v" (a), "v" (b));
- return result;
-}
-# endif /* XXH_vec_mulo, XXH_vec_mule */
-#endif /* XXH_VECTOR == XXH_VSX */
-
-
-/* prefetch
- * can be disabled, by declaring XXH_NO_PREFETCH build macro */
-#if defined(XXH_NO_PREFETCH)
-# define XXH_PREFETCH(ptr) (void)(ptr) /* disabled */
-#else
-# if defined(_MSC_VER) && (defined(_M_X64) || defined(_M_I86)) /* _mm_prefetch() is not defined outside of x86/x64 */
-# include /* https://msdn.microsoft.com/fr-fr/library/84szxsww(v=vs.90).aspx */
-# define XXH_PREFETCH(ptr) _mm_prefetch((const char*)(ptr), _MM_HINT_T0)
-# elif defined(__GNUC__) && ( (__GNUC__ >= 4) || ( (__GNUC__ == 3) && (__GNUC_MINOR__ >= 1) ) )
-# define XXH_PREFETCH(ptr) __builtin_prefetch((ptr), 0 /* rw==read */, 3 /* locality */)
-# else
-# define XXH_PREFETCH(ptr) (void)(ptr) /* disabled */
-# endif
-#endif /* XXH_NO_PREFETCH */
-
-
-/* ==========================================
- * XXH3 default settings
- * ========================================== */
-
-#define XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE 192 /* minimum XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN */
-
-#if (XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE < XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN)
-# error "default keyset is not large enough"
-#endif
-
-/* Pseudorandom secret taken directly from FARSH */
-XXH_ALIGN(64) static const xxh_u8 kSecret[XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE] = {
- 0xb8, 0xfe, 0x6c, 0x39, 0x23, 0xa4, 0x4b, 0xbe, 0x7c, 0x01, 0x81, 0x2c, 0xf7, 0x21, 0xad, 0x1c,
- 0xde, 0xd4, 0x6d, 0xe9, 0x83, 0x90, 0x97, 0xdb, 0x72, 0x40, 0xa4, 0xa4, 0xb7, 0xb3, 0x67, 0x1f,
- 0xcb, 0x79, 0xe6, 0x4e, 0xcc, 0xc0, 0xe5, 0x78, 0x82, 0x5a, 0xd0, 0x7d, 0xcc, 0xff, 0x72, 0x21,
- 0xb8, 0x08, 0x46, 0x74, 0xf7, 0x43, 0x24, 0x8e, 0xe0, 0x35, 0x90, 0xe6, 0x81, 0x3a, 0x26, 0x4c,
- 0x3c, 0x28, 0x52, 0xbb, 0x91, 0xc3, 0x00, 0xcb, 0x88, 0xd0, 0x65, 0x8b, 0x1b, 0x53, 0x2e, 0xa3,
- 0x71, 0x64, 0x48, 0x97, 0xa2, 0x0d, 0xf9, 0x4e, 0x38, 0x19, 0xef, 0x46, 0xa9, 0xde, 0xac, 0xd8,
- 0xa8, 0xfa, 0x76, 0x3f, 0xe3, 0x9c, 0x34, 0x3f, 0xf9, 0xdc, 0xbb, 0xc7, 0xc7, 0x0b, 0x4f, 0x1d,
- 0x8a, 0x51, 0xe0, 0x4b, 0xcd, 0xb4, 0x59, 0x31, 0xc8, 0x9f, 0x7e, 0xc9, 0xd9, 0x78, 0x73, 0x64,
-
- 0xea, 0xc5, 0xac, 0x83, 0x34, 0xd3, 0xeb, 0xc3, 0xc5, 0x81, 0xa0, 0xff, 0xfa, 0x13, 0x63, 0xeb,
- 0x17, 0x0d, 0xdd, 0x51, 0xb7, 0xf0, 0xda, 0x49, 0xd3, 0x16, 0x55, 0x26, 0x29, 0xd4, 0x68, 0x9e,
- 0x2b, 0x16, 0xbe, 0x58, 0x7d, 0x47, 0xa1, 0xfc, 0x8f, 0xf8, 0xb8, 0xd1, 0x7a, 0xd0, 0x31, 0xce,
- 0x45, 0xcb, 0x3a, 0x8f, 0x95, 0x16, 0x04, 0x28, 0xaf, 0xd7, 0xfb, 0xca, 0xbb, 0x4b, 0x40, 0x7e,
-};
-
-/*
- * Does a 32-bit to 64-bit long multiply.
- *
- * Wraps __emulu on MSVC x86 because it tends to call __allmul when it doesn't
- * need to (but it shouldn't need to anyways, it is about 7 instructions to do
- * a 64x64 multiply...). Since we know that this will _always_ emit MULL, we
- * use that instead of the normal method.
- *
- * If you are compiling for platforms like Thumb-1 and don't have a better option,
- * you may also want to write your own long multiply routine here.
- *
- * XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH_mult32to64(xxh_u64 x, xxh_u64 y)
- * {
- * return (x & 0xFFFFFFFF) * (y & 0xFFFFFFFF);
- * }
- */
-#if defined(_MSC_VER) && defined(_M_IX86)
-# include
-# define XXH_mult32to64(x, y) __emulu((unsigned)(x), (unsigned)(y))
-#else
-/*
- * Downcast + upcast is usually better than masking on older compilers like
- * GCC 4.2 (especially 32-bit ones), all without affecting newer compilers.
- *
- * The other method, (x & 0xFFFFFFFF) * (y & 0xFFFFFFFF), will AND both operands
- * and perform a full 64x64 multiply -- entirely redundant on 32-bit.
- */
-# define XXH_mult32to64(x, y) ((xxh_u64)(xxh_u32)(x) * (xxh_u64)(xxh_u32)(y))
-#endif
-
-/*
- * Calculates a 64->128-bit long multiply.
- *
- * Uses __uint128_t and _umul128 if available, otherwise uses a scalar version.
- */
-static XXH128_hash_t
-XXH_mult64to128(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs)
-{
- /*
- * GCC/Clang __uint128_t method.
- *
- * On most 64-bit targets, GCC and Clang define a __uint128_t type.
- * This is usually the best way as it usually uses a native long 64-bit
- * multiply, such as MULQ on x86_64 or MUL + UMULH on aarch64.
- *
- * Usually.
- *
- * Despite being a 32-bit platform, Clang (and emscripten) define this type
- * despite not having the arithmetic for it. This results in a laggy
- * compiler builtin call which calculates a full 128-bit multiply.
- * In that case it is best to use the portable one.
- * https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/issues/211#issuecomment-515575677
- */
-#if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__wasm__) \
- && defined(__SIZEOF_INT128__) \
- || (defined(_INTEGRAL_MAX_BITS) && _INTEGRAL_MAX_BITS >= 128)
-
- __uint128_t product = (__uint128_t)lhs * (__uint128_t)rhs;
- XXH128_hash_t const r128 = { (xxh_u64)(product), (xxh_u64)(product >> 64) };
- return r128;
-
- /*
- * MSVC for x64's _umul128 method.
- *
- * xxh_u64 _umul128(xxh_u64 Multiplier, xxh_u64 Multiplicand, xxh_u64 *HighProduct);
- *
- * This compiles to single operand MUL on x64.
- */
-#elif defined(_M_X64) || defined(_M_IA64)
-
-#ifndef _MSC_VER
-# pragma intrinsic(_umul128)
-#endif
- xxh_u64 product_high;
- xxh_u64 const product_low = _umul128(lhs, rhs, &product_high);
- XXH128_hash_t const r128 = { product_low, product_high };
- return r128;
-
-#else
- /*
- * Portable scalar method. Optimized for 32-bit and 64-bit ALUs.
- *
- * This is a fast and simple grade school multiply, which is shown below
- * with base 10 arithmetic instead of base 0x100000000.
- *
- * 9 3 // D2 lhs = 93
- * x 7 5 // D2 rhs = 75
- * ----------
- * 1 5 // D2 lo_lo = (93 % 10) * (75 % 10) = 15
- * 4 5 | // D2 hi_lo = (93 / 10) * (75 % 10) = 45
- * 2 1 | // D2 lo_hi = (93 % 10) * (75 / 10) = 21
- * + 6 3 | | // D2 hi_hi = (93 / 10) * (75 / 10) = 63
- * ---------
- * 2 7 | // D2 cross = (15 / 10) + (45 % 10) + 21 = 27
- * + 6 7 | | // D2 upper = (27 / 10) + (45 / 10) + 63 = 67
- * ---------
- * 6 9 7 5 // D4 res = (27 * 10) + (15 % 10) + (67 * 100) = 6975
- *
- * The reasons for adding the products like this are:
- * 1. It avoids manual carry tracking. Just like how
- * (9 * 9) + 9 + 9 = 99, the same applies with this for UINT64_MAX.
- * This avoids a lot of complexity.
- *
- * 2. It hints for, and on Clang, compiles to, the powerful UMAAL
- * instruction available in ARM's Digital Signal Processing extension
- * in 32-bit ARMv6 and later, which is shown below:
- *
- * void UMAAL(xxh_u32 *RdLo, xxh_u32 *RdHi, xxh_u32 Rn, xxh_u32 Rm)
- * {
- * xxh_u64 product = (xxh_u64)*RdLo * (xxh_u64)*RdHi + Rn + Rm;
- * *RdLo = (xxh_u32)(product & 0xFFFFFFFF);
- * *RdHi = (xxh_u32)(product >> 32);
- * }
- *
- * This instruction was designed for efficient long multiplication, and
- * allows this to be calculated in only 4 instructions at speeds
- * comparable to some 64-bit ALUs.
- *
- * 3. It isn't terrible on other platforms. Usually this will be a couple
- * of 32-bit ADD/ADCs.
- */
-
- /* First calculate all of the cross products. */
- xxh_u64 const lo_lo = XXH_mult32to64(lhs & 0xFFFFFFFF, rhs & 0xFFFFFFFF);
- xxh_u64 const hi_lo = XXH_mult32to64(lhs >> 32, rhs & 0xFFFFFFFF);
- xxh_u64 const lo_hi = XXH_mult32to64(lhs & 0xFFFFFFFF, rhs >> 32);
- xxh_u64 const hi_hi = XXH_mult32to64(lhs >> 32, rhs >> 32);
-
- /* Now add the products together. These will never overflow. */
- xxh_u64 const cross = (lo_lo >> 32) + (hi_lo & 0xFFFFFFFF) + lo_hi;
- xxh_u64 const upper = (hi_lo >> 32) + (cross >> 32) + hi_hi;
- xxh_u64 const lower = (cross << 32) | (lo_lo & 0xFFFFFFFF);
-
- XXH128_hash_t r128 = { lower, upper };
- return r128;
-#endif
-}
-
-/*
- * Does a 64-bit to 128-bit multiply, then XOR folds it.
- *
- * The reason for the separate function is to prevent passing too many structs
- * around by value. This will hopefully inline the multiply, but we don't force it.
- */
-static xxh_u64
-XXH3_mul128_fold64(xxh_u64 lhs, xxh_u64 rhs)
-{
- XXH128_hash_t product = XXH_mult64to128(lhs, rhs);
- return product.low64 ^ product.high64;
-}
-
-/* Seems to produce slightly better code on GCC for some reason. */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH_xorshift64(xxh_u64 v64, int shift)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(0 <= shift && shift < 64);
- return v64 ^ (v64 >> shift);
-}
-
-/*
- * We don't need to (or want to) mix as much as XXH64.
- *
- * Short hashes are more evenly distributed, so it isn't necessary.
- */
-static XXH64_hash_t XXH3_avalanche(xxh_u64 h64)
-{
- h64 = XXH_xorshift64(h64, 37);
- h64 *= 0x165667919E3779F9ULL;
- h64 = XXH_xorshift64(h64, 32);
- return h64;
-}
-
-
-/* ==========================================
- * Short keys
- * ==========================================
- * One of the shortcomings of XXH32 and XXH64 was that their performance was
- * sub-optimal on short lengths. It used an iterative algorithm which strongly
- * favored lengths that were a multiple of 4 or 8.
- *
- * Instead of iterating over individual inputs, we use a set of single shot
- * functions which piece together a range of lengths and operate in constant time.
- *
- * Additionally, the number of multiplies has been significantly reduced. This
- * reduces latency, especially when emulating 64-bit multiplies on 32-bit.
- *
- * Depending on the platform, this may or may not be faster than XXH32, but it
- * is almost guaranteed to be faster than XXH64.
- */
-
-/*
- * At very short lengths, there isn't enough input to fully hide secrets, or use
- * the entire secret.
- *
- * There is also only a limited amount of mixing we can do before significantly
- * impacting performance.
- *
- * Therefore, we use different sections of the secret and always mix two secret
- * samples with an XOR. This should have no effect on performance on the
- * seedless or withSeed variants because everything _should_ be constant folded
- * by modern compilers.
- *
- * The XOR mixing hides individual parts of the secret and increases entropy.
- *
- * This adds an extra layer of strength for custom secrets.
- */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_len_1to3_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL);
- XXH_ASSERT(1 <= len && len <= 3);
- XXH_ASSERT(secret != NULL);
- /*
- * len = 1: combined = { input[0], 0x01, input[0], input[0] }
- * len = 2: combined = { input[1], 0x02, input[0], input[1] }
- * len = 3: combined = { input[2], 0x03, input[0], input[1] }
- */
- { xxh_u8 const c1 = input[0];
- xxh_u8 const c2 = input[len >> 1];
- xxh_u8 const c3 = input[len - 1];
- xxh_u32 const combined = ((xxh_u32)c1<<16) | (((xxh_u32)c2) << 24) | (((xxh_u32)c3) << 0) | (((xxh_u32)len) << 8);
- xxh_u64 const bitflip = (XXH_readLE32(secret) ^ XXH_readLE32(secret+4)) + seed;
- xxh_u64 const keyed = (xxh_u64)combined ^ bitflip;
- xxh_u64 const mixed = keyed * PRIME64_1;
- return XXH3_avalanche(mixed);
- }
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_len_4to8_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL);
- XXH_ASSERT(secret != NULL);
- XXH_ASSERT(4 <= len && len < 8);
- seed ^= (xxh_u64)XXH_swap32((xxh_u32)seed) << 32;
- { xxh_u32 const input1 = XXH_readLE32(input);
- xxh_u32 const input2 = XXH_readLE32(input + len - 4);
- xxh_u64 const bitflip = (XXH_readLE64(secret+8) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+16)) - seed;
- xxh_u64 const input64 = input2 + (((xxh_u64)input1) << 32);
- xxh_u64 x = input64 ^ bitflip;
- /* this mix is inspired by Pelle Evensen's rrmxmx */
- x ^= XXH_rotl64(x, 49) ^ XXH_rotl64(x, 24);
- x *= 0x9FB21C651E98DF25ULL;
- x ^= (x >> 35) + len ;
- x *= 0x9FB21C651E98DF25ULL;
- return XXH_xorshift64(x, 28);
- }
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_len_9to16_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL);
- XXH_ASSERT(secret != NULL);
- XXH_ASSERT(8 <= len && len <= 16);
- { xxh_u64 const bitflip1 = (XXH_readLE64(secret+24) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+32)) + seed;
- xxh_u64 const bitflip2 = (XXH_readLE64(secret+40) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+48)) - seed;
- xxh_u64 const input_lo = XXH_readLE64(input) ^ bitflip1;
- xxh_u64 const input_hi = XXH_readLE64(input + len - 8) ^ bitflip2;
- xxh_u64 const acc = len
- + XXH_swap64(input_lo) + input_hi
- + XXH3_mul128_fold64(input_lo, input_hi);
- return XXH3_avalanche(acc);
- }
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_len_0to16_64b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(len <= 16);
- { if (XXH_likely(len > 8)) return XXH3_len_9to16_64b(input, len, secret, seed);
- if (XXH_likely(len >= 4)) return XXH3_len_4to8_64b(input, len, secret, seed);
- if (len) return XXH3_len_1to3_64b(input, len, secret, seed);
- return XXH3_avalanche((PRIME64_1 + seed) ^ (XXH_readLE64(secret+56) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+64)));
- }
-}
-
-/*
- * DISCLAIMER: There are known *seed-dependent* multicollisions here due to
- * multiplication by zero, affecting hashes of lengths 17 to 240.
- *
- * However, they are very unlikely.
- *
- * Keep this in mind when using the unseeded XXH3_64bits() variant: As with all
- * unseeded non-cryptographic hashes, it does not attempt to defend itself
- * against specially crafted inputs, only random inputs.
- *
- * Compared to classic UMAC where a 1 in 2^31 chance of 4 consecutive bytes
- * cancelling out the secret is taken an arbitrary number of times (addressed
- * in XXH3_accumulate_512), this collision is very unlikely with random inputs
- * and/or proper seeding:
- *
- * This only has a 1 in 2^63 chance of 8 consecutive bytes cancelling out, in a
- * function that is only called up to 16 times per hash with up to 240 bytes of
- * input.
- *
- * This is not too bad for a non-cryptographic hash function, especially with
- * only 64 bit outputs.
- *
- * The 128-bit variant (which trades some speed for strength) is NOT affected
- * by this, although it is always a good idea to use a proper seed if you care
- * about strength.
- */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH3_mix16B(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, xxh_u64 seed64)
-{
-#if defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) /* GCC, not Clang */ \
- && defined(__i386__) && defined(__SSE2__) /* x86 + SSE2 */ \
- && !defined(XXH_ENABLE_AUTOVECTORIZE) /* Define to disable like XXH32 hack */
- /*
- * UGLY HACK:
- * GCC for x86 tends to autovectorize the 128-bit multiply, resulting in
- * slower code.
- *
- * By forcing seed64 into a register, we disrupt the cost model and
- * cause it to scalarize. See `XXH32_round()`
- *
- * FIXME: Clang's output is still _much_ faster -- On an AMD Ryzen 3600,
- * XXH3_64bits @ len=240 runs at 4.6 GB/s with Clang 9, but 3.3 GB/s on
- * GCC 9.2, despite both emitting scalar code.
- *
- * GCC generates much better scalar code than Clang for the rest of XXH3,
- * which is why finding a more optimal codepath is an interest.
- */
- __asm__ ("" : "+r" (seed64));
-#endif
- { xxh_u64 const input_lo = XXH_readLE64(input);
- xxh_u64 const input_hi = XXH_readLE64(input+8);
- return XXH3_mul128_fold64(
- input_lo ^ (XXH_readLE64(secret) + seed64),
- input_hi ^ (XXH_readLE64(secret+8) - seed64)
- );
- }
-}
-
-/* For mid range keys, XXH3 uses a Mum-hash variant. */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_len_17to128_64b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize,
- XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN); (void)secretSize;
- XXH_ASSERT(16 < len && len <= 128);
-
- { xxh_u64 acc = len * PRIME64_1;
- if (len > 32) {
- if (len > 64) {
- if (len > 96) {
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+48, secret+96, seed);
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+len-64, secret+112, seed);
- }
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+32, secret+64, seed);
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+len-48, secret+80, seed);
- }
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+16, secret+32, seed);
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+len-32, secret+48, seed);
- }
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+0, secret+0, seed);
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+len-16, secret+16, seed);
-
- return XXH3_avalanche(acc);
- }
-}
-
-#define XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX 240
-
-XXH_NO_INLINE XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_len_129to240_64b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize,
- XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN); (void)secretSize;
- XXH_ASSERT(128 < len && len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX);
-
- #define XXH3_MIDSIZE_STARTOFFSET 3
- #define XXH3_MIDSIZE_LASTOFFSET 17
-
- { xxh_u64 acc = len * PRIME64_1;
- int const nbRounds = (int)len / 16;
- int i;
- for (i=0; i<8; i++) {
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+(16*i), secret+(16*i), seed);
- }
- acc = XXH3_avalanche(acc);
- XXH_ASSERT(nbRounds >= 8);
-#if defined(__clang__) /* Clang */ \
- && (defined(__ARM_NEON) || defined(__ARM_NEON__)) /* NEON */ \
- && !defined(XXH_ENABLE_AUTOVECTORIZE) /* Define to disable */
- /*
- * UGLY HACK:
- * Clang for ARMv7-A tries to vectorize this loop, similar to GCC x86.
- * In everywhere else, it uses scalar code.
- *
- * For 64->128-bit multiplies, even if the NEON was 100% optimal, it
- * would still be slower than UMAAL (see XXH_mult64to128).
- *
- * Unfortunately, Clang doesn't handle the long multiplies properly and
- * converts them to the nonexistent "vmulq_u64" intrinsic, which is then
- * scalarized into an ugly mess of VMOV.32 instructions.
- *
- * This mess is difficult to avoid without turning autovectorization
- * off completely, but they are usually relatively minor and/or not
- * worth it to fix.
- *
- * This loop is the easiest to fix, as unlike XXH32, this pragma
- * _actually works_ because it is a loop vectorization instead of an
- * SLP vectorization.
- */
- #pragma clang loop vectorize(disable)
-#endif
- for (i=8 ; i < nbRounds; i++) {
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input+(16*i), secret+(16*(i-8)) + XXH3_MIDSIZE_STARTOFFSET, seed);
- }
- /* last bytes */
- acc += XXH3_mix16B(input + len - 16, secret + XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN - XXH3_MIDSIZE_LASTOFFSET, seed);
- return XXH3_avalanche(acc);
- }
-}
-
-
-/* === Long Keys === */
-
-#define STRIPE_LEN 64
-#define XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE 8 /* nb of secret bytes consumed at each accumulation */
-#define ACC_NB (STRIPE_LEN / sizeof(xxh_u64))
-
-typedef enum { XXH3_acc_64bits, XXH3_acc_128bits } XXH3_accWidth_e;
-
-/*
- * XXH3_accumulate_512 is the tightest loop for long inputs, and it is the most optimized.
- *
- * It is a hardened version of UMAC, based off of FARSH's implementation.
- *
- * This was chosen because it adapts quite well to 32-bit, 64-bit, and SIMD
- * implementations, and it is ridiculously fast.
- *
- * We harden it by mixing the original input to the accumulators as well as the product.
- *
- * This means that in the (relatively likely) case of a multiply by zero, the
- * original input is preserved.
- *
- * On 128-bit inputs, we swap 64-bit pairs when we add the input to improve
- * cross-pollination, as otherwise the upper and lower halves would be
- * essentially independent.
- *
- * This doesn't matter on 64-bit hashes since they all get merged together in
- * the end, so we skip the extra step.
- *
- * Both XXH3_64bits and XXH3_128bits use this subroutine.
- */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE void
-XXH3_accumulate_512( void* XXH_RESTRICT acc,
- const void* XXH_RESTRICT input,
- const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret,
- XXH3_accWidth_e accWidth)
-{
-#if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2)
-
- XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 31) == 0);
- { XXH_ALIGN(32) __m256i* const xacc = (__m256i *) acc;
- /* Unaligned. This is mainly for pointer arithmetic, and because
- * _mm256_loadu_si256 requires a const __m256i * pointer for some reason. */
- const __m256i* const xinput = (const __m256i *) input;
- /* Unaligned. This is mainly for pointer arithmetic, and because
- * _mm256_loadu_si256 requires a const __m256i * pointer for some reason. */
- const __m256i* const xsecret = (const __m256i *) secret;
-
- size_t i;
- for (i=0; i < STRIPE_LEN/sizeof(__m256i); i++) {
- /* data_vec = xinput[i]; */
- __m256i const data_vec = _mm256_loadu_si256 (xinput+i);
- /* key_vec = xsecret[i]; */
- __m256i const key_vec = _mm256_loadu_si256 (xsecret+i);
- /* data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec; */
- __m256i const data_key = _mm256_xor_si256 (data_vec, key_vec);
- /* data_key_lo = data_key >> 32; */
- __m256i const data_key_lo = _mm256_shuffle_epi32 (data_key, _MM_SHUFFLE(0, 3, 0, 1));
- /* product = (data_key & 0xffffffff) * (data_key_lo & 0xffffffff); */
- __m256i const product = _mm256_mul_epu32 (data_key, data_key_lo);
- if (accWidth == XXH3_acc_128bits) {
- /* xacc[i] += swap(data_vec); */
- __m256i const data_swap = _mm256_shuffle_epi32(data_vec, _MM_SHUFFLE(1, 0, 3, 2));
- __m256i const sum = _mm256_add_epi64(xacc[i], data_swap);
- /* xacc[i] += product; */
- xacc[i] = _mm256_add_epi64(product, sum);
- } else { /* XXH3_acc_64bits */
- /* xacc[i] += data_vec; */
- __m256i const sum = _mm256_add_epi64(xacc[i], data_vec);
- /* xacc[i] += product; */
- xacc[i] = _mm256_add_epi64(product, sum);
- }
- } }
-
-#elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SSE2)
-
- /* SSE2 is just a half-scale version of the AVX2 version. */
- XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 15) == 0);
- { XXH_ALIGN(16) __m128i* const xacc = (__m128i *) acc;
- /* Unaligned. This is mainly for pointer arithmetic, and because
- * _mm_loadu_si128 requires a const __m128i * pointer for some reason. */
- const __m128i* const xinput = (const __m128i *) input;
- /* Unaligned. This is mainly for pointer arithmetic, and because
- * _mm_loadu_si128 requires a const __m128i * pointer for some reason. */
- const __m128i* const xsecret = (const __m128i *) secret;
-
- size_t i;
- for (i=0; i < STRIPE_LEN/sizeof(__m128i); i++) {
- /* data_vec = xinput[i]; */
- __m128i const data_vec = _mm_loadu_si128 (xinput+i);
- /* key_vec = xsecret[i]; */
- __m128i const key_vec = _mm_loadu_si128 (xsecret+i);
- /* data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec; */
- __m128i const data_key = _mm_xor_si128 (data_vec, key_vec);
- /* data_key_lo = data_key >> 32; */
- __m128i const data_key_lo = _mm_shuffle_epi32 (data_key, _MM_SHUFFLE(0, 3, 0, 1));
- /* product = (data_key & 0xffffffff) * (data_key_lo & 0xffffffff); */
- __m128i const product = _mm_mul_epu32 (data_key, data_key_lo);
- if (accWidth == XXH3_acc_128bits) {
- /* xacc[i] += swap(data_vec); */
- __m128i const data_swap = _mm_shuffle_epi32(data_vec, _MM_SHUFFLE(1,0,3,2));
- __m128i const sum = _mm_add_epi64(xacc[i], data_swap);
- /* xacc[i] += product; */
- xacc[i] = _mm_add_epi64(product, sum);
- } else { /* XXH3_acc_64bits */
- /* xacc[i] += data_vec; */
- __m128i const sum = _mm_add_epi64(xacc[i], data_vec);
- /* xacc[i] += product; */
- xacc[i] = _mm_add_epi64(product, sum);
- }
- } }
-
-#elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_NEON)
-
- XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 15) == 0);
- {
- XXH_ALIGN(16) uint64x2_t* const xacc = (uint64x2_t *) acc;
- /* We don't use a uint32x4_t pointer because it causes bus errors on ARMv7. */
- uint8_t const* const xinput = (const uint8_t *) input;
- uint8_t const* const xsecret = (const uint8_t *) secret;
-
- size_t i;
- for (i=0; i < STRIPE_LEN / sizeof(uint64x2_t); i++) {
- /* data_vec = xinput[i]; */
- uint8x16_t data_vec = vld1q_u8(xinput + (i * 16));
- /* key_vec = xsecret[i]; */
- uint8x16_t key_vec = vld1q_u8(xsecret + (i * 16));
- /* data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec; */
- uint64x2_t data_key = vreinterpretq_u64_u8(veorq_u8(data_vec, key_vec));
- uint32x2_t data_key_lo, data_key_hi;
- if (accWidth == XXH3_acc_64bits) {
- /* xacc[i] += data_vec; */
- xacc[i] = vaddq_u64 (xacc[i], vreinterpretq_u64_u8(data_vec));
- } else { /* XXH3_acc_128bits */
- /* xacc[i] += swap(data_vec); */
- uint64x2_t const data64 = vreinterpretq_u64_u8(data_vec);
- uint64x2_t const swapped = vextq_u64(data64, data64, 1);
- xacc[i] = vaddq_u64 (xacc[i], swapped);
- }
- /* data_key_lo = (uint32x2_t) (data_key & 0xFFFFFFFF);
- * data_key_hi = (uint32x2_t) (data_key >> 32);
- * data_key = UNDEFINED; */
- XXH_SPLIT_IN_PLACE(data_key, data_key_lo, data_key_hi);
- /* xacc[i] += (uint64x2_t) data_key_lo * (uint64x2_t) data_key_hi; */
- xacc[i] = vmlal_u32 (xacc[i], data_key_lo, data_key_hi);
-
- }
- }
-
-#elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_VSX)
- xxh_u64x2* const xacc = (xxh_u64x2*) acc; /* presumed aligned */
- xxh_u64x2 const* const xinput = (xxh_u64x2 const*) input; /* no alignment restriction */
- xxh_u64x2 const* const xsecret = (xxh_u64x2 const*) secret; /* no alignment restriction */
- xxh_u64x2 const v32 = { 32, 32 };
- size_t i;
- for (i = 0; i < STRIPE_LEN / sizeof(xxh_u64x2); i++) {
- /* data_vec = xinput[i]; */
- xxh_u64x2 const data_vec = XXH_vec_loadu(xinput + i);
- /* key_vec = xsecret[i]; */
- xxh_u64x2 const key_vec = XXH_vec_loadu(xsecret + i);
- xxh_u64x2 const data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec;
- /* shuffled = (data_key << 32) | (data_key >> 32); */
- xxh_u32x4 const shuffled = (xxh_u32x4)vec_rl(data_key, v32);
- /* product = ((xxh_u64x2)data_key & 0xFFFFFFFF) * ((xxh_u64x2)shuffled & 0xFFFFFFFF); */
- xxh_u64x2 const product = XXH_vec_mulo((xxh_u32x4)data_key, shuffled);
- xacc[i] += product;
-
- if (accWidth == XXH3_acc_64bits) {
- xacc[i] += data_vec;
- } else { /* XXH3_acc_128bits */
- /* swap high and low halves */
-#ifdef __s390x__
- xxh_u64x2 const data_swapped = vec_permi(data_vec, data_vec, 2);
-#else
- xxh_u64x2 const data_swapped = vec_xxpermdi(data_vec, data_vec, 2);
-#endif
- xacc[i] += data_swapped;
- }
- }
-
-#else /* scalar variant of Accumulator - universal */
-
- XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) xxh_u64* const xacc = (xxh_u64*) acc; /* presumed aligned */
- const xxh_u8* const xinput = (const xxh_u8*) input; /* no alignment restriction */
- const xxh_u8* const xsecret = (const xxh_u8*) secret; /* no alignment restriction */
- size_t i;
- XXH_ASSERT(((size_t)acc & (XXH_ACC_ALIGN-1)) == 0);
- for (i=0; i < ACC_NB; i++) {
- xxh_u64 const data_val = XXH_readLE64(xinput + 8*i);
- xxh_u64 const data_key = data_val ^ XXH_readLE64(xsecret + i*8);
-
- if (accWidth == XXH3_acc_64bits) {
- xacc[i] += data_val;
- } else {
- xacc[i ^ 1] += data_val; /* swap adjacent lanes */
- }
- xacc[i] += XXH_mult32to64(data_key & 0xFFFFFFFF, data_key >> 32);
- }
-#endif
-}
-
-/*
- * XXH3_scrambleAcc: Scrambles the accumulators to improve mixing.
- *
- * Multiplication isn't perfect, as explained by Google in HighwayHash:
- *
- * // Multiplication mixes/scrambles bytes 0-7 of the 64-bit result to
- * // varying degrees. In descending order of goodness, bytes
- * // 3 4 2 5 1 6 0 7 have quality 228 224 164 160 100 96 36 32.
- * // As expected, the upper and lower bytes are much worse.
- *
- * Source: https://github.com/google/highwayhash/blob/0aaf66b/highwayhash/hh_avx2.h#L291
- *
- * Since our algorithm uses a pseudorandom secret to add some variance into the
- * mix, we don't need to (or want to) mix as often or as much as HighwayHash does.
- *
- * This isn't as tight as XXH3_accumulate, but still written in SIMD to avoid
- * extraction.
- *
- * Both XXH3_64bits and XXH3_128bits use this subroutine.
- */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE void
-XXH3_scrambleAcc(void* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const void* XXH_RESTRICT secret)
-{
-#if (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2)
-
- XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 31) == 0);
- { XXH_ALIGN(32) __m256i* const xacc = (__m256i*) acc;
- /* Unaligned. This is mainly for pointer arithmetic, and because
- * _mm256_loadu_si256 requires a const __m256i * pointer for some reason. */
- const __m256i* const xsecret = (const __m256i *) secret;
- const __m256i prime32 = _mm256_set1_epi32((int)PRIME32_1);
-
- size_t i;
- for (i=0; i < STRIPE_LEN/sizeof(__m256i); i++) {
- /* xacc[i] ^= (xacc[i] >> 47) */
- __m256i const acc_vec = xacc[i];
- __m256i const shifted = _mm256_srli_epi64 (acc_vec, 47);
- __m256i const data_vec = _mm256_xor_si256 (acc_vec, shifted);
- /* xacc[i] ^= xsecret; */
- __m256i const key_vec = _mm256_loadu_si256 (xsecret+i);
- __m256i const data_key = _mm256_xor_si256 (data_vec, key_vec);
-
- /* xacc[i] *= PRIME32_1; */
- __m256i const data_key_hi = _mm256_shuffle_epi32 (data_key, _MM_SHUFFLE(0, 3, 0, 1));
- __m256i const prod_lo = _mm256_mul_epu32 (data_key, prime32);
- __m256i const prod_hi = _mm256_mul_epu32 (data_key_hi, prime32);
- xacc[i] = _mm256_add_epi64(prod_lo, _mm256_slli_epi64(prod_hi, 32));
- }
- }
-
-#elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_SSE2)
-
- XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 15) == 0);
- { XXH_ALIGN(16) __m128i* const xacc = (__m128i*) acc;
- /* Unaligned. This is mainly for pointer arithmetic, and because
- * _mm_loadu_si128 requires a const __m128i * pointer for some reason. */
- const __m128i* const xsecret = (const __m128i *) secret;
- const __m128i prime32 = _mm_set1_epi32((int)PRIME32_1);
-
- size_t i;
- for (i=0; i < STRIPE_LEN/sizeof(__m128i); i++) {
- /* xacc[i] ^= (xacc[i] >> 47) */
- __m128i const acc_vec = xacc[i];
- __m128i const shifted = _mm_srli_epi64 (acc_vec, 47);
- __m128i const data_vec = _mm_xor_si128 (acc_vec, shifted);
- /* xacc[i] ^= xsecret[i]; */
- __m128i const key_vec = _mm_loadu_si128 (xsecret+i);
- __m128i const data_key = _mm_xor_si128 (data_vec, key_vec);
-
- /* xacc[i] *= PRIME32_1; */
- __m128i const data_key_hi = _mm_shuffle_epi32 (data_key, _MM_SHUFFLE(0, 3, 0, 1));
- __m128i const prod_lo = _mm_mul_epu32 (data_key, prime32);
- __m128i const prod_hi = _mm_mul_epu32 (data_key_hi, prime32);
- xacc[i] = _mm_add_epi64(prod_lo, _mm_slli_epi64(prod_hi, 32));
- }
- }
-
-#elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_NEON)
-
- XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 15) == 0);
-
- { uint64x2_t* xacc = (uint64x2_t*) acc;
- uint8_t const* xsecret = (uint8_t const*) secret;
- uint32x2_t prime = vdup_n_u32 (PRIME32_1);
-
- size_t i;
- for (i=0; i < STRIPE_LEN/sizeof(uint64x2_t); i++) {
- /* xacc[i] ^= (xacc[i] >> 47); */
- uint64x2_t acc_vec = xacc[i];
- uint64x2_t shifted = vshrq_n_u64 (acc_vec, 47);
- uint64x2_t data_vec = veorq_u64 (acc_vec, shifted);
-
- /* xacc[i] ^= xsecret[i]; */
- uint8x16_t key_vec = vld1q_u8(xsecret + (i * 16));
- uint64x2_t data_key = veorq_u64(data_vec, vreinterpretq_u64_u8(key_vec));
-
- /* xacc[i] *= PRIME32_1 */
- uint32x2_t data_key_lo, data_key_hi;
- /* data_key_lo = (uint32x2_t) (xacc[i] & 0xFFFFFFFF);
- * data_key_hi = (uint32x2_t) (xacc[i] >> 32);
- * xacc[i] = UNDEFINED; */
- XXH_SPLIT_IN_PLACE(data_key, data_key_lo, data_key_hi);
- { /*
- * prod_hi = (data_key >> 32) * PRIME32_1;
- *
- * Avoid vmul_u32 + vshll_n_u32 since Clang 6 and 7 will
- * incorrectly "optimize" this:
- * tmp = vmul_u32(vmovn_u64(a), vmovn_u64(b));
- * shifted = vshll_n_u32(tmp, 32);
- * to this:
- * tmp = "vmulq_u64"(a, b); // no such thing!
