Table of Contents
- Demo overview
- Intel® GPU Device Plugin demo video
- Intel® FPGA Device Plugin demo videos
- Intel® SGX Device Plugin demo videos
- Intel® QuickAssist Technology Device Plugin OpenSSL demo video
- Intel® QuickAssist Technology Device Plugin with DPDK demo video
Acceleration of compute and data processing of workloads like video transcoding, compression, and encryption is enabled in Kubernetes with the Device Plugin Framework. This repository contains a set of Kubernetes plugins and instructions to enable Intel devices for the acceleration of your workloads orchestrated by Kubernetes.
The current list of supported Intel Device Plugins includes:
- GPU Device Plugin with support for Intel® Graphics Technology
- Intel® FPGA Device Plugin
- Intel® QuickAssist Technology (QAT) Device Plugin
We have included an example demo and configuration information for the Intel Device Plugins for Kubernetes below. Please join us on the sig-node-rtk channel on kubernetes.slack.com to ask questions, contribute to the community, and learn about the work we are doing with Kubernetes and the Device Plugin Framework.
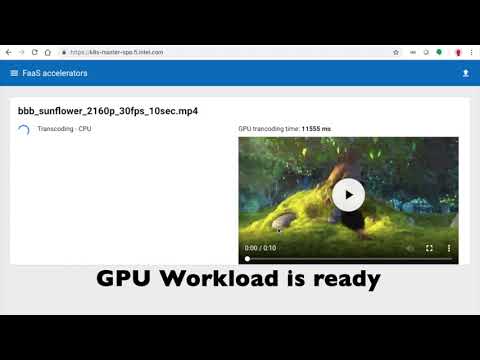
The screencast demonstrates the deployment of the Intel® GPU Device Plugin for Kubernetes including Kubeless Function as a Service (FaaS) media transcoder JavaScript function. The media transcoding workload is scheduled on two different worker nodes. Only one worker node has a GPU. The time difference in transcoding speed is captured.
- Hardware 2-nodes
- 1x Virtual Machine on Intel® Xeon® E5-2687 CPU @ 3.0 GHz
- 1x Intel® NUC KIT NUC6i7KYK (Skull Canyon) with Intel integrated GPU
- Software
- Ubuntu* 18.04 (Kernel: 4.15.0-36-generic)
- Kubernetes* 1.11
- Docker* 18.3.1
- Intel® GPU Device Plugin built from main branch
The screencasts demonstrate the deployment of the Intel® FPGA Device Plugin for Kubernetes.
- Demo 1 executes a native loopback 3 (NLB3) workload in preprogrammed mode
- Demo 2 executes NLB3 workload in orchestrated mode
- Demo 3 runs an OpenCL workload to do English letters recognition, and compares time used with and without FPGA to show the acceleration.
The demos begin with a fully configured Kubernetes cluster.
- Hardware
- 1-node, Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2650 0 @ 2.00GHz
- Total memory 62 GB
- 2 x Intel® Arria® 10 GX FPGA Programmable Acceleration Card(PAC)
- Software
- openSUSE Leap 15.1 (Kernel: 5.4.5-1.g47eef04-default)
- Kubernetes* 1.17
- CRI-O 1.13.1 (for orchestrated mode)
- Docker 19.03.1 (for preprogrammed mode)
- runc 1.0.0-rc8
- Intel® FPGA Device Plugin built from main branch
- Hardware
- Multi-node, FPGA host has 24 cores Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6252N CPU @ 2.30GHz
- Total memory 195 GB
- Intel® FPGA Programmable Acceleration Card D5005
- Software
- Centos 7 (Kernel: 3.10.0-1062.12.1.el7.x86_64) on worker node host
- Kubernetes* 1.17
- CRI-O 1.17.3
- Intel® FPGA Device Plugin built from main branch
- Validate the status of the Kubernetes cluster.
- Provision the Intel® FPGA Device Plugin.
- Create bitstream storage (for orchestrated mode only)
- Run the NLB3 or OpenCL workload.
- Intel® FPGA Device Plugin deployment in preprogrammed mode and NLB workload:
- Intel® FPGA Device Plugin deployment with orchestrated/region mode and NLB workload:
- Intel® FPGA Device Plugin deployment with orchestrated/region mode and OpenCL workload:
This video demonstrates the Intel® Software Guard Extensions ECDSA Quote Generation in Kubernetes*
- Hardware
- 1-node, 3rd Generation Intel® Xeon® Scalable Platform, code-named “Ice Lake”
- Software
- 18.04.5 LTS
- Kubernetes* 1.19
- containerd 1.3.3
- Intel® SGX Device Plugin built from main branch
- Intel® SGX SDK 2.12 and DCAP 1.9
- node-feature-discovery 0.6.0
- Validate the status of the Kubernetes cluster.
- Provision node-feature-discovery.
- Provision the Intel® SGX Device Plugin using Intel® Device Plugin Operator.
- Check the SGX resources and labels are correctly registered.
- Run Intel® SGX DCAP ECDSA Quote Generation in both "out-of-proc" and "in-proc" modes.
Intel® SGX Device Plugin and SGX DCAP ECDSA Quote Generation demo
The screencast demonstrates the deployment of the Intel® QAT Device Plugin for Kubernetes and executes a sample QAT accelerated OpenSSL workload with the OCI compatible Kata Containers runtime, a lightweight Virtual Machine (VM) that feels and performs like traditional containers, but provides the workload isolation and security advantages of VMs. The demo begins with a fully configured Kubernetes cluster and Kata Containers runtime for workloads.
- Hardware
- 1-node, 2x Intel® Xeon® CPU E5-2687W v4 @ 3.00GHz
- Total memory 251 GB DDR4
- Intel® QAT C62x chipset
- Software
- OpenSUSE* 15 (Kernel:4.12.14-lp150.12.22-default)
- Kubernetes* 1.12
- Containerd 1.2
- Kata Containers* 1.3.0
- Intel® QAT Device Plugin built from main
- QAT 1.7 L.4.3.0-00033
- Load the host drivers and prepare the virtual function (VF) devices.
- Check the Kubernetes cluster is in good shape.
- Deploy the Intel® QAT device plugin for Kubernetes.
- Deploy an Intel® QAT Accelerated OpenSSL workload.
- Testing!
Intel® QAT Device Plugin deployment
- Check health of Kubernetes nodes.
- Check for allocatable resources.
- List QAT Virtual Functions.
- Deploy QAT Device Plugin as a Daemonset.
- Check again for allocatable resources.
- List QAT Virtual Functions again, ensuring they are now bound to DPDK driver.
- View pod specification file for pod requesting QAT VFs.
- Create pod requesting QAT VFs.
- Get a shell to the running container and run a DPDK application.
Intel® QAT Device Plugin with DPDK: