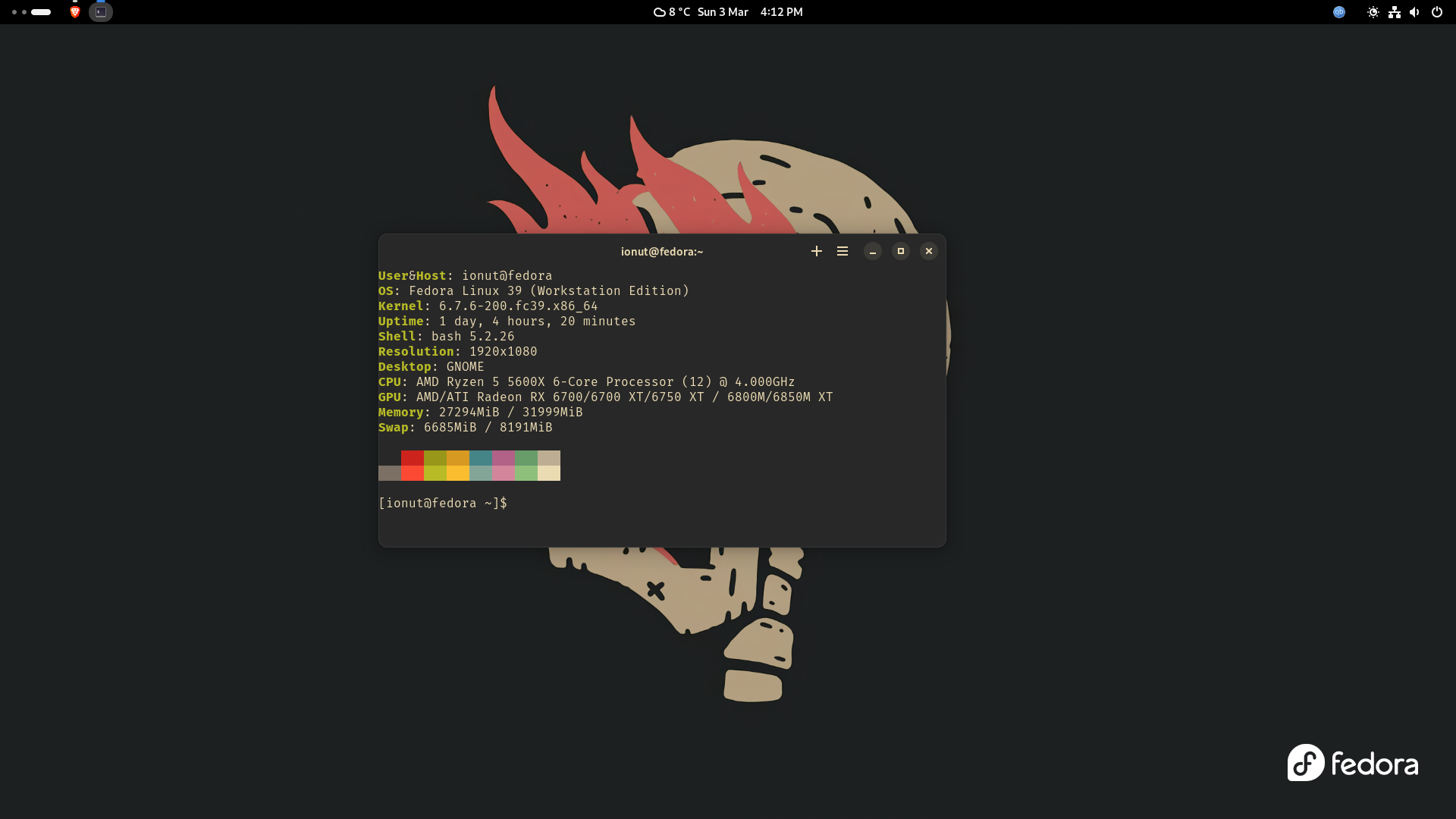
It has almost the same functionality as neofetch, without being too bloated.
I made and tested this tool on my main Fedora machine and I don't plan on testing it on anything else.
(EDIT: Also tested on an Asus laptop, running Debian, with an Nvidia GPU, and it worked first try)
If you wish to test it on different Linux distributions or on MacOS/BSD, report any issues you encounter.
All of the information are collected from various parts of the system, which means you don't need any fancy packages or programs. The less dependencies, the better.
Make sure you have installed:
// This binaries should already be installed by default on all Linux Distributions
- grep
- awk
- uptime
- basename
- xdpyinfo
(works on wayland too) - cut
- tr
- printf
- sed
- awk
// Some of these you may need to install by yourself
- lspci
- gcc
// or any C compiler - musl-gcc
// for static compilation or any other C compiler which will do a static compilation
There is a makefile for ease of use
make // default dynamic linking build
make static // musl static linked buildTo make the binary available from everywhere it's quite easy
# make a symbolic link from the local/bin to synfo
ln -s /path/to/the/synfo /usr/local/bin # you may need to use sudo for this
#update the PATH environment variable to reflect our newly added symbolic link
export PATH="/usr/local/bin:$PATH" # do this every time you move the symbolic link
#update the source
source ~/.bashrc # I run bash, so I refresh the bashrc file. If you use some other shell, find out what you need to doNow you can type synfo like you would any other command. Enjoy! :)