- * shifted = vshlq_n_u64(tmp, 32);
- *
- * However, unlike SSE, Clang lacks a 64-bit multiply routine
- * for NEON, and it scalarizes two 64-bit multiplies instead.
- *
- * vmull_u32 has the same timing as vmul_u32, and it avoids
- * this bug completely.
- * See https://bugs.llvm.org/show_bug.cgi?id=39967
- */
- uint64x2_t prod_hi = vmull_u32 (data_key_hi, prime);
- /* xacc[i] = prod_hi << 32; */
- xacc[i] = vshlq_n_u64(prod_hi, 32);
- /* xacc[i] += (prod_hi & 0xFFFFFFFF) * PRIME32_1; */
- xacc[i] = vmlal_u32(xacc[i], data_key_lo, prime);
- }
- } }
-
-#elif (XXH_VECTOR == XXH_VSX)
-
- XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & 15) == 0);
-
- { xxh_u64x2* const xacc = (xxh_u64x2*) acc;
- const xxh_u64x2* const xsecret = (const xxh_u64x2*) secret;
- /* constants */
- xxh_u64x2 const v32 = { 32, 32 };
- xxh_u64x2 const v47 = { 47, 47 };
- xxh_u32x4 const prime = { PRIME32_1, PRIME32_1, PRIME32_1, PRIME32_1 };
- size_t i;
- for (i = 0; i < STRIPE_LEN / sizeof(xxh_u64x2); i++) {
- /* xacc[i] ^= (xacc[i] >> 47); */
- xxh_u64x2 const acc_vec = xacc[i];
- xxh_u64x2 const data_vec = acc_vec ^ (acc_vec >> v47);
-
- /* xacc[i] ^= xsecret[i]; */
- xxh_u64x2 const key_vec = XXH_vec_loadu(xsecret + i);
- xxh_u64x2 const data_key = data_vec ^ key_vec;
-
- /* xacc[i] *= PRIME32_1 */
- /* prod_lo = ((xxh_u64x2)data_key & 0xFFFFFFFF) * ((xxh_u64x2)prime & 0xFFFFFFFF); */
- xxh_u64x2 const prod_even = XXH_vec_mule((xxh_u32x4)data_key, prime);
- /* prod_hi = ((xxh_u64x2)data_key >> 32) * ((xxh_u64x2)prime >> 32); */
- xxh_u64x2 const prod_odd = XXH_vec_mulo((xxh_u32x4)data_key, prime);
- xacc[i] = prod_odd + (prod_even << v32);
- } }
-
-#else /* scalar variant of Scrambler - universal */
-
- XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) xxh_u64* const xacc = (xxh_u64*) acc; /* presumed aligned */
- const xxh_u8* const xsecret = (const xxh_u8*) secret; /* no alignment restriction */
- size_t i;
- XXH_ASSERT((((size_t)acc) & (XXH_ACC_ALIGN-1)) == 0);
- for (i=0; i < ACC_NB; i++) {
- xxh_u64 const key64 = XXH_readLE64(xsecret + 8*i);
- xxh_u64 acc64 = xacc[i];
- acc64 = XXH_xorshift64(acc64, 47);
- acc64 ^= key64;
- acc64 *= PRIME32_1;
- xacc[i] = acc64;
- }
-
-#endif
-}
-
-#define XXH_PREFETCH_DIST 384
-
-/*
- * XXH3_accumulate()
- * Loops over XXH3_accumulate_512().
- * Assumption: nbStripes will not overflow the secret size
- */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE void
-XXH3_accumulate( xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret,
- size_t nbStripes,
- XXH3_accWidth_e accWidth)
-{
- size_t n;
- for (n = 0; n < nbStripes; n++ ) {
- const xxh_u8* const in = input + n*STRIPE_LEN;
- XXH_PREFETCH(in + XXH_PREFETCH_DIST);
- XXH3_accumulate_512(acc,
- in,
- secret + n*XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE,
- accWidth);
- }
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE void
-XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop( xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize,
- XXH3_accWidth_e accWidth)
-{
- size_t const nb_rounds = (secretSize - STRIPE_LEN) / XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE;
- size_t const block_len = STRIPE_LEN * nb_rounds;
- size_t const nb_blocks = len / block_len;
-
- size_t n;
-
- XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN);
-
- for (n = 0; n < nb_blocks; n++) {
- XXH3_accumulate(acc, input + n*block_len, secret, nb_rounds, accWidth);
- XXH3_scrambleAcc(acc, secret + secretSize - STRIPE_LEN);
- }
-
- /* last partial block */
- XXH_ASSERT(len > STRIPE_LEN);
- { size_t const nbStripes = (len - (block_len * nb_blocks)) / STRIPE_LEN;
- XXH_ASSERT(nbStripes <= (secretSize / XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE));
- XXH3_accumulate(acc, input + nb_blocks*block_len, secret, nbStripes, accWidth);
-
- /* last stripe */
- if (len & (STRIPE_LEN - 1)) {
- const xxh_u8* const p = input + len - STRIPE_LEN;
- /* Do not align on 8, so that the secret is different from the scrambler */
-#define XXH_SECRET_LASTACC_START 7
- XXH3_accumulate_512(acc, p, secret + secretSize - STRIPE_LEN - XXH_SECRET_LASTACC_START, accWidth);
- } }
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64
-XXH3_mix2Accs(const xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret)
-{
- return XXH3_mul128_fold64(
- acc[0] ^ XXH_readLE64(secret),
- acc[1] ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+8) );
-}
-
-static XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_mergeAccs(const xxh_u64* XXH_RESTRICT acc, const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, xxh_u64 start)
-{
- xxh_u64 result64 = start;
-
- result64 += XXH3_mix2Accs(acc+0, secret + 0);
- result64 += XXH3_mix2Accs(acc+2, secret + 16);
- result64 += XXH3_mix2Accs(acc+4, secret + 32);
- result64 += XXH3_mix2Accs(acc+6, secret + 48);
-
- return XXH3_avalanche(result64);
-}
-
-#define XXH3_INIT_ACC { PRIME32_3, PRIME64_1, PRIME64_2, PRIME64_3, \
- PRIME64_4, PRIME32_2, PRIME64_5, PRIME32_1 };
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_hashLong_internal(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize)
-{
- XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) xxh_u64 acc[ACC_NB] = XXH3_INIT_ACC;
-
- XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop(acc, input, len, secret, secretSize, XXH3_acc_64bits);
-
- /* converge into final hash */
- XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(acc) == 64);
- /* do not align on 8, so that the secret is different from the accumulator */
-#define XXH_SECRET_MERGEACCS_START 11
- XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= sizeof(acc) + XXH_SECRET_MERGEACCS_START);
- return XXH3_mergeAccs(acc, secret + XXH_SECRET_MERGEACCS_START, (xxh_u64)len * PRIME64_1);
-}
-
-/*
- * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. Not sure
- * why (uop cache maybe?), but the difference is large and easily measurable.
- */
-XXH_NO_INLINE XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_hashLong_64b_defaultSecret(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len)
-{
- return XXH3_hashLong_internal(input, len, kSecret, sizeof(kSecret));
-}
-
-/*
- * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. Not sure
- * why (uop cache maybe?), but the difference is large and easily measurable.
- */
-XXH_NO_INLINE XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSecret(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize)
-{
- return XXH3_hashLong_internal(input, len, secret, secretSize);
-}
-
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH_writeLE64(void* dst, xxh_u64 v64)
-{
- if (!XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN) v64 = XXH_swap64(v64);
- memcpy(dst, &v64, sizeof(v64));
-}
-
-/* XXH3_initCustomSecret() :
- * destination `customSecret` is presumed allocated and same size as `kSecret`.
- */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE void XXH3_initCustomSecret(xxh_u8* customSecret, xxh_u64 seed64)
-{
- int const nbRounds = XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE / 16;
- int i;
-
- XXH_STATIC_ASSERT((XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE & 15) == 0);
-
- for (i=0; i < nbRounds; i++) {
- XXH_writeLE64(customSecret + 16*i, XXH_readLE64(kSecret + 16*i) + seed64);
- XXH_writeLE64(customSecret + 16*i + 8, XXH_readLE64(kSecret + 16*i + 8) - seed64);
- }
-}
-
-
-/*
- * XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSeed():
- * Generate a custom key based on alteration of default kSecret with the seed,
- * and then use this key for long mode hashing.
- *
- * This operation is decently fast but nonetheless costs a little bit of time.
- * Try to avoid it whenever possible (typically when seed==0).
- *
- * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. Not sure
- * why (uop cache maybe?), but the difference is large and easily measurable.
- */
-XXH_NO_INLINE XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSeed(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ALIGN(8) xxh_u8 secret[XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE];
- if (seed==0) return XXH3_hashLong_64b_defaultSecret(input, len);
- XXH3_initCustomSecret(secret, seed);
- return XXH3_hashLong_internal(input, len, secret, sizeof(secret));
-}
-
-/* === Public entry point === */
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits(const void* input, size_t len)
-{
- if (len <= 16) return XXH3_len_0to16_64b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, 0);
- if (len <= 128) return XXH3_len_17to128_64b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, sizeof(kSecret), 0);
- if (len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) return XXH3_len_129to240_64b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, sizeof(kSecret), 0);
- return XXH3_hashLong_64b_defaultSecret((const xxh_u8*)input, len);
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_64bits_withSecret(const void* input, size_t len, const void* secret, size_t secretSize)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN);
- /*
- * If an action is to be taken if `secret` conditions are not respected,
- * it should be done here.
- * For now, it's a contract pre-condition.
- * Adding a check and a branch here would cost performance at every hash.
- */
- if (len <= 16) return XXH3_len_0to16_64b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, 0);
- if (len <= 128) return XXH3_len_17to128_64b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize, 0);
- if (len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) return XXH3_len_129to240_64b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize, 0);
- return XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSecret((const xxh_u8*)input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize);
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t
-XXH3_64bits_withSeed(const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- if (len <= 16) return XXH3_len_0to16_64b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, seed);
- if (len <= 128) return XXH3_len_17to128_64b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, sizeof(kSecret), seed);
- if (len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) return XXH3_len_129to240_64b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, sizeof(kSecret), seed);
- return XXH3_hashLong_64b_withSeed((const xxh_u8*)input, len, seed);
-}
-
-/* === XXH3 streaming === */
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH3_state_t* XXH3_createState(void)
-{
- return (XXH3_state_t*)XXH_malloc(sizeof(XXH3_state_t));
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_freeState(XXH3_state_t* statePtr)
-{
- XXH_free(statePtr);
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void
-XXH3_copyState(XXH3_state_t* dst_state, const XXH3_state_t* src_state)
-{
- memcpy(dst_state, src_state, sizeof(*dst_state));
-}
-
-static void
-XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(XXH3_state_t* statePtr,
- XXH64_hash_t seed,
- const xxh_u8* secret, size_t secretSize)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(statePtr != NULL);
- memset(statePtr, 0, sizeof(*statePtr));
- statePtr->acc[0] = PRIME32_3;
- statePtr->acc[1] = PRIME64_1;
- statePtr->acc[2] = PRIME64_2;
- statePtr->acc[3] = PRIME64_3;
- statePtr->acc[4] = PRIME64_4;
- statePtr->acc[5] = PRIME32_2;
- statePtr->acc[6] = PRIME64_5;
- statePtr->acc[7] = PRIME32_1;
- statePtr->seed = seed;
- XXH_ASSERT(secret != NULL);
- statePtr->secret = secret;
- XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN);
- statePtr->secretLimit = (XXH32_hash_t)(secretSize - STRIPE_LEN);
- statePtr->nbStripesPerBlock = statePtr->secretLimit / XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode
-XXH3_64bits_reset(XXH3_state_t* statePtr)
-{
- if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR;
- XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(statePtr, 0, kSecret, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE);
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode
-XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* secret, size_t secretSize)
-{
- if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR;
- XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(statePtr, 0, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize);
- if (secret == NULL) return XXH_ERROR;
- if (secretSize < XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN) return XXH_ERROR;
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode
-XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR;
- XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(statePtr, seed, kSecret, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE);
- XXH3_initCustomSecret(statePtr->customSecret, seed);
- statePtr->secret = statePtr->customSecret;
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE void
-XXH3_consumeStripes( xxh_u64* acc,
- XXH32_hash_t* nbStripesSoFarPtr, XXH32_hash_t nbStripesPerBlock,
- const xxh_u8* input, size_t totalStripes,
- const xxh_u8* secret, size_t secretLimit,
- XXH3_accWidth_e accWidth)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(*nbStripesSoFarPtr < nbStripesPerBlock);
- if (nbStripesPerBlock - *nbStripesSoFarPtr <= totalStripes) {
- /* need a scrambling operation */
- size_t const nbStripes = nbStripesPerBlock - *nbStripesSoFarPtr;
- XXH3_accumulate(acc, input, secret + nbStripesSoFarPtr[0] * XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE, nbStripes, accWidth);
- XXH3_scrambleAcc(acc, secret + secretLimit);
- XXH3_accumulate(acc, input + nbStripes * STRIPE_LEN, secret, totalStripes - nbStripes, accWidth);
- *nbStripesSoFarPtr = (XXH32_hash_t)(totalStripes - nbStripes);
- } else {
- XXH3_accumulate(acc, input, secret + nbStripesSoFarPtr[0] * XXH_SECRET_CONSUME_RATE, totalStripes, accWidth);
- *nbStripesSoFarPtr += (XXH32_hash_t)totalStripes;
- }
-}
-
-/*
- * Both XXH3_64bits_update and XXH3_128bits_update use this routine.
- */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH_errorcode
-XXH3_update(XXH3_state_t* state, const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, XXH3_accWidth_e accWidth)
-{
- if (input==NULL)
-#if defined(XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER) && (XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER>=1)
- return XXH_OK;
-#else
- return XXH_ERROR;
-#endif
-
- { const xxh_u8* const bEnd = input + len;
-
- state->totalLen += len;
-
- if (state->bufferedSize + len <= XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE) { /* fill in tmp buffer */
- XXH_memcpy(state->buffer + state->bufferedSize, input, len);
- state->bufferedSize += (XXH32_hash_t)len;
- return XXH_OK;
- }
- /* input is now > XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE */
-
- #define XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_STRIPES (XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE / STRIPE_LEN)
- XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE % STRIPE_LEN == 0); /* clean multiple */
-
- /*
- * There is some input left inside the internal buffer.
- * Fill it, then consume it.
- */
- if (state->bufferedSize) {
- size_t const loadSize = XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE - state->bufferedSize;
- XXH_memcpy(state->buffer + state->bufferedSize, input, loadSize);
- input += loadSize;
- XXH3_consumeStripes(state->acc,
- &state->nbStripesSoFar, state->nbStripesPerBlock,
- state->buffer, XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_STRIPES,
- state->secret, state->secretLimit,
- accWidth);
- state->bufferedSize = 0;
- }
-
- /* Consume input by full buffer quantities */
- if (input+XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE <= bEnd) {
- const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE;
- do {
- XXH3_consumeStripes(state->acc,
- &state->nbStripesSoFar, state->nbStripesPerBlock,
- input, XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_STRIPES,
- state->secret, state->secretLimit,
- accWidth);
- input += XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE;
- } while (input<=limit);
- }
-
- if (input < bEnd) { /* Some remaining input: buffer it */
- XXH_memcpy(state->buffer, input, (size_t)(bEnd-input));
- state->bufferedSize = (XXH32_hash_t)(bEnd-input);
- }
- }
-
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode
-XXH3_64bits_update(XXH3_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len)
-{
- return XXH3_update(state, (const xxh_u8*)input, len, XXH3_acc_64bits);
-}
-
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE void
-XXH3_digest_long (XXH64_hash_t* acc, const XXH3_state_t* state, XXH3_accWidth_e accWidth)
-{
- /*
- * Digest on a local copy. This way, the state remains unaltered, and it can
- * continue ingesting more input afterwards.
- */
- memcpy(acc, state->acc, sizeof(state->acc));
- if (state->bufferedSize >= STRIPE_LEN) {
- size_t const totalNbStripes = state->bufferedSize / STRIPE_LEN;
- XXH32_hash_t nbStripesSoFar = state->nbStripesSoFar;
- XXH3_consumeStripes(acc,
- &nbStripesSoFar, state->nbStripesPerBlock,
- state->buffer, totalNbStripes,
- state->secret, state->secretLimit,
- accWidth);
- if (state->bufferedSize % STRIPE_LEN) { /* one last partial stripe */
- XXH3_accumulate_512(acc,
- state->buffer + state->bufferedSize - STRIPE_LEN,
- state->secret + state->secretLimit - XXH_SECRET_LASTACC_START,
- accWidth);
- }
- } else { /* bufferedSize < STRIPE_LEN */
- if (state->bufferedSize) { /* one last stripe */
- xxh_u8 lastStripe[STRIPE_LEN];
- size_t const catchupSize = STRIPE_LEN - state->bufferedSize;
- memcpy(lastStripe, state->buffer + sizeof(state->buffer) - catchupSize, catchupSize);
- memcpy(lastStripe + catchupSize, state->buffer, state->bufferedSize);
- XXH3_accumulate_512(acc,
- lastStripe,
- state->secret + state->secretLimit - XXH_SECRET_LASTACC_START,
- accWidth);
- } }
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* state)
-{
- if (state->totalLen > XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) {
- XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) XXH64_hash_t acc[ACC_NB];
- XXH3_digest_long(acc, state, XXH3_acc_64bits);
- return XXH3_mergeAccs(acc, state->secret + XXH_SECRET_MERGEACCS_START, (xxh_u64)state->totalLen * PRIME64_1);
- }
- /* len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX : short code */
- if (state->seed)
- return XXH3_64bits_withSeed(state->buffer, (size_t)state->totalLen, state->seed);
- return XXH3_64bits_withSecret(state->buffer, (size_t)(state->totalLen), state->secret, state->secretLimit + STRIPE_LEN);
-}
-
-/* ==========================================
- * XXH3 128 bits (=> XXH128)
- * ========================================== */
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_len_1to3_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL);
- XXH_ASSERT(1 <= len && len <= 3);
- XXH_ASSERT(secret != NULL);
- /*
- * len = 1: combinedl = { input[0], 0x01, input[0], input[0] }
- * len = 2: combinedl = { input[1], 0x02, input[0], input[1] }
- * len = 3: combinedl = { input[2], 0x03, input[0], input[1] }
- */
- { xxh_u8 const c1 = input[0];
- xxh_u8 const c2 = input[len >> 1];
- xxh_u8 const c3 = input[len - 1];
- xxh_u32 const combinedl = ((xxh_u32)c1<<16) | (((xxh_u32)c2) << 24) | (((xxh_u32)c3) << 0) | (((xxh_u32)len) << 8);
- xxh_u32 const combinedh = XXH_rotl32(XXH_swap32(combinedl), 13);
- xxh_u64 const bitflipl = (XXH_readLE32(secret) ^ XXH_readLE32(secret+4)) + seed;
- xxh_u64 const bitfliph = (XXH_readLE32(secret+8) ^ XXH_readLE32(secret+12)) - seed;
- xxh_u64 const keyed_lo = (xxh_u64)combinedl ^ bitflipl;
- xxh_u64 const keyed_hi = (xxh_u64)combinedh ^ bitfliph;
- xxh_u64 const mixedl = keyed_lo * PRIME64_1;
- xxh_u64 const mixedh = keyed_hi * PRIME64_5;
- XXH128_hash_t const h128 = { XXH3_avalanche(mixedl) /*low64*/, XXH3_avalanche(mixedh) /*high64*/ };
- return h128;
- }
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_len_4to8_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL);
- XXH_ASSERT(secret != NULL);
- XXH_ASSERT(4 <= len && len <= 8);
- seed ^= (xxh_u64)XXH_swap32((xxh_u32)seed) << 32;
- { xxh_u32 const input_lo = XXH_readLE32(input);
- xxh_u32 const input_hi = XXH_readLE32(input + len - 4);
- xxh_u64 const input_64 = input_lo + ((xxh_u64)input_hi << 32);
- xxh_u64 const bitflip = (XXH_readLE64(secret+16) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+24)) + seed;
- xxh_u64 const keyed = input_64 ^ bitflip;
-
- /* Shift len to the left to ensure it is even, this avoids even multiplies. */
- XXH128_hash_t m128 = XXH_mult64to128(keyed, PRIME64_1 + (len << 2));
-
- m128.high64 += (m128.low64 << 1);
- m128.low64 ^= (m128.high64 >> 3);
-
- m128.low64 = XXH_xorshift64(m128.low64, 35);
- m128.low64 *= 0x9FB21C651E98DF25ULL;
- m128.low64 = XXH_xorshift64(m128.low64, 28);
- m128.high64 = XXH3_avalanche(m128.high64);
- return m128;
- }
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_len_9to16_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(input != NULL);
- XXH_ASSERT(secret != NULL);
- XXH_ASSERT(9 <= len && len <= 16);
- { xxh_u64 const bitflipl = (XXH_readLE64(secret+32) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+40)) - seed;
- xxh_u64 const bitfliph = (XXH_readLE64(secret+48) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+56)) + seed;
- xxh_u64 const input_lo = XXH_readLE64(input);
- xxh_u64 input_hi = XXH_readLE64(input + len - 8);
- XXH128_hash_t m128 = XXH_mult64to128(input_lo ^ input_hi ^ bitflipl, PRIME64_1);
- /*
- * Put len in the middle of m128 to ensure that the length gets mixed to
- * both the low and high bits in the 128x64 multiply below.
- */
- m128.low64 += (xxh_u64)(len - 1) << 54;
- input_hi ^= bitfliph;
- /*
- * Add the high 32 bits of input_hi to the high 32 bits of m128, then
- * add the long product of the low 32 bits of input_hi and PRIME32_2 to
- * the high 64 bits of m128.
- *
- * The best approach to this operation is different on 32-bit and 64-bit.
- */
- if (sizeof(void *) < sizeof(xxh_u64)) { /* 32-bit */
- /*
- * 32-bit optimized version, which is more readable.
- *
- * On 32-bit, it removes an ADC and delays a dependency between the two
- * halves of m128.high64, but it generates an extra mask on 64-bit.
- */
- m128.high64 += (input_hi & 0xFFFFFFFF00000000) + XXH_mult32to64((xxh_u32)input_hi, PRIME32_2);
- } else {
- /*
- * 64-bit optimized (albeit more confusing) version.
- *
- * Uses some properties of addition and multiplication to remove the mask:
- *
- * Let:
- * a = input_hi.lo = (input_hi & 0x00000000FFFFFFFF)
- * b = input_hi.hi = (input_hi & 0xFFFFFFFF00000000)
- * c = PRIME32_2
- *
- * a + (b * c)
- * Inverse Property: x + y - x == y
- * a + (b * (1 + c - 1))
- * Distributive Property: x * (y + z) == (x * y) + (x * z)
- * a + (b * 1) + (b * (c - 1))
- * Identity Property: x * 1 == x
- * a + b + (b * (c - 1))
- *
- * Substitute a, b, and c:
- * input_hi.hi + input_hi.lo + ((xxh_u64)input_hi.lo * (PRIME32_2 - 1))
- *
- * Since input_hi.hi + input_hi.lo == input_hi, we get this:
- * input_hi + ((xxh_u64)input_hi.lo * (PRIME32_2 - 1))
- */
- m128.high64 += input_hi + XXH_mult32to64((xxh_u32)input_hi, PRIME32_2 - 1);
- }
- /* m128 ^= XXH_swap64(m128 >> 64); */
- m128.low64 ^= XXH_swap64(m128.high64);
-
- { /* 128x64 multiply: h128 = m128 * PRIME64_2; */
- XXH128_hash_t h128 = XXH_mult64to128(m128.low64, PRIME64_2);
- h128.high64 += m128.high64 * PRIME64_2;
-
- h128.low64 = XXH3_avalanche(h128.low64);
- h128.high64 = XXH3_avalanche(h128.high64);
- return h128;
- } }
-}
-
-/* Assumption : `secret` size is >= 16
- * Note : it should be >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN anyway */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_len_0to16_128b(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(len <= 16);
- { if (len > 8) return XXH3_len_9to16_128b(input, len, secret, seed);
- if (len >= 4) return XXH3_len_4to8_128b(input, len, secret, seed);
- if (len) return XXH3_len_1to3_128b(input, len, secret, seed);
- { XXH128_hash_t h128;
- xxh_u64 const bitflipl = XXH_readLE64(secret+64) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+72);
- xxh_u64 const bitfliph = XXH_readLE64(secret+80) ^ XXH_readLE64(secret+88);
- h128.low64 = XXH3_avalanche((PRIME64_1 + seed) ^ bitflipl);
- h128.high64 = XXH3_avalanche((PRIME64_2 - seed) ^ bitfliph);
- return h128;
- } }
-}
-
-/*
- * A bit slower than XXH3_mix16B, but handles multiply by zero better.
- */
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH128_mix32B(XXH128_hash_t acc, const xxh_u8* input_1, const xxh_u8* input_2, const xxh_u8* secret, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- acc.low64 += XXH3_mix16B (input_1, secret+0, seed);
- acc.low64 ^= XXH_readLE64(input_2) + XXH_readLE64(input_2 + 8);
- acc.high64 += XXH3_mix16B (input_2, secret+16, seed);
- acc.high64 ^= XXH_readLE64(input_1) + XXH_readLE64(input_1 + 8);
- return acc;
-}
-
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_len_17to128_128b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize,
- XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN); (void)secretSize;
- XXH_ASSERT(16 < len && len <= 128);
-
- { XXH128_hash_t acc;
- acc.low64 = len * PRIME64_1;
- acc.high64 = 0;
- if (len > 32) {
- if (len > 64) {
- if (len > 96) {
- acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, input+48, input+len-64, secret+96, seed);
- }
- acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, input+32, input+len-48, secret+64, seed);
- }
- acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, input+16, input+len-32, secret+32, seed);
- }
- acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, input, input+len-16, secret, seed);
- { xxh_u64 const low64 = acc.low64 + acc.high64;
- xxh_u64 const high64 = (acc.low64 * PRIME64_1) + (acc.high64 * PRIME64_4) + ((len - seed) * PRIME64_2);
- XXH128_hash_t const h128 = { XXH3_avalanche(low64), (XXH64_hash_t)0 - XXH3_avalanche(high64) };
- return h128;
- }
- }
-}
-
-XXH_NO_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_len_129to240_128b(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize,
- XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN); (void)secretSize;
- XXH_ASSERT(128 < len && len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX);
-
- { XXH128_hash_t acc;
- int const nbRounds = (int)len / 32;
- int i;
- acc.low64 = len * PRIME64_1;
- acc.high64 = 0;
- for (i=0; i<4; i++) {
- acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, input+(32*i), input+(32*i)+16, secret+(32*i), seed);
- }
- acc.low64 = XXH3_avalanche(acc.low64);
- acc.high64 = XXH3_avalanche(acc.high64);
- XXH_ASSERT(nbRounds >= 4);
- for (i=4 ; i < nbRounds; i++) {
- acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, input+(32*i), input+(32*i)+16, secret+XXH3_MIDSIZE_STARTOFFSET+(32*(i-4)), seed);
- }
- /* last bytes */
- acc = XXH128_mix32B(acc, input + len - 16, input + len - 32, secret + XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN - XXH3_MIDSIZE_LASTOFFSET - 16, 0ULL - seed);
-
- { xxh_u64 const low64 = acc.low64 + acc.high64;
- xxh_u64 const high64 = (acc.low64 * PRIME64_1) + (acc.high64 * PRIME64_4) + ((len - seed) * PRIME64_2);
- XXH128_hash_t const h128 = { XXH3_avalanche(low64), (XXH64_hash_t)0 - XXH3_avalanche(high64) };
- return h128;
- }
- }
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_hashLong_128b_internal(const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT input, size_t len,
- const xxh_u8* XXH_RESTRICT secret, size_t secretSize)
-{
- XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) xxh_u64 acc[ACC_NB] = XXH3_INIT_ACC;
-
- XXH3_hashLong_internal_loop(acc, input, len, secret, secretSize, XXH3_acc_128bits);
-
- /* converge into final hash */
- XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(acc) == 64);
- XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= sizeof(acc) + XXH_SECRET_MERGEACCS_START);
- { xxh_u64 const low64 = XXH3_mergeAccs(acc, secret + XXH_SECRET_MERGEACCS_START, (xxh_u64)len * PRIME64_1);
- xxh_u64 const high64 = XXH3_mergeAccs(acc, secret + secretSize - sizeof(acc) - XXH_SECRET_MERGEACCS_START, ~((xxh_u64)len * PRIME64_2));
- XXH128_hash_t const h128 = { low64, high64 };
- return h128;
- }
-}
-
-/*
- * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. Not sure
- * why (uop cache maybe?), but the difference is large and easily measurable.
- */
-XXH_NO_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_hashLong_128b_defaultSecret(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len)
-{
- return XXH3_hashLong_128b_internal(input, len, kSecret, sizeof(kSecret));
-}
-
-/*
- * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. Not sure
- * why (uop cache maybe?), but the difference is large and easily measurable.
- */
-XXH_NO_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSecret(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len,
- const xxh_u8* secret, size_t secretSize)
-{
- return XXH3_hashLong_128b_internal(input, len, secret, secretSize);
-}
-
-/*
- * It's important for performance that XXH3_hashLong is not inlined. Not sure
- * why (uop cache maybe?), but the difference is large and easily measurable.
- */
-XXH_NO_INLINE XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSeed(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH_ALIGN(8) xxh_u8 secret[XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE];
- if (seed == 0) return XXH3_hashLong_128b_defaultSecret(input, len);
- XXH3_initCustomSecret(secret, seed);
- return XXH3_hashLong_128b_internal(input, len, secret, sizeof(secret));
-}
-
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits(const void* input, size_t len)
-{
- if (len <= 16) return XXH3_len_0to16_128b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, 0);
- if (len <= 128) return XXH3_len_17to128_128b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, sizeof(kSecret), 0);
- if (len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) return XXH3_len_129to240_128b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, sizeof(kSecret), 0);
- return XXH3_hashLong_128b_defaultSecret((const xxh_u8*)input, len);
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_128bits_withSecret(const void* input, size_t len, const void* secret, size_t secretSize)
-{
- XXH_ASSERT(secretSize >= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN);
- /*
- * If an action is to be taken if `secret` conditions are not respected,
- * it should be done here.
- * For now, it's a contract pre-condition.
- * Adding a check and a branch here would cost performance at every hash.
- */
- if (len <= 16) return XXH3_len_0to16_128b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, 0);
- if (len <= 128) return XXH3_len_17to128_128b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize, 0);
- if (len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) return XXH3_len_129to240_128b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize, 0);
- return XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSecret((const xxh_u8*)input, len, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize);
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t
-XXH3_128bits_withSeed(const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- if (len <= 16) return XXH3_len_0to16_128b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, seed);
- if (len <= 128) return XXH3_len_17to128_128b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, sizeof(kSecret), seed);
- if (len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) return XXH3_len_129to240_128b((const xxh_u8*)input, len, kSecret, sizeof(kSecret), seed);
- return XXH3_hashLong_128b_withSeed((const xxh_u8*)input, len, seed);
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t
-XXH128(const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- return XXH3_128bits_withSeed(input, len, seed);
-}
-
-
-/* === XXH3 128-bit streaming === */
-
-/* all the functions are actually the same as for 64-bit streaming variant,
- just the reset one is different (different initial acc values for 0,5,6,7),
- and near the end of the digest function */
-
-static void
-XXH3_128bits_reset_internal(XXH3_state_t* statePtr,
- XXH64_hash_t seed,
- const xxh_u8* secret, size_t secretSize)
-{
- XXH3_64bits_reset_internal(statePtr, seed, secret, secretSize);
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode
-XXH3_128bits_reset(XXH3_state_t* statePtr)
-{
- if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR;
- XXH3_128bits_reset_internal(statePtr, 0, kSecret, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE);
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode
-XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* secret, size_t secretSize)
-{
- if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR;
- XXH3_128bits_reset_internal(statePtr, 0, (const xxh_u8*)secret, secretSize);
- if (secret == NULL) return XXH_ERROR;
- if (secretSize < XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN) return XXH_ERROR;
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode
-XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- if (statePtr == NULL) return XXH_ERROR;
- XXH3_128bits_reset_internal(statePtr, seed, kSecret, XXH_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE);
- XXH3_initCustomSecret(statePtr->customSecret, seed);
- statePtr->secret = statePtr->customSecret;
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode
-XXH3_128bits_update(XXH3_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len)
-{
- return XXH3_update(state, (const xxh_u8*)input, len, XXH3_acc_128bits);
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* state)
-{
- if (state->totalLen > XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX) {
- XXH_ALIGN(XXH_ACC_ALIGN) XXH64_hash_t acc[ACC_NB];
- XXH3_digest_long(acc, state, XXH3_acc_128bits);
- XXH_ASSERT(state->secretLimit + STRIPE_LEN >= sizeof(acc) + XXH_SECRET_MERGEACCS_START);
- { xxh_u64 const low64 = XXH3_mergeAccs(acc, state->secret + XXH_SECRET_MERGEACCS_START, (xxh_u64)state->totalLen * PRIME64_1);
- xxh_u64 const high64 = XXH3_mergeAccs(acc, state->secret + state->secretLimit + STRIPE_LEN - sizeof(acc) - XXH_SECRET_MERGEACCS_START, ~((xxh_u64)state->totalLen * PRIME64_2));
- XXH128_hash_t const h128 = { low64, high64 };
- return h128;
- }
- }
- /* len <= XXH3_MIDSIZE_MAX : short code */
- if (state->seed)
- return XXH3_128bits_withSeed(state->buffer, (size_t)state->totalLen, state->seed);
- return XXH3_128bits_withSecret(state->buffer, (size_t)(state->totalLen), state->secret, state->secretLimit + STRIPE_LEN);
-}
-
-/* 128-bit utility functions */
-
-#include /* memcmp, memcpy */
-
-/* return : 1 is equal, 0 if different */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_isEqual(XXH128_hash_t h1, XXH128_hash_t h2)
-{
- /* note : XXH128_hash_t is compact, it has no padding byte */
- return !(memcmp(&h1, &h2, sizeof(h1)));
-}
-
-/* This prototype is compatible with stdlib's qsort().
