UltraOpt : 比HyperOpt更强的分布式异步超参优化库。
UltraOpt 是一个简单有效的优化库用于优化含噪音且评估代价大的黑盒函数,他能在大量的领域中应用,如超参优化(HyperParameter Optimization,HPO)和自动机器学习(Automatic Machine Learning,AutoML)。
在吸收了已有的优化库,如HyperOpt[5], SMAC3[3], scikit-optimize[4] and HpBandSter[2]的优点后,我们开发了 UltraOpt ,它实现了一个新的贝叶斯优化算法:ETPE(Embedding-Tree-Parzen-Estimator,嵌入树形Parzen估计器),在我们的实验中,这个算法比HyperOpt的TPE算法表现更好。除此之外,UltraOpt 的优化器被重新设计为能够适应HyperBand 和 SuccessiveHalving 评价策略[6][7]和MapReduce 和 异步通信 计算场景。最后,你可以通过UltraOpt的工具函数对配置空间和优化过程与结果进行可视化。
其他语言: English README
-
Documentation
-
English Documentation is not available now.
-
-
Tutorials
-
English Tutorials is not available now.
-
Table of Contents
UltraOpt 需要 Python 3.6 或更高.
You can install the latest release by pip:
pip install ultraopt你可以下载仓库后手动安装:
git clone https://github.com/auto-flow/ultraopt.git && cd ultraopt
python setup.py install让我们通过几个例子学习UltraOpt(你可以在Jupyter Notebook中尝试)。
在开始一个黑盒优化任务前,你需要提供两个东西:
- 参数的取值范围,或称 配置空间(Config Space)
- 目标函数, 接受
config(config是 Config Space的一个采样), 返回loss
让我们定义一个随机森林的 Config Space 通过 UltraOpt的 HDL (Hyperparameter Description Language,超参描述语言):
HDL = {
"n_estimators": {"_type": "int_quniform","_value": [10, 200, 10], "_default": 100},
"criterion": {"_type": "choice","_value": ["gini", "entropy"],"_default": "gini"},
"max_features": {"_type": "choice","_value": ["sqrt","log2"],"_default": "sqrt"},
"min_samples_split": {"_type": "int_uniform", "_value": [2, 20],"_default": 2},
"min_samples_leaf": {"_type": "int_uniform", "_value": [1, 20],"_default": 1},
"bootstrap": {"_type": "choice","_value": [True, False],"_default": True},
"random_state": 42
}然后再定义一个目标函数:
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, StratifiedKFold
from ultraopt.hdl import layering_config
X, y = load_digits(return_X_y=True)