- * return : >0 if *h128_1 > *h128_2
- * <0 if *h128_1 < *h128_2
- * =0 if *h128_1 == *h128_2 */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_cmp(const void* h128_1, const void* h128_2)
-{
- XXH128_hash_t const h1 = *(const XXH128_hash_t*)h128_1;
- XXH128_hash_t const h2 = *(const XXH128_hash_t*)h128_2;
- int const hcmp = (h1.high64 > h2.high64) - (h2.high64 > h1.high64);
- /* note : bets that, in most cases, hash values are different */
- if (hcmp) return hcmp;
- return (h1.low64 > h2.low64) - (h2.low64 > h1.low64);
-}
-
-
-/*====== Canonical representation ======*/
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void
-XXH128_canonicalFromHash(XXH128_canonical_t* dst, XXH128_hash_t hash)
-{
- XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(XXH128_canonical_t) == sizeof(XXH128_hash_t));
- if (XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN) {
- hash.high64 = XXH_swap64(hash.high64);
- hash.low64 = XXH_swap64(hash.low64);
- }
- memcpy(dst, &hash.high64, sizeof(hash.high64));
- memcpy((char*)dst + sizeof(hash.high64), &hash.low64, sizeof(hash.low64));
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t
-XXH128_hashFromCanonical(const XXH128_canonical_t* src)
-{
- XXH128_hash_t h;
- h.high64 = XXH_readBE64(src);
- h.low64 = XXH_readBE64(src->digest + 8);
- return h;
-}
-
-/* Pop our optimization override from above */
-#if XXH_VECTOR == XXH_AVX2 /* AVX2 */ \
- && defined(__GNUC__) && !defined(__clang__) /* GCC, not Clang */ \
- && defined(__OPTIMIZE__) && !defined(__OPTIMIZE_SIZE__) /* respect -O0 and -Os */
-# pragma GCC pop_options
-#endif
-
-#endif /* XXH3_H_1397135465 */
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/xxhash.c b/core/deps/xxHash/xxhash.c
deleted file mode 100644
index 3e0da98f3e..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/xxhash.c
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * xxHash - Extremely Fast Hash algorithm
- * Copyright (C) 2012-present, Yann Collet
- *
- * BSD 2-Clause License (https://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php)
- *
- * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
- * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
- * met:
- *
- * * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
- * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
- * * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
- * copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
- * in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
- * distribution.
- *
- * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
- * "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
- * LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
- * A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
- * OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
- * SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
- * LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
- * DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
- * THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
- * (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
- * OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
- * - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
- */
-
-
-/*
- * xxhash.c instantiates functions defined in xxhash.h
- */
-
-#define XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY /* access advanced declarations */
-#define XXH_IMPLEMENTATION /* access definitions */
-
-#include "xxhash.h"
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/xxhash.h b/core/deps/xxHash/xxhash.h
deleted file mode 100644
index f711b34e35..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/xxhash.h
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,1941 +0,0 @@
-/*
- * xxHash - Extremely Fast Hash algorithm
- * Header File
- * Copyright (C) 2012-present, Yann Collet.
- *
- * BSD 2-Clause License (https://www.opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php)
- *
- * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
- * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
- * met:
- *
- * * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
- * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
- * * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
- * copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
- * in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
- * distribution.
- *
- * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
- * "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
- * LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
- * A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
- * OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
- * SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
- * LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
- * DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
- * THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
- * (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
- * OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
- *
- * You can contact the author at:
- * - xxHash homepage: https://www.xxhash.com
- * - xxHash source repository: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash
- */
-
-/* TODO: update */
-/* Notice extracted from xxHash homepage:
-
-xxHash is an extremely fast hash algorithm, running at RAM speed limits.
-It also successfully passes all tests from the SMHasher suite.
-
-Comparison (single thread, Windows Seven 32 bits, using SMHasher on a Core 2 Duo @3GHz)
-
-Name Speed Q.Score Author
-xxHash 5.4 GB/s 10
-CrapWow 3.2 GB/s 2 Andrew
-MumurHash 3a 2.7 GB/s 10 Austin Appleby
-SpookyHash 2.0 GB/s 10 Bob Jenkins
-SBox 1.4 GB/s 9 Bret Mulvey
-Lookup3 1.2 GB/s 9 Bob Jenkins
-SuperFastHash 1.2 GB/s 1 Paul Hsieh
-CityHash64 1.05 GB/s 10 Pike & Alakuijala
-FNV 0.55 GB/s 5 Fowler, Noll, Vo
-CRC32 0.43 GB/s 9
-MD5-32 0.33 GB/s 10 Ronald L. Rivest
-SHA1-32 0.28 GB/s 10
-
-Q.Score is a measure of quality of the hash function.
-It depends on successfully passing SMHasher test set.
-10 is a perfect score.
-
-Note: SMHasher's CRC32 implementation is not the fastest one.
-Other speed-oriented implementations can be faster,
-especially in combination with PCLMUL instruction:
-https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2019/03/presenting-xxh3.html?showComment=1552696407071#c3490092340461170735
-
-A 64-bit version, named XXH64, is available since r35.
-It offers much better speed, but for 64-bit applications only.
-Name Speed on 64 bits Speed on 32 bits
-XXH64 13.8 GB/s 1.9 GB/s
-XXH32 6.8 GB/s 6.0 GB/s
-*/
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-extern "C" {
-#endif
-
-/* ****************************
- * INLINE mode
- ******************************/
-/*!
- * XXH_INLINE_ALL (and XXH_PRIVATE_API)
- * Use these build macros to inline xxhash into the target unit.
- * Inlining improves performance on small inputs, especially when the length is
- * expressed as a compile-time constant:
- *
- * https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2018/03/xxhash-for-small-keys-impressive-power.html
- *
- * It also keeps xxHash symbols private to the unit, so they are not exported.
- *
- * Usage:
- * #define XXH_INLINE_ALL
- * #include "xxhash.h"
- *
- * Do not compile and link xxhash.o as a separate object, as it is not useful.
- */
-#if (defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL) || defined(XXH_PRIVATE_API)) \
- && !defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL_31684351384)
- /* this section should be traversed only once */
-# define XXH_INLINE_ALL_31684351384
- /* give access to the advanced API, required to compile implementations */
-# undef XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY /* avoid macro redef */
-# define XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY
- /* make all functions private */
-# undef XXH_PUBLIC_API
-# if defined(__GNUC__)
-# define XXH_PUBLIC_API static __inline __attribute__((unused))
-# elif defined (__cplusplus) || (defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L) /* C99 */)
-# define XXH_PUBLIC_API static inline
-# elif defined(_MSC_VER)
-# define XXH_PUBLIC_API static __inline
-# else
- /* note: this version may generate warnings for unused static functions */
-# define XXH_PUBLIC_API static
-# endif
-
- /*
- * This part deals with the special case where a unit wants to inline xxHash,
- * but "xxhash.h" has previously been included without XXH_INLINE_ALL, such
- * as part of some previously included *.h header file.
- * Without further action, the new include would just be ignored,
- * and functions would effectively _not_ be inlined (silent failure).
- * The following macros solve this situation by prefixing all inlined names,
- * avoiding naming collision with previous inclusions.
- */
-# ifdef XXH_NAMESPACE
-# error "XXH_INLINE_ALL with XXH_NAMESPACE is not supported"
- /*
- * Note: Alternative: #undef all symbols (it's a pretty large list).
- * Without #error: it compiles, but functions are actually not inlined.
- */
-# endif
-# define XXH_NAMESPACE XXH_INLINE_
- /*
- * Some identifiers (enums, type names) are not symbols, but they must
- * still be renamed to avoid redeclaration.
- * Alternative solution: do not redeclare them.
- * However, this requires some #ifdefs, and is a more dispersed action.
- * Meanwhile, renaming can be achieved in a single block
- */
-# define XXH_IPREF(Id) XXH_INLINE_ ## Id
-# define XXH_OK XXH_IPREF(XXH_OK)
-# define XXH_ERROR XXH_IPREF(XXH_ERROR)
-# define XXH_errorcode XXH_IPREF(XXH_errorcode)
-# define XXH32_canonical_t XXH_IPREF(XXH32_canonical_t)
-# define XXH64_canonical_t XXH_IPREF(XXH64_canonical_t)
-# define XXH128_canonical_t XXH_IPREF(XXH128_canonical_t)
-# define XXH32_state_s XXH_IPREF(XXH32_state_s)
-# define XXH32_state_t XXH_IPREF(XXH32_state_t)
-# define XXH64_state_s XXH_IPREF(XXH64_state_s)
-# define XXH64_state_t XXH_IPREF(XXH64_state_t)
-# define XXH3_state_s XXH_IPREF(XXH3_state_s)
-# define XXH3_state_t XXH_IPREF(XXH3_state_t)
-# define XXH128_hash_t XXH_IPREF(XXH128_hash_t)
- /* Ensure the header is parsed again, even if it was previously included */
-# undef XXHASH_H_5627135585666179
-# undef XXHASH_H_STATIC_13879238742
-#endif /* XXH_INLINE_ALL || XXH_PRIVATE_API */
-
-
-
-/* ****************************************************************
- * Stable API
- *****************************************************************/
-#ifndef XXHASH_H_5627135585666179
-#define XXHASH_H_5627135585666179 1
-
-/* specific declaration modes for Windows */
-#if !defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL) && !defined(XXH_PRIVATE_API)
-# if defined(WIN32) && defined(_MSC_VER) && (defined(XXH_IMPORT) || defined(XXH_EXPORT))
-# ifdef XXH_EXPORT
-# define XXH_PUBLIC_API __declspec(dllexport)
-# elif XXH_IMPORT
-# define XXH_PUBLIC_API __declspec(dllimport)
-# endif
-# else
-# define XXH_PUBLIC_API /* do nothing */
-# endif
-#endif
-
-/*!
- * XXH_NAMESPACE, aka Namespace Emulation:
- *
- * If you want to include _and expose_ xxHash functions from within your own
- * library, but also want to avoid symbol collisions with other libraries which
- * may also include xxHash, you can use XXH_NAMESPACE to automatically prefix
- * any public symbol from xxhash library with the value of XXH_NAMESPACE
- * (therefore, avoid empty or numeric values).
- *
- * Note that no change is required within the calling program as long as it
- * includes `xxhash.h`: Regular symbol names will be automatically translated
- * by this header.
- */
-#ifdef XXH_NAMESPACE
-# define XXH_CAT(A,B) A##B
-# define XXH_NAME2(A,B) XXH_CAT(A,B)
-# define XXH_versionNumber XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH_versionNumber)
-# define XXH32 XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH32)
-# define XXH32_createState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH32_createState)
-# define XXH32_freeState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH32_freeState)
-# define XXH32_reset XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH32_reset)
-# define XXH32_update XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH32_update)
-# define XXH32_digest XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH32_digest)
-# define XXH32_copyState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH32_copyState)
-# define XXH32_canonicalFromHash XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH32_canonicalFromHash)
-# define XXH32_hashFromCanonical XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH32_hashFromCanonical)
-# define XXH64 XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH64)
-# define XXH64_createState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH64_createState)
-# define XXH64_freeState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH64_freeState)
-# define XXH64_reset XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH64_reset)
-# define XXH64_update XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH64_update)
-# define XXH64_digest XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH64_digest)
-# define XXH64_copyState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH64_copyState)
-# define XXH64_canonicalFromHash XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH64_canonicalFromHash)
-# define XXH64_hashFromCanonical XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH64_hashFromCanonical)
-#endif
-
-
-/* *************************************
-* Version
-***************************************/
-#define XXH_VERSION_MAJOR 0
-#define XXH_VERSION_MINOR 7
-#define XXH_VERSION_RELEASE 3
-#define XXH_VERSION_NUMBER (XXH_VERSION_MAJOR *100*100 + XXH_VERSION_MINOR *100 + XXH_VERSION_RELEASE)
-XXH_PUBLIC_API unsigned XXH_versionNumber (void);
-
-
-/* ****************************
-* Definitions
-******************************/
-#include /* size_t */
-typedef enum { XXH_OK=0, XXH_ERROR } XXH_errorcode;
-
-
-/*-**********************************************************************
-* 32-bit hash
-************************************************************************/
-#if !defined (__VMS) \
- && (defined (__cplusplus) \
- || (defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L) /* C99 */) )
-# include
- typedef uint32_t XXH32_hash_t;
-#else
-# include
-# if UINT_MAX == 0xFFFFFFFFUL
- typedef unsigned int XXH32_hash_t;
-# else
-# if ULONG_MAX == 0xFFFFFFFFUL
- typedef unsigned long XXH32_hash_t;
-# else
-# error "unsupported platform: need a 32-bit type"
-# endif
-# endif
-#endif
-
-/*!
- * XXH32():
- * Calculate the 32-bit hash of sequence "length" bytes stored at memory address "input".
- * The memory between input & input+length must be valid (allocated and read-accessible).
- * "seed" can be used to alter the result predictably.
- * Speed on Core 2 Duo @ 3 GHz (single thread, SMHasher benchmark): 5.4 GB/s
- */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32 (const void* input, size_t length, XXH32_hash_t seed);
-
-/******* Streaming *******/
-
-/*
- * Streaming functions generate the xxHash value from an incrememtal input.
- * This method is slower than single-call functions, due to state management.
- * For small inputs, prefer `XXH32()` and `XXH64()`, which are better optimized.
- *
- * An XXH state must first be allocated using `XXH*_createState()`.
- *
- * Start a new hash by initializing the state with a seed using `XXH*_reset()`.
- *
- * Then, feed the hash state by calling `XXH*_update()` as many times as necessary.
- *
- * The function returns an error code, with 0 meaning OK, and any other value
- * meaning there is an error.
- *
- * Finally, a hash value can be produced anytime, by using `XXH*_digest()`.
- * This function returns the nn-bits hash as an int or long long.
- *
- * It's still possible to continue inserting input into the hash state after a
- * digest, and generate new hash values later on by invoking `XXH*_digest()`.
- *
- * When done, release the state using `XXH*_freeState()`.
- */
-
-typedef struct XXH32_state_s XXH32_state_t; /* incomplete type */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_state_t* XXH32_createState(void);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_freeState(XXH32_state_t* statePtr);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH32_copyState(XXH32_state_t* dst_state, const XXH32_state_t* src_state);
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_reset (XXH32_state_t* statePtr, XXH32_hash_t seed);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_update (XXH32_state_t* statePtr, const void* input, size_t length);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_digest (const XXH32_state_t* statePtr);
-
-/******* Canonical representation *******/
-
-/*
- * The default return values from XXH functions are unsigned 32 and 64 bit
- * integers.
- * This the simplest and fastest format for further post-processing.
- *
- * However, this leaves open the question of what is the order on the byte level,
- * since little and big endian conventions will store the same number differently.
- *
- * The canonical representation settles this issue by mandating big-endian
- * convention, the same convention as human-readable numbers (large digits first).
- *
- * When writing hash values to storage, sending them over a network, or printing
- * them, it's highly recommended to use the canonical representation to ensure
- * portability across a wider range of systems, present and future.
- *
- * The following functions allow transformation of hash values to and from
- * canonical format.
- */
-
-typedef struct { unsigned char digest[4]; } XXH32_canonical_t;
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH32_canonicalFromHash(XXH32_canonical_t* dst, XXH32_hash_t hash);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_hashFromCanonical(const XXH32_canonical_t* src);
-
-
-#ifndef XXH_NO_LONG_LONG
-/*-**********************************************************************
-* 64-bit hash
-************************************************************************/
-#if !defined (__VMS) \
- && (defined (__cplusplus) \
- || (defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L) /* C99 */) )
-# include
- typedef uint64_t XXH64_hash_t;
-#else
- /* the following type must have a width of 64-bit */
- typedef unsigned long long XXH64_hash_t;
-#endif
-
-/*!
- * XXH64():
- * Returns the 64-bit hash of sequence of length @length stored at memory
- * address @input.
- * @seed can be used to alter the result predictably.
- * This function usually runs faster on 64-bit systems, but slower on 32-bit
- * systems (see benchmark).
- */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64 (const void* input, size_t length, XXH64_hash_t seed);
-
-/******* Streaming *******/
-typedef struct XXH64_state_s XXH64_state_t; /* incomplete type */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_state_t* XXH64_createState(void);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_freeState(XXH64_state_t* statePtr);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_copyState(XXH64_state_t* dst_state, const XXH64_state_t* src_state);
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_reset (XXH64_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_update (XXH64_state_t* statePtr, const void* input, size_t length);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_digest (const XXH64_state_t* statePtr);
-
-/******* Canonical representation *******/
-typedef struct { unsigned char digest[8]; } XXH64_canonical_t;
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_canonicalFromHash(XXH64_canonical_t* dst, XXH64_hash_t hash);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src);
-
-
-#endif /* XXH_NO_LONG_LONG */
-
-#endif /* XXHASH_H_5627135585666179 */
-
-
-
-#if defined(XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY) && !defined(XXHASH_H_STATIC_13879238742)
-#define XXHASH_H_STATIC_13879238742
-/* ****************************************************************************
- * This section contains declarations which are not guaranteed to remain stable.
- * They may change in future versions, becoming incompatible with a different
- * version of the library.
- * These declarations should only be used with static linking.
- * Never use them in association with dynamic linking!
- ***************************************************************************** */
-
-/*
- * These definitions are only present to allow static allocation of an XXH
- * state, for example, on the stack or in a struct.
- * Never **ever** access members directly.
- */
-
-struct XXH32_state_s {
- XXH32_hash_t total_len_32;
- XXH32_hash_t large_len;
- XXH32_hash_t v1;
- XXH32_hash_t v2;
- XXH32_hash_t v3;
- XXH32_hash_t v4;
- XXH32_hash_t mem32[4];
- XXH32_hash_t memsize;
- XXH32_hash_t reserved; /* never read nor write, might be removed in a future version */
-}; /* typedef'd to XXH32_state_t */
-
-
-#ifndef XXH_NO_LONG_LONG /* defined when there is no 64-bit support */
-
-struct XXH64_state_s {
- XXH64_hash_t total_len;
- XXH64_hash_t v1;
- XXH64_hash_t v2;
- XXH64_hash_t v3;
- XXH64_hash_t v4;
- XXH64_hash_t mem64[4];
- XXH32_hash_t memsize;
- XXH32_hash_t reserved32; /* required for padding anyway */
- XXH64_hash_t reserved64; /* never read nor write, might be removed in a future version */
-}; /* typedef'd to XXH64_state_t */
-
-
-/*-**********************************************************************
-* XXH3
-* New experimental hash
-************************************************************************/
-
-/* ************************************************************************
- * XXH3 is a new hash algorithm featuring:
- * - Improved speed for both small and large inputs
- * - True 64-bit and 128-bit outputs
- * - SIMD acceleration
- * - Improved 32-bit viability
- *
- * Speed analysis methodology is explained here:
- *
- * https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2019/03/presenting-xxh3.html
- *
- * In general, expect XXH3 to run about ~2x faster on large inputs and >3x
- * faster on small ones compared to XXH64, though exact differences depend on
- * the platform.
- *
- * The algorithm is portable: Like XXH32 and XXH64, it generates the same hash
- * on all platforms.
- *
- * It benefits greatly from SIMD and 64-bit arithmetic, but does not require it.
- *
- * Almost all 32-bit and 64-bit targets that can run XXH32 smoothly can run
- * XXH3 at usable speeds, even if XXH64 runs slowly. Further details are
- * explained in the implementation.
- *
- * Optimized implementations are provided for AVX2, SSE2, NEON, POWER8, ZVector,
- * and scalar targets. This can be controlled with the XXH_VECTOR macro.
- *
- * XXH3 offers 2 variants, _64bits and _128bits.
- * When only 64 bits are needed, prefer calling the _64bits variant, as it
- * reduces the amount of mixing, resulting in faster speed on small inputs.
- *
- * It's also generally simpler to manipulate a scalar return type than a struct.
- *
- * The 128-bit version adds additional strength, but it is slightly slower.
- *
- * The XXH3 algorithm is still in development.
- * The results it produces may still change in future versions.
- *
- * Results produced by v0.7.x are not comparable with results from v0.7.y.
- * However, the API is completely stable, and it can safely be used for
- * ephemeral data (local sessions).
- *
- * Avoid storing values in long-term storage until the algorithm is finalized.
- *
- * The API supports one-shot hashing, streaming mode, and custom secrets.
- */
-
-#ifdef XXH_NAMESPACE
-# define XXH3_64bits XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits)
-# define XXH3_64bits_withSecret XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_withSecret)
-# define XXH3_64bits_withSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_withSeed)
-
-# define XXH3_createState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_createState)
-# define XXH3_freeState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_freeState)
-# define XXH3_copyState XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_copyState)
-
-# define XXH3_64bits_reset XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_reset)
-# define XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed)
-# define XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret)
-# define XXH3_64bits_update XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_update)
-# define XXH3_64bits_digest XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_64bits_digest)
-#endif
-
-/* XXH3_64bits():
- * default 64-bit variant, using default secret and default seed of 0.
- * It's the fastest variant. */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits(const void* data, size_t len);
-
-/*
- * XXH3_64bits_withSecret():
- * It's possible to provide any blob of bytes as a "secret" to generate the hash.
- * This makes it more difficult for an external actor to prepare an intentional
- * collision.
- * The secret *must* be large enough (>= XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN).
- * It should consist of random bytes.
- * Avoid trivial sequences, such as repeating sequences and especially '\0',
- * as this can cancel out itself.
- * Failure to respect these conditions will result in a poor quality hash.
- */
-#define XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN 136
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_withSecret(const void* data, size_t len, const void* secret, size_t secretSize);
-
-/*
- * XXH3_64bits_withSeed():
- * This variant generates a custom secret on the fly based on the default
- * secret, altered using the `seed` value.
- * While this operation is decently fast, note that it's not completely free.
- * Note: seed==0 produces the same results as XXH3_64bits().
- */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_withSeed(const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed);
-
-
-/* streaming 64-bit */
-
-#if defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 201112L) /* C11+ */
-# include
-# define XXH_ALIGN(n) alignas(n)
-#elif defined(__GNUC__)
-# define XXH_ALIGN(n) __attribute__ ((aligned(n)))
-#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
-# define XXH_ALIGN(n) __declspec(align(n))
-#else
-# define XXH_ALIGN(n) /* disabled */
-#endif
-
-/* Old GCC versions only accept the attribute after the type in structures. */
-#if !(defined(__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 201112L)) /* C11+ */ \
- && defined(__GNUC__)
-# define XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER(align, type) type XXH_ALIGN(align)
-#else
-# define XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER(align, type) XXH_ALIGN(align) type
-#endif
-
-typedef struct XXH3_state_s XXH3_state_t;
-
-#define XXH3_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE 192 /* minimum XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN */
-#define XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE 256
-struct XXH3_state_s {
- XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER(64, XXH64_hash_t acc[8]);
- /* used to store a custom secret generated from the seed. Makes state larger.
- * Design might change */
- XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER(64, unsigned char customSecret[XXH3_SECRET_DEFAULT_SIZE]);
- XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER(64, unsigned char buffer[XXH3_INTERNALBUFFER_SIZE]);
- XXH32_hash_t bufferedSize;
- XXH32_hash_t nbStripesPerBlock;
- XXH32_hash_t nbStripesSoFar;
- XXH32_hash_t secretLimit;
- XXH32_hash_t reserved32;
- XXH32_hash_t reserved32_2;
- XXH64_hash_t totalLen;
- XXH64_hash_t seed;
- XXH64_hash_t reserved64;
- /* note: there is some padding after due to alignment on 64 bytes */
- const unsigned char* secret;
-}; /* typedef'd to XXH3_state_t */
-
-#undef XXH_ALIGN_MEMBER
-
-/*
- * Streaming requires state maintenance.
- * This operation costs memory and CPU.
- * As a consequence, streaming is slower than one-shot hashing.
- * For better performance, prefer one-shot functions whenever possible.
- */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH3_state_t* XXH3_createState(void);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_freeState(XXH3_state_t* statePtr);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH3_copyState(XXH3_state_t* dst_state, const XXH3_state_t* src_state);
-
-
-/*
- * XXH3_64bits_reset():
- * Initialize with the default parameters.
- * The result will be equivalent to `XXH3_64bits()`.
- */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_reset(XXH3_state_t* statePtr);
-/*
- * XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed():
- * Generate a custom secret from `seed`, and store it into `statePtr`.
- * digest will be equivalent to `XXH3_64bits_withSeed()`.
- */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_reset_withSeed(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed);
-/*
- * XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret():
- * `secret` is referenced, and must outlive the hash streaming session, so
- * be careful when using stack arrays.
- * `secretSize` must be >= `XXH3_SECRET_SIZE_MIN`.
- */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_reset_withSecret(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* secret, size_t secretSize);
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_64bits_update (XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* input, size_t length);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH3_64bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* statePtr);
-
-
-/* 128-bit */
-
-#ifdef XXH_NAMESPACE
-# define XXH128 XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH128)
-# define XXH3_128bits XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits)
-# define XXH3_128bits_withSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_withSeed)
-# define XXH3_128bits_withSecret XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_withSecret)
-
-# define XXH3_128bits_reset XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_reset)
-# define XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed)
-# define XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret)
-# define XXH3_128bits_update XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_update)
-# define XXH3_128bits_digest XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH3_128bits_digest)
-
-# define XXH128_isEqual XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH128_isEqual)
-# define XXH128_cmp XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH128_cmp)
-# define XXH128_canonicalFromHash XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH128_canonicalFromHash)
-# define XXH128_hashFromCanonical XXH_NAME2(XXH_NAMESPACE, XXH128_hashFromCanonical)
-#endif
-
-typedef struct {
- XXH64_hash_t low64;
- XXH64_hash_t high64;
-} XXH128_hash_t;
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH128(const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits(const void* data, size_t len);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_withSeed(const void* data, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed); /* == XXH128() */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_withSecret(const void* data, size_t len, const void* secret, size_t secretSize);
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_reset(XXH3_state_t* statePtr);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_reset_withSeed(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_reset_withSecret(XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* secret, size_t secretSize);
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH3_128bits_update (XXH3_state_t* statePtr, const void* input, size_t length);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH3_128bits_digest (const XXH3_state_t* statePtr);
-
-
-/* Note: For better performance, these functions can be inlined using XXH_INLINE_ALL */
-
-/*!
- * XXH128_isEqual():
- * Return: 1 if `h1` and `h2` are equal, 0 if they are not.
- */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_isEqual(XXH128_hash_t h1, XXH128_hash_t h2);
-
-/*!
- * XXH128_cmp():
- *
- * This comparator is compatible with stdlib's `qsort()`/`bsearch()`.
- *
- * return: >0 if *h128_1 > *h128_2
- * <0 if *h128_1 < *h128_2
- * =0 if *h128_1 == *h128_2
- */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API int XXH128_cmp(const void* h128_1, const void* h128_2);
-
-
-/******* Canonical representation *******/
-typedef struct { unsigned char digest[16]; } XXH128_canonical_t;
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH128_canonicalFromHash(XXH128_canonical_t* dst, XXH128_hash_t hash);
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH128_hash_t XXH128_hashFromCanonical(const XXH128_canonical_t* src);
-
-
-#endif /* XXH_NO_LONG_LONG */
-
-#if defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL) || defined(XXH_PRIVATE_API)
-# define XXH_IMPLEMENTATION
-#endif
-
-#endif /* defined(XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY) && !defined(XXHASH_H_STATIC_13879238742) */
-
-
-/* ======================================================================== */
-/* ======================================================================== */
-/* ======================================================================== */
-
-
-/*-**********************************************************************
- * xxHash implementation
- *-**********************************************************************
- * xxHash's implementation used to be found in xxhash.c.
- *
- * However, code inlining requires the implementation to be visible to the
- * compiler, usually within the header.
- *
- * As a workaround, xxhash.c used to be included within xxhash.h. This caused
- * some issues with some build systems, especially ones which treat .c files
- * as source files.
- *
- * Therefore, the implementation is now directly integrated within xxhash.h.
- * Another small advantage is that xxhash.c is no longer needed in /include.
- ************************************************************************/
-
-#if ( defined(XXH_INLINE_ALL) || defined(XXH_PRIVATE_API) \
- || defined(XXH_IMPLEMENTATION) ) && !defined(XXH_IMPLEM_13a8737387)
-# define XXH_IMPLEM_13a8737387
-
-/* *************************************
-* Tuning parameters
-***************************************/
-/*!
- * XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS:
- * By default, access to unaligned memory is controlled by `memcpy()`, which is
- * safe and portable.
- *
- * Unfortunately, on some target/compiler combinations, the generated assembly
- * is sub-optimal.
- *
- * The below switch allow to select a different access method for improved
- * performance.
- * Method 0 (default):
- * Use `memcpy()`. Safe and portable.
- * Method 1:
- * `__attribute__((packed))` statement. It depends on compiler extensions
- * and is therefore not portable.
- * This method is safe if your compiler supports it, and *generally* as
- * fast or faster than `memcpy`.
- * Method 2:
- * Direct access via cast. This method doesn't depend on the compiler but
- * violates the C standard.
- * It can generate buggy code on targets which do not support unaligned
- * memory accesses.
- * But in some circumstances, it's the only known way to get the most
- * performance (ie GCC + ARMv6)
- * Method 3:
- * Byteshift. This can generate the best code on old compilers which don't
- * inline small `memcpy()` calls, and it might also be faster on big-endian
- * systems which lack a native byteswap instruction.
- * See https://stackoverflow.com/a/32095106/646947 for details.
- * Prefer these methods in priority order (0 > 1 > 2 > 3)
- */
-#ifndef XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS /* can be defined externally, on command line for example */
-# if !defined(__clang__) && defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__ARM_FEATURE_UNALIGNED) && defined(__ARM_ARCH) && (__ARM_ARCH == 6)
-# define XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS 2
-# elif !defined(__clang__) && ((defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) && !defined(_WIN32)) || \
- (defined(__GNUC__) && (defined(__ARM_ARCH) && __ARM_ARCH >= 7)))
-# define XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS 1
-# endif
-#endif
-
-/*!
- *XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER:
- * If the input pointer is NULL, xxHash's default behavior is to dereference it,
- * triggering a segfault.
- * When this macro is enabled, xxHash actively checks the input for a null pointer.
- * If it is, the result for null input pointers is the same as a zero-length input.
- */
-#ifndef XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER /* can be defined externally */
-# define XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER 0
-#endif
-
-/*!
- * XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK:
- * This is a minor performance trick, only useful with lots of very small keys.
- * It means: check for aligned/unaligned input.
- * The check costs one initial branch per hash;
- * Set it to 0 when the input is guaranteed to be aligned or when alignment
- * doesn't matter for performance.
- *
- * This option does not affect XXH3.
- */
-#ifndef XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK /* can be defined externally */
-# if defined(__i386) || defined(_M_IX86) || defined(__x86_64__) || defined(_M_X64)
-# define XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK 0
-# else
-# define XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK 1
-# endif
-#endif
-
-/*!
- * XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS:
- *
- * By default, xxHash tries to force the compiler to inline almost all internal
- * functions.
- *
- * This can usually improve performance due to reduced jumping and improved
- * constant folding, but significantly increases the size of the binary which
- * might not be favorable.
- *
- * Additionally, sometimes the forced inlining can be detrimental to performance,
- * depending on the architecture.
- *
- * XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS marks all internal functions as static, giving the
- * compiler full control on whether to inline or not.
- *
- * When not optimizing (-O0), optimizing for size (-Os, -Oz), or using
- * -fno-inline with GCC or Clang, this will automatically be defined.
- */
-#ifndef XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS
-# if defined(__OPTIMIZE_SIZE__) /* -Os, -Oz */ \
- || defined(__NO_INLINE__) /* -O0, -fno-inline */
-# define XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS 1
-# else
-# define XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS 0
-# endif
-#endif
-
-/*!
- * XXH_REROLL:
- * Whether to reroll XXH32_finalize, and XXH64_finalize,
- * instead of using an unrolled jump table/if statement loop.
- *
- * This is automatically defined on -Os/-Oz on GCC and Clang.
- */
-#ifndef XXH_REROLL
-# if defined(__OPTIMIZE_SIZE__)
-# define XXH_REROLL 1
-# else
-# define XXH_REROLL 0
-# endif
-#endif
-
-
-/* *************************************
-* Includes & Memory related functions
-***************************************/
-/*!
- * Modify the local functions below should you wish to use some other memory
- * routines for malloc() and free()
- */
-#include
-static void* XXH_malloc(size_t s) { return malloc(s); }
-static void XXH_free (void* p) { free(p); }
-/*! and for memcpy() */
-#include
-static void* XXH_memcpy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t size)
-{
- return memcpy(dest,src,size);
-}
-
-#include /* ULLONG_MAX */
-
-
-/* *************************************
-* Compiler Specific Options
-***************************************/
-#ifdef _MSC_VER /* Visual Studio warning fix */
-# pragma warning(disable : 4127) /* disable: C4127: conditional expression is constant */
-#endif
-
-#if XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS /* disable inlining hints */
-# define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static
-# define XXH_NO_INLINE static
-#elif defined(_MSC_VER) /* Visual Studio */
-# define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static __forceinline
-# define XXH_NO_INLINE static __declspec(noinline)
-#else
-# if defined (__cplusplus) \
- || defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L /* C99 */
-# ifdef __GNUC__
-# define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static inline __attribute__((always_inline))
-# define XXH_NO_INLINE static __attribute__((noinline))
-# else
-# define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static inline
-# define XXH_NO_INLINE static
-# endif
-# else
-# define XXH_FORCE_INLINE static
-# define XXH_NO_INLINE static
-# endif /* __STDC_VERSION__ */
-#endif
-
-
-
-/* *************************************
-* Debug
-***************************************/
-/*
- * DEBUGLEVEL is expected to be defined externally, typically via the compiler's
- * command line options. The value must be a number.
- */
-#ifndef DEBUGLEVEL
-# define DEBUGLEVEL 0
-#endif
-
-#if (DEBUGLEVEL>=1)
-# include /* note: can still be disabled with NDEBUG */
-# define XXH_ASSERT(c) assert(c)
-#else
-# define XXH_ASSERT(c) ((void)0)
-#endif
-
-/* note: use after variable declarations */
-#define XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(c) { enum { XXH_sa = 1/(int)(!!(c)) }; }
-
-
-/* *************************************
-* Basic Types
-***************************************/
-#if !defined (__VMS) \
- && (defined (__cplusplus) \
- || (defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && (__STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L) /* C99 */) )
-# include
- typedef uint8_t xxh_u8;
-#else
- typedef unsigned char xxh_u8;
-#endif
-typedef XXH32_hash_t xxh_u32;
-
-
-/* *** Memory access *** */
-
-#if (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==3))
-/*
- * Manual byteshift. Best for old compilers which don't inline memcpy.
- * We actually directly use XXH_readLE32 and XXH_readBE32.
- */
-#elif (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==2))
-
-/*
- * Force direct memory access. Only works on CPU which support unaligned memory
- * access in hardware.
- */
-static xxh_u32 XXH_read32(const void* memPtr) { return *(const xxh_u32*) memPtr; }
-
-#elif (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==1))
-
-/*
- * __pack instructions are safer but compiler specific, hence potentially
- * problematic for some compilers.
- *
- * Currently only defined for GCC and ICC.
- */
-typedef union { xxh_u32 u32; } __attribute__((packed)) unalign;
-static xxh_u32 XXH_read32(const void* ptr) { return ((const unalign*)ptr)->u32; }
-
-#else
-
-/*
- * Portable and safe solution. Generally efficient.
- * see: https://stackoverflow.com/a/32095106/646947
- */
-static xxh_u32 XXH_read32(const void* memPtr)
-{
- xxh_u32 val;
- memcpy(&val, memPtr, sizeof(val));
- return val;
-}
-
-#endif /* XXH_FORCE_DIRECT_MEMORY_ACCESS */
-
-
-/* *** Endianess *** */
-typedef enum { XXH_bigEndian=0, XXH_littleEndian=1 } XXH_endianess;
-
-/*!
- * XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN:
- * Defined to 1 if the target is little endian, or 0 if it is big endian.
- * It can be defined externally, for example on the compiler command line.
- *
- * If it is not defined, a runtime check (which is usually constant folded)
- * is used instead.
- */
-#ifndef XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN
-/*
- * Try to detect endianness automatically, to avoid the nonstandard behavior
- * in `XXH_isLittleEndian()`
- */
-# if defined(_WIN32) /* Windows is always little endian */ \
- || defined(__LITTLE_ENDIAN__) \
- || (defined(__BYTE_ORDER__) && __BYTE_ORDER__ == __ORDER_LITTLE_ENDIAN__)
-# define XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN 1
-# elif defined(__BIG_ENDIAN__) \
- || (defined(__BYTE_ORDER__) && __BYTE_ORDER__ == __ORDER_BIG_ENDIAN__)
-# define XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN 0
-# else
-static int XXH_isLittleEndian(void)
-{
- /*
- * Nonstandard, but well-defined behavior in practice.
- * Don't use static: it is detrimental to performance.
- */
- const union { xxh_u32 u; xxh_u8 c[4]; } one = { 1 };
- return one.c[0];
-}
-# define XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN XXH_isLittleEndian()
-# endif
-#endif
-
-
-
-
-/* ****************************************
-* Compiler-specific Functions and Macros
-******************************************/
-#define XXH_GCC_VERSION (__GNUC__ * 100 + __GNUC_MINOR__)
-
-#ifndef __has_builtin
-# define __has_builtin(x) 0
-#endif
-
-#if !defined(NO_CLANG_BUILTIN) && __has_builtin(__builtin_rotateleft32) \
- && __has_builtin(__builtin_rotateleft64)
-# define XXH_rotl32 __builtin_rotateleft32
-# define XXH_rotl64 __builtin_rotateleft64
-/* Note: although _rotl exists for minGW (GCC under windows), performance seems poor */
-#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
-# define XXH_rotl32(x,r) _rotl(x,r)
-# define XXH_rotl64(x,r) _rotl64(x,r)
-#else
-# define XXH_rotl32(x,r) (((x) << (r)) | ((x) >> (32 - (r))))
-# define XXH_rotl64(x,r) (((x) << (r)) | ((x) >> (64 - (r))))
-#endif
-
-#if defined(_MSC_VER) /* Visual Studio */
-# define XXH_swap32 _byteswap_ulong
-#elif XXH_GCC_VERSION >= 403
-# define XXH_swap32 __builtin_bswap32
-#else
-static xxh_u32 XXH_swap32 (xxh_u32 x)
-{
- return ((x << 24) & 0xff000000 ) |
- ((x << 8) & 0x00ff0000 ) |
- ((x >> 8) & 0x0000ff00 ) |
- ((x >> 24) & 0x000000ff );
-}
-#endif
-
-
-/* ***************************
-* Memory reads
-*****************************/
-typedef enum { XXH_aligned, XXH_unaligned } XXH_alignment;
-
-/*
- * XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==3 is an endian-independent byteshift load.
- *
- * This is ideal for older compilers which don't inline memcpy.
- */
-#if (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==3))
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u32 XXH_readLE32(const void* memPtr)
-{
- const xxh_u8* bytePtr = (const xxh_u8 *)memPtr;
- return bytePtr[0]
- | ((xxh_u32)bytePtr[1] << 8)
- | ((xxh_u32)bytePtr[2] << 16)
- | ((xxh_u32)bytePtr[3] << 24);
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u32 XXH_readBE32(const void* memPtr)
-{
- const xxh_u8* bytePtr = (const xxh_u8 *)memPtr;
- return bytePtr[3]
- | ((xxh_u32)bytePtr[2] << 8)
- | ((xxh_u32)bytePtr[1] << 16)
- | ((xxh_u32)bytePtr[0] << 24);
-}
-
-#else
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u32 XXH_readLE32(const void* ptr)
-{
- return XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN ? XXH_read32(ptr) : XXH_swap32(XXH_read32(ptr));
-}
-
-static xxh_u32 XXH_readBE32(const void* ptr)
-{
- return XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN ? XXH_swap32(XXH_read32(ptr)) : XXH_read32(ptr);
-}
-#endif
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u32
-XXH_readLE32_align(const void* ptr, XXH_alignment align)
-{
- if (align==XXH_unaligned) {
- return XXH_readLE32(ptr);
- } else {
- return XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN ? *(const xxh_u32*)ptr : XXH_swap32(*(const xxh_u32*)ptr);
- }
-}
-
-
-/* *************************************
-* Misc
-***************************************/
-XXH_PUBLIC_API unsigned XXH_versionNumber (void) { return XXH_VERSION_NUMBER; }
-
-
-/* *******************************************************************
-* 32-bit hash functions
-*********************************************************************/
-static const xxh_u32 PRIME32_1 = 0x9E3779B1U; /* 0b10011110001101110111100110110001 */
-static const xxh_u32 PRIME32_2 = 0x85EBCA77U; /* 0b10000101111010111100101001110111 */
-static const xxh_u32 PRIME32_3 = 0xC2B2AE3DU; /* 0b11000010101100101010111000111101 */
-static const xxh_u32 PRIME32_4 = 0x27D4EB2FU; /* 0b00100111110101001110101100101111 */
-static const xxh_u32 PRIME32_5 = 0x165667B1U; /* 0b00010110010101100110011110110001 */
-
-static xxh_u32 XXH32_round(xxh_u32 acc, xxh_u32 input)
-{
- acc += input * PRIME32_2;
- acc = XXH_rotl32(acc, 13);
- acc *= PRIME32_1;
-#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__SSE4_1__) && !defined(XXH_ENABLE_AUTOVECTORIZE)
- /*
- * UGLY HACK:
- * This inline assembly hack forces acc into a normal register. This is the
- * only thing that prevents GCC and Clang from autovectorizing the XXH32
- * loop (pragmas and attributes don't work for some resason) without globally
- * disabling SSE4.1.
- *
- * The reason we want to avoid vectorization is because despite working on
- * 4 integers at a time, there are multiple factors slowing XXH32 down on
- * SSE4:
- * - There's a ridiculous amount of lag from pmulld (10 cycles of latency on
- * newer chips!) making it slightly slower to multiply four integers at
- * once compared to four integers independently. Even when pmulld was
- * fastest, Sandy/Ivy Bridge, it is still not worth it to go into SSE
- * just to multiply unless doing a long operation.
- *
- * - Four instructions are required to rotate,
- * movqda tmp, v // not required with VEX encoding
- * pslld tmp, 13 // tmp <<= 13
- * psrld v, 19 // x >>= 19
- * por v, tmp // x |= tmp
- * compared to one for scalar:
- * roll v, 13 // reliably fast across the board
- * shldl v, v, 13 // Sandy Bridge and later prefer this for some reason
- *
- * - Instruction level parallelism is actually more beneficial here because
- * the SIMD actually serializes this operation: While v1 is rotating, v2
- * can load data, while v3 can multiply. SSE forces them to operate
- * together.
- *
- * How this hack works:
- * __asm__("" // Declare an assembly block but don't declare any instructions
- * : // However, as an Input/Output Operand,
- * "+r" // constrain a read/write operand (+) as a general purpose register (r).
- * (acc) // and set acc as the operand
- * );
- *
- * Because of the 'r', the compiler has promised that seed will be in a
- * general purpose register and the '+' says that it will be 'read/write',
- * so it has to assume it has changed. It is like volatile without all the
- * loads and stores.
- *
- * Since the argument has to be in a normal register (not an SSE register),
- * each time XXH32_round is called, it is impossible to vectorize.
- */
- __asm__("" : "+r" (acc));
-#endif
- return acc;
-}
-
-/* mix all bits */
-static xxh_u32 XXH32_avalanche(xxh_u32 h32)
-{
- h32 ^= h32 >> 15;
- h32 *= PRIME32_2;
- h32 ^= h32 >> 13;
- h32 *= PRIME32_3;
- h32 ^= h32 >> 16;
- return(h32);
-}
-
-#define XXH_get32bits(p) XXH_readLE32_align(p, align)
-
-static xxh_u32
-XXH32_finalize(xxh_u32 h32, const xxh_u8* ptr, size_t len, XXH_alignment align)
-{
-#define PROCESS1 \
- h32 += (*ptr++) * PRIME32_5; \
- h32 = XXH_rotl32(h32, 11) * PRIME32_1 ;
-
-#define PROCESS4 \
- h32 += XXH_get32bits(ptr) * PRIME32_3; \
- ptr+=4; \
- h32 = XXH_rotl32(h32, 17) * PRIME32_4 ;
-
- /* Compact rerolled version */
- if (XXH_REROLL) {
- len &= 15;
- while (len >= 4) {
- PROCESS4;
- len -= 4;
- }
- while (len > 0) {
- PROCESS1;
- --len;
- }
- return XXH32_avalanche(h32);
- } else {
- switch(len&15) /* or switch(bEnd - p) */ {
- case 12: PROCESS4;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 8: PROCESS4;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 4: PROCESS4;
- return XXH32_avalanche(h32);
-
- case 13: PROCESS4;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 9: PROCESS4;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 5: PROCESS4;
- PROCESS1;
- return XXH32_avalanche(h32);
-
- case 14: PROCESS4;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 10: PROCESS4;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 6: PROCESS4;
- PROCESS1;
- PROCESS1;
- return XXH32_avalanche(h32);
-
- case 15: PROCESS4;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 11: PROCESS4;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 7: PROCESS4;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 3: PROCESS1;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 2: PROCESS1;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 1: PROCESS1;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 0: return XXH32_avalanche(h32);
- }
- XXH_ASSERT(0);
- return h32; /* reaching this point is deemed impossible */
- }
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u32
-XXH32_endian_align(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, xxh_u32 seed, XXH_alignment align)
-{
- const xxh_u8* bEnd = input + len;
- xxh_u32 h32;
-
-#if defined(XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER) && (XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER>=1)
- if (input==NULL) {
- len=0;
- bEnd=input=(const xxh_u8*)(size_t)16;
- }
-#endif
-
- if (len>=16) {
- const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - 15;
- xxh_u32 v1 = seed + PRIME32_1 + PRIME32_2;
- xxh_u32 v2 = seed + PRIME32_2;
- xxh_u32 v3 = seed + 0;
- xxh_u32 v4 = seed - PRIME32_1;
-
- do {
- v1 = XXH32_round(v1, XXH_get32bits(input)); input += 4;
- v2 = XXH32_round(v2, XXH_get32bits(input)); input += 4;
- v3 = XXH32_round(v3, XXH_get32bits(input)); input += 4;
- v4 = XXH32_round(v4, XXH_get32bits(input)); input += 4;
- } while (input < limit);
-
- h32 = XXH_rotl32(v1, 1) + XXH_rotl32(v2, 7)
- + XXH_rotl32(v3, 12) + XXH_rotl32(v4, 18);
- } else {
- h32 = seed + PRIME32_5;
- }
-
- h32 += (xxh_u32)len;
-
- return XXH32_finalize(h32, input, len&15, align);
-}
-
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32 (const void* input, size_t len, XXH32_hash_t seed)
-{
-#if 0
- /* Simple version, good for code maintenance, but unfortunately slow for small inputs */
- XXH32_state_t state;
- XXH32_reset(&state, seed);
- XXH32_update(&state, (const xxh_u8*)input, len);
- return XXH32_digest(&state);
-
-#else
-
- if (XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK) {
- if ((((size_t)input) & 3) == 0) { /* Input is 4-bytes aligned, leverage the speed benefit */
- return XXH32_endian_align((const xxh_u8*)input, len, seed, XXH_aligned);
- } }
-
- return XXH32_endian_align((const xxh_u8*)input, len, seed, XXH_unaligned);
-#endif
-}
-
-
-
-/******* Hash streaming *******/
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_state_t* XXH32_createState(void)
-{
- return (XXH32_state_t*)XXH_malloc(sizeof(XXH32_state_t));
-}
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_freeState(XXH32_state_t* statePtr)
-{
- XXH_free(statePtr);
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH32_copyState(XXH32_state_t* dstState, const XXH32_state_t* srcState)
-{
- memcpy(dstState, srcState, sizeof(*dstState));
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH32_reset(XXH32_state_t* statePtr, XXH32_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH32_state_t state; /* using a local state to memcpy() in order to avoid strict-aliasing warnings */
- memset(&state, 0, sizeof(state));
- state.v1 = seed + PRIME32_1 + PRIME32_2;
- state.v2 = seed + PRIME32_2;
- state.v3 = seed + 0;
- state.v4 = seed - PRIME32_1;
- /* do not write into reserved, planned to be removed in a future version */
- memcpy(statePtr, &state, sizeof(state) - sizeof(state.reserved));
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode
-XXH32_update(XXH32_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len)
-{
- if (input==NULL)
-#if defined(XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER) && (XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER>=1)
- return XXH_OK;
-#else
- return XXH_ERROR;
-#endif
-
- { const xxh_u8* p = (const xxh_u8*)input;
- const xxh_u8* const bEnd = p + len;
-
- state->total_len_32 += (XXH32_hash_t)len;
- state->large_len |= (XXH32_hash_t)((len>=16) | (state->total_len_32>=16));
-
- if (state->memsize + len < 16) { /* fill in tmp buffer */
- XXH_memcpy((xxh_u8*)(state->mem32) + state->memsize, input, len);
- state->memsize += (XXH32_hash_t)len;
- return XXH_OK;
- }
-
- if (state->memsize) { /* some data left from previous update */
- XXH_memcpy((xxh_u8*)(state->mem32) + state->memsize, input, 16-state->memsize);
- { const xxh_u32* p32 = state->mem32;
- state->v1 = XXH32_round(state->v1, XXH_readLE32(p32)); p32++;
- state->v2 = XXH32_round(state->v2, XXH_readLE32(p32)); p32++;
- state->v3 = XXH32_round(state->v3, XXH_readLE32(p32)); p32++;
- state->v4 = XXH32_round(state->v4, XXH_readLE32(p32));
- }
- p += 16-state->memsize;
- state->memsize = 0;
- }
-
- if (p <= bEnd-16) {
- const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - 16;
- xxh_u32 v1 = state->v1;
- xxh_u32 v2 = state->v2;
- xxh_u32 v3 = state->v3;
- xxh_u32 v4 = state->v4;
-
- do {
- v1 = XXH32_round(v1, XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4;
- v2 = XXH32_round(v2, XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4;
- v3 = XXH32_round(v3, XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4;
- v4 = XXH32_round(v4, XXH_readLE32(p)); p+=4;
- } while (p<=limit);
-
- state->v1 = v1;
- state->v2 = v2;
- state->v3 = v3;
- state->v4 = v4;
- }
-
- if (p < bEnd) {
- XXH_memcpy(state->mem32, p, (size_t)(bEnd-p));
- state->memsize = (unsigned)(bEnd-p);
- }
- }
-
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_digest (const XXH32_state_t* state)
-{
- xxh_u32 h32;
-
- if (state->large_len) {
- h32 = XXH_rotl32(state->v1, 1)
- + XXH_rotl32(state->v2, 7)
- + XXH_rotl32(state->v3, 12)
- + XXH_rotl32(state->v4, 18);
- } else {
- h32 = state->v3 /* == seed */ + PRIME32_5;
- }
-
- h32 += state->total_len_32;
-
- return XXH32_finalize(h32, (const xxh_u8*)state->mem32, state->memsize, XXH_aligned);
-}
-
-
-/******* Canonical representation *******/
-
-/*
- * The default return values from XXH functions are unsigned 32 and 64 bit
- * integers.
- *
- * The canonical representation uses big endian convention, the same convention
- * as human-readable numbers (large digits first).
- *
- * This way, hash values can be written into a file or buffer, remaining
- * comparable across different systems.
- *
- * The following functions allow transformation of hash values to and from their
- * canonical format.
- */
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH32_canonicalFromHash(XXH32_canonical_t* dst, XXH32_hash_t hash)
-{
- XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(XXH32_canonical_t) == sizeof(XXH32_hash_t));
- if (XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN) hash = XXH_swap32(hash);
- memcpy(dst, &hash, sizeof(*dst));
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH32_hash_t XXH32_hashFromCanonical(const XXH32_canonical_t* src)
-{
- return XXH_readBE32(src);
-}
-
-
-#ifndef XXH_NO_LONG_LONG
-
-/* *******************************************************************
-* 64-bit hash functions
-*********************************************************************/
-
-/******* Memory access *******/
-
-typedef XXH64_hash_t xxh_u64;
-
-
-/*!
- * XXH_REROLL_XXH64:
- * Whether to reroll the XXH64_finalize() loop.
- *
- * Just like XXH32, we can unroll the XXH64_finalize() loop. This can be a
- * performance gain on 64-bit hosts, as only one jump is required.
- *
- * However, on 32-bit hosts, because arithmetic needs to be done with two 32-bit
- * registers, and 64-bit arithmetic needs to be simulated, it isn't beneficial
- * to unroll. The code becomes ridiculously large (the largest function in the
- * binary on i386!), and rerolling it saves anywhere from 3kB to 20kB. It is
- * also slightly faster because it fits into cache better and is more likely
- * to be inlined by the compiler.
- *
- * If XXH_REROLL is defined, this is ignored and the loop is always rerolled.
- */
-#ifndef XXH_REROLL_XXH64
-# if (defined(__ILP32__) || defined(_ILP32)) /* ILP32 is often defined on 32-bit GCC family */ \
- || !(defined(__x86_64__) || defined(_M_X64) || defined(_M_AMD64) /* x86-64 */ \
- || defined(_M_ARM64) || defined(__aarch64__) || defined(__arm64__) /* aarch64 */ \
- || defined(__PPC64__) || defined(__PPC64LE__) || defined(__ppc64__) || defined(__powerpc64__) /* ppc64 */ \
- || defined(__mips64__) || defined(__mips64)) /* mips64 */ \
- || (!defined(SIZE_MAX) || SIZE_MAX < ULLONG_MAX) /* check limits */
-# define XXH_REROLL_XXH64 1
-# else
-# define XXH_REROLL_XXH64 0
-# endif
-#endif /* !defined(XXH_REROLL_XXH64) */
-
-#if (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==3))
-/*
- * Manual byteshift. Best for old compilers which don't inline memcpy.
- * We actually directly use XXH_readLE64 and XXH_readBE64.
- */
-#elif (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==2))
-
-/* Force direct memory access. Only works on CPU which support unaligned memory access in hardware */
-static xxh_u64 XXH_read64(const void* memPtr) { return *(const xxh_u64*) memPtr; }
-
-#elif (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==1))
-
-/*
- * __pack instructions are safer, but compiler specific, hence potentially
- * problematic for some compilers.
- *
- * Currently only defined for GCC and ICC.
- */
-typedef union { xxh_u32 u32; xxh_u64 u64; } __attribute__((packed)) unalign64;
-static xxh_u64 XXH_read64(const void* ptr) { return ((const unalign64*)ptr)->u64; }
-
-#else
-
-/*
- * Portable and safe solution. Generally efficient.
- * see: https://stackoverflow.com/a/32095106/646947
- */
-static xxh_u64 XXH_read64(const void* memPtr)
-{
- xxh_u64 val;
- memcpy(&val, memPtr, sizeof(val));
- return val;
-}
-
-#endif /* XXH_FORCE_DIRECT_MEMORY_ACCESS */
-
-#if defined(_MSC_VER) /* Visual Studio */
-# define XXH_swap64 _byteswap_uint64
-#elif XXH_GCC_VERSION >= 403
-# define XXH_swap64 __builtin_bswap64
-#else
-static xxh_u64 XXH_swap64 (xxh_u64 x)
-{
- return ((x << 56) & 0xff00000000000000ULL) |
- ((x << 40) & 0x00ff000000000000ULL) |
- ((x << 24) & 0x0000ff0000000000ULL) |
- ((x << 8) & 0x000000ff00000000ULL) |
- ((x >> 8) & 0x00000000ff000000ULL) |
- ((x >> 24) & 0x0000000000ff0000ULL) |
- ((x >> 40) & 0x000000000000ff00ULL) |
- ((x >> 56) & 0x00000000000000ffULL);
-}
-#endif
-
-
-/* XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==3 is an endian-independent byteshift load. */
-#if (defined(XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS) && (XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS==3))
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH_readLE64(const void* memPtr)
-{
- const xxh_u8* bytePtr = (const xxh_u8 *)memPtr;
- return bytePtr[0]
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[1] << 8)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[2] << 16)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[3] << 24)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[4] << 32)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[5] << 40)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[6] << 48)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[7] << 56);
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH_readBE64(const void* memPtr)
-{
- const xxh_u8* bytePtr = (const xxh_u8 *)memPtr;
- return bytePtr[7]
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[6] << 8)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[5] << 16)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[4] << 24)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[3] << 32)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[2] << 40)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[1] << 48)
- | ((xxh_u64)bytePtr[0] << 56);
-}
-
-#else
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64 XXH_readLE64(const void* ptr)
-{
- return XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN ? XXH_read64(ptr) : XXH_swap64(XXH_read64(ptr));
-}
-
-static xxh_u64 XXH_readBE64(const void* ptr)
-{
- return XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN ? XXH_swap64(XXH_read64(ptr)) : XXH_read64(ptr);
-}
-#endif
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64
-XXH_readLE64_align(const void* ptr, XXH_alignment align)
-{
- if (align==XXH_unaligned)
- return XXH_readLE64(ptr);
- else
- return XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN ? *(const xxh_u64*)ptr : XXH_swap64(*(const xxh_u64*)ptr);
-}
-
-
-/******* xxh64 *******/
-
-static const xxh_u64 PRIME64_1 = 0x9E3779B185EBCA87ULL; /* 0b1001111000110111011110011011000110000101111010111100101010000111 */
-static const xxh_u64 PRIME64_2 = 0xC2B2AE3D27D4EB4FULL; /* 0b1100001010110010101011100011110100100111110101001110101101001111 */
-static const xxh_u64 PRIME64_3 = 0x165667B19E3779F9ULL; /* 0b0001011001010110011001111011000110011110001101110111100111111001 */
-static const xxh_u64 PRIME64_4 = 0x85EBCA77C2B2AE63ULL; /* 0b1000010111101011110010100111011111000010101100101010111001100011 */
-static const xxh_u64 PRIME64_5 = 0x27D4EB2F165667C5ULL; /* 0b0010011111010100111010110010111100010110010101100110011111000101 */
-
-static xxh_u64 XXH64_round(xxh_u64 acc, xxh_u64 input)
-{
- acc += input * PRIME64_2;
- acc = XXH_rotl64(acc, 31);
- acc *= PRIME64_1;
- return acc;
-}
-
-static xxh_u64 XXH64_mergeRound(xxh_u64 acc, xxh_u64 val)
-{
- val = XXH64_round(0, val);
- acc ^= val;
- acc = acc * PRIME64_1 + PRIME64_4;
- return acc;
-}
-
-static xxh_u64 XXH64_avalanche(xxh_u64 h64)
-{
- h64 ^= h64 >> 33;
- h64 *= PRIME64_2;
- h64 ^= h64 >> 29;
- h64 *= PRIME64_3;
- h64 ^= h64 >> 32;
- return h64;
-}
-
-
-#define XXH_get64bits(p) XXH_readLE64_align(p, align)
-
-static xxh_u64
-XXH64_finalize(xxh_u64 h64, const xxh_u8* ptr, size_t len, XXH_alignment align)
-{
-#define PROCESS1_64 \
- h64 ^= (*ptr++) * PRIME64_5; \
- h64 = XXH_rotl64(h64, 11) * PRIME64_1;
-
-#define PROCESS4_64 \
- h64 ^= (xxh_u64)(XXH_get32bits(ptr)) * PRIME64_1; \
- ptr+=4; \
- h64 = XXH_rotl64(h64, 23) * PRIME64_2 + PRIME64_3;
-
-#define PROCESS8_64 { \
- xxh_u64 const k1 = XXH64_round(0, XXH_get64bits(ptr)); \
- ptr+=8; \
- h64 ^= k1; \
- h64 = XXH_rotl64(h64,27) * PRIME64_1 + PRIME64_4; \
-}
-
- /* Rerolled version for 32-bit targets is faster and much smaller. */
- if (XXH_REROLL || XXH_REROLL_XXH64) {
- len &= 31;
- while (len >= 8) {
- PROCESS8_64;
- len -= 8;
- }
- if (len >= 4) {
- PROCESS4_64;
- len -= 4;
- }
- while (len > 0) {
- PROCESS1_64;
- --len;
- }
- return XXH64_avalanche(h64);
- } else {
- switch(len & 31) {
- case 24: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 16: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 8: PROCESS8_64;
- return XXH64_avalanche(h64);
-
- case 28: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 20: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 12: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 4: PROCESS4_64;
- return XXH64_avalanche(h64);
-
- case 25: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 17: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 9: PROCESS8_64;
- PROCESS1_64;
- return XXH64_avalanche(h64);
-
- case 29: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 21: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 13: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 5: PROCESS4_64;
- PROCESS1_64;
- return XXH64_avalanche(h64);
-
- case 26: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 18: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 10: PROCESS8_64;
- PROCESS1_64;
- PROCESS1_64;
- return XXH64_avalanche(h64);
-
- case 30: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 22: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 14: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 6: PROCESS4_64;
- PROCESS1_64;
- PROCESS1_64;
- return XXH64_avalanche(h64);
-
- case 27: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 19: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 11: PROCESS8_64;
- PROCESS1_64;
- PROCESS1_64;
- PROCESS1_64;
- return XXH64_avalanche(h64);
-
- case 31: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 23: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 15: PROCESS8_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 7: PROCESS4_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 3: PROCESS1_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 2: PROCESS1_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 1: PROCESS1_64;
- /* fallthrough */
- case 0: return XXH64_avalanche(h64);
- }
- }
- /* impossible to reach */
- XXH_ASSERT(0);
- return 0; /* unreachable, but some compilers complain without it */
-}
-
-XXH_FORCE_INLINE xxh_u64
-XXH64_endian_align(const xxh_u8* input, size_t len, xxh_u64 seed, XXH_alignment align)
-{
- const xxh_u8* bEnd = input + len;
- xxh_u64 h64;
-
-#if defined(XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER) && (XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER>=1)
- if (input==NULL) {
- len=0;
- bEnd=input=(const xxh_u8*)(size_t)32;
- }
-#endif
-
- if (len>=32) {
- const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - 32;
- xxh_u64 v1 = seed + PRIME64_1 + PRIME64_2;
- xxh_u64 v2 = seed + PRIME64_2;
- xxh_u64 v3 = seed + 0;
- xxh_u64 v4 = seed - PRIME64_1;
-
- do {
- v1 = XXH64_round(v1, XXH_get64bits(input)); input+=8;
- v2 = XXH64_round(v2, XXH_get64bits(input)); input+=8;
- v3 = XXH64_round(v3, XXH_get64bits(input)); input+=8;
- v4 = XXH64_round(v4, XXH_get64bits(input)); input+=8;
- } while (input<=limit);
-
- h64 = XXH_rotl64(v1, 1) + XXH_rotl64(v2, 7) + XXH_rotl64(v3, 12) + XXH_rotl64(v4, 18);
- h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v1);
- h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v2);
- h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v3);
- h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v4);
-
- } else {
- h64 = seed + PRIME64_5;
- }
-
- h64 += (xxh_u64) len;
-
- return XXH64_finalize(h64, input, len, align);
-}
-
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64 (const void* input, size_t len, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
-#if 0
- /* Simple version, good for code maintenance, but unfortunately slow for small inputs */
- XXH64_state_t state;
- XXH64_reset(&state, seed);
- XXH64_update(&state, (const xxh_u8*)input, len);
- return XXH64_digest(&state);
-
-#else
-
- if (XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK) {
- if ((((size_t)input) & 7)==0) { /* Input is aligned, let's leverage the speed advantage */
- return XXH64_endian_align((const xxh_u8*)input, len, seed, XXH_aligned);
- } }
-
- return XXH64_endian_align((const xxh_u8*)input, len, seed, XXH_unaligned);
-
-#endif
-}
-
-/******* Hash Streaming *******/
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_state_t* XXH64_createState(void)
-{
- return (XXH64_state_t*)XXH_malloc(sizeof(XXH64_state_t));
-}
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_freeState(XXH64_state_t* statePtr)
-{
- XXH_free(statePtr);
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_copyState(XXH64_state_t* dstState, const XXH64_state_t* srcState)
-{
- memcpy(dstState, srcState, sizeof(*dstState));
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode XXH64_reset(XXH64_state_t* statePtr, XXH64_hash_t seed)
-{
- XXH64_state_t state; /* use a local state to memcpy() in order to avoid strict-aliasing warnings */
- memset(&state, 0, sizeof(state));
- state.v1 = seed + PRIME64_1 + PRIME64_2;
- state.v2 = seed + PRIME64_2;
- state.v3 = seed + 0;
- state.v4 = seed - PRIME64_1;
- /* do not write into reserved64, might be removed in a future version */
- memcpy(statePtr, &state, sizeof(state) - sizeof(state.reserved64));
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH_errorcode
-XXH64_update (XXH64_state_t* state, const void* input, size_t len)
-{
- if (input==NULL)
-#if defined(XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER) && (XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER>=1)
- return XXH_OK;
-#else
- return XXH_ERROR;
-#endif
-
- { const xxh_u8* p = (const xxh_u8*)input;
- const xxh_u8* const bEnd = p + len;
-
- state->total_len += len;
-
- if (state->memsize + len < 32) { /* fill in tmp buffer */
- XXH_memcpy(((xxh_u8*)state->mem64) + state->memsize, input, len);
- state->memsize += (xxh_u32)len;
- return XXH_OK;
- }
-
- if (state->memsize) { /* tmp buffer is full */
- XXH_memcpy(((xxh_u8*)state->mem64) + state->memsize, input, 32-state->memsize);
- state->v1 = XXH64_round(state->v1, XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+0));
- state->v2 = XXH64_round(state->v2, XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+1));
- state->v3 = XXH64_round(state->v3, XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+2));
- state->v4 = XXH64_round(state->v4, XXH_readLE64(state->mem64+3));
- p += 32-state->memsize;
- state->memsize = 0;
- }
-
- if (p+32 <= bEnd) {
- const xxh_u8* const limit = bEnd - 32;
- xxh_u64 v1 = state->v1;
- xxh_u64 v2 = state->v2;
- xxh_u64 v3 = state->v3;
- xxh_u64 v4 = state->v4;
-
- do {
- v1 = XXH64_round(v1, XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8;
- v2 = XXH64_round(v2, XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8;
- v3 = XXH64_round(v3, XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8;
- v4 = XXH64_round(v4, XXH_readLE64(p)); p+=8;
- } while (p<=limit);
-
- state->v1 = v1;
- state->v2 = v2;
- state->v3 = v3;
- state->v4 = v4;
- }
-
- if (p < bEnd) {
- XXH_memcpy(state->mem64, p, (size_t)(bEnd-p));
- state->memsize = (unsigned)(bEnd-p);
- }
- }
-
- return XXH_OK;
-}
-
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_digest (const XXH64_state_t* state)
-{
- xxh_u64 h64;
-
- if (state->total_len >= 32) {
- xxh_u64 const v1 = state->v1;
- xxh_u64 const v2 = state->v2;
- xxh_u64 const v3 = state->v3;
- xxh_u64 const v4 = state->v4;
-
- h64 = XXH_rotl64(v1, 1) + XXH_rotl64(v2, 7) + XXH_rotl64(v3, 12) + XXH_rotl64(v4, 18);
- h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v1);
- h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v2);
- h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v3);
- h64 = XXH64_mergeRound(h64, v4);
- } else {
- h64 = state->v3 /*seed*/ + PRIME64_5;
- }
-
- h64 += (xxh_u64) state->total_len;
-
- return XXH64_finalize(h64, (const xxh_u8*)state->mem64, (size_t)state->total_len, XXH_aligned);
-}
-
-
-/******* Canonical representation *******/
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API void XXH64_canonicalFromHash(XXH64_canonical_t* dst, XXH64_hash_t hash)
-{
- XXH_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(XXH64_canonical_t) == sizeof(XXH64_hash_t));
- if (XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN) hash = XXH_swap64(hash);
- memcpy(dst, &hash, sizeof(*dst));
-}
-
-XXH_PUBLIC_API XXH64_hash_t XXH64_hashFromCanonical(const XXH64_canonical_t* src)
-{
- return XXH_readBE64(src);
-}
-
-
-
-/* *********************************************************************
-* XXH3
-* New generation hash designed for speed on small keys and vectorization
-************************************************************************ */
-
-#include "xxh3.h"
-
-
-#endif /* XXH_NO_LONG_LONG */
-
-
-#endif /* XXH_IMPLEMENTATION */
-
-
-#if defined (__cplusplus)
-}
-#endif
diff --git a/core/deps/xxHash/xxhsum.1 b/core/deps/xxHash/xxhsum.1
deleted file mode 100644
index 1ae06dc143..0000000000
--- a/core/deps/xxHash/xxhsum.1
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,160 +0,0 @@
-.
-.TH "XXHSUM" "1" "December 2019" "xxhsum 0.7.2" "User Commands"
-.
-.SH "NAME"
-\fBxxhsum\fR \- print or check xxHash non\-cryptographic checksums
-.
-.SH "SYNOPSIS"
-\fBxxhsum [