cv = StratifiedKFold(5, True, 0)
def evaluate(config: dict) -> float:
model = RandomForestClassifier(**layering_config(config))
return 1 - float(cross_val_score(model, X, y, cv=cv).mean())现在,让我们开启一个优化过程:
from ultraopt import fmin
result = fmin(eval_func=evaluate, config_space=HDL, optimizer="ETPE", n_iterations=30)
result100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:36<00:00, 1.23s/trial, best loss: 0.023]
+-----------------------------------+
| HyperParameters | Optimal Value |
+-------------------+---------------+
| bootstrap | True:bool |
| criterion | gini |
| max_features | log2 |
| min_samples_leaf | 1 |
| min_samples_split | 2 |
| n_estimators | 200 |
+-------------------+---------------+
| Optimal Loss | 0.0228 |
+-------------------+---------------+
| Num Configs | 30 |
+-------------------+---------------+
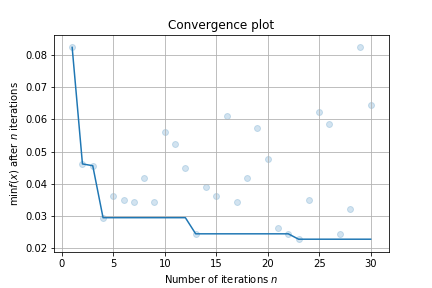
最后,进行一个简单的可视化:
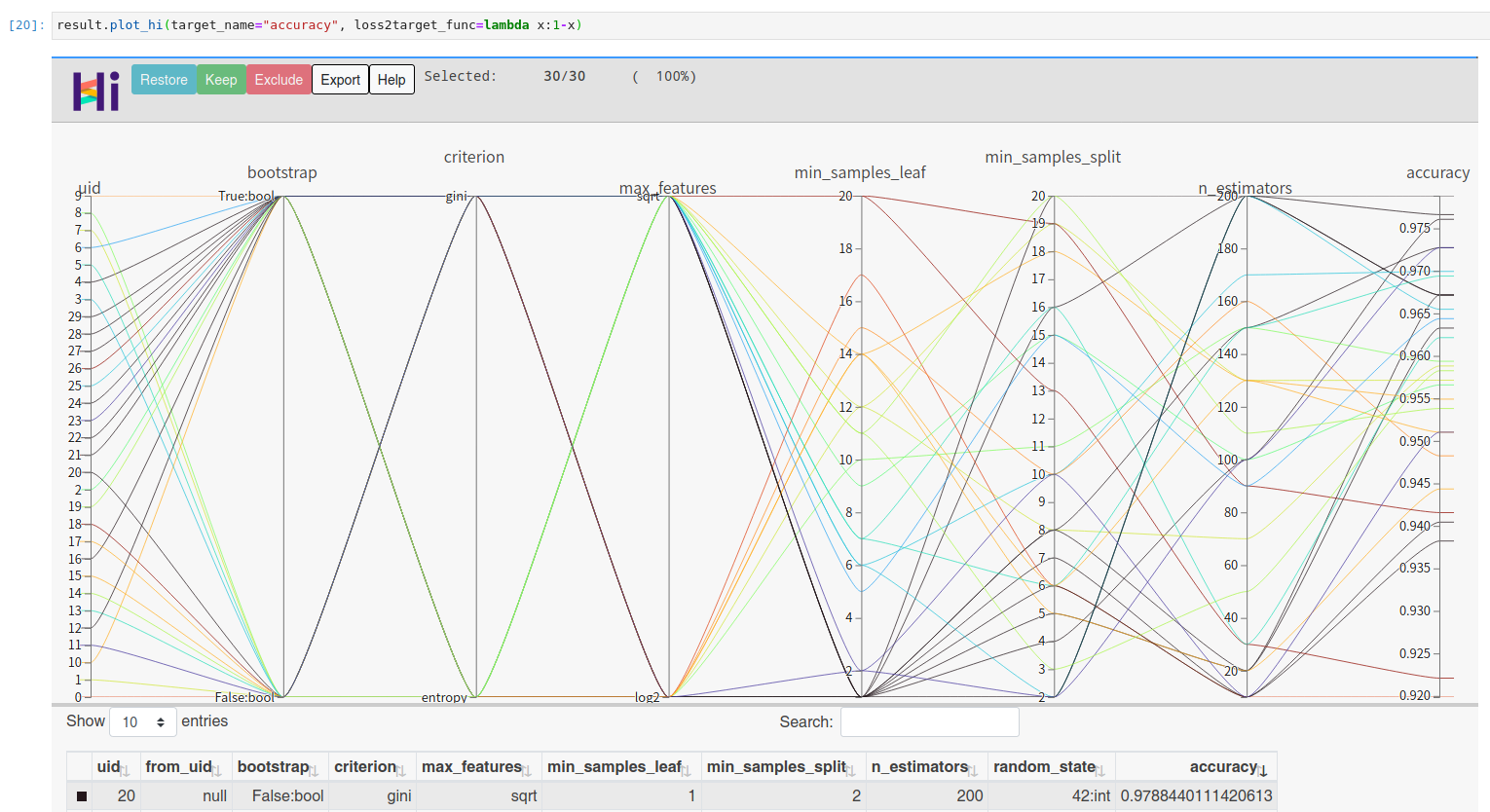
result.plot_convergence()你可以通过 facebook 的 hiplot 查看高维交互图:
!pip install hiplot
result.plot_hi(target_name="accuracy", loss2target_func=lambda x:1-x)让我们尝试一个更复杂的例子:通过BOHB算法[2](结合了HyperBand[6]评价策略和 UltraOpt的 ETPE 优化器)解决AutoML的 CASH 问题 [1] (Combination problem of Algorithm Selection and Hyperparameter optimization).
你可以在这里学习条件参数和复杂HDL的定义,在这里学习怎么实现一个简单的AutoML,在这里学习AutoML的实现。
首先,我们需要定义一个解决 CASH 问题 的 HDL :
HDL = {
'classifier(choice)':{
"RandomForestClassifier": {
"n_estimators": {"_type": "int_quniform","_value": [10, 200, 10], "_default": 100},
"criterion": {"_type": "choice","_value": ["gini", "entropy"],"_default": "gini"},
"max_features": {"_type": "choice","_value": ["sqrt","log2"],"_default": "sqrt"},
"min_samples_split": {"_type": "int_uniform", "_value": [2, 20],"_default": 2},
"min_samples_leaf": {"_type": "int_uniform", "_value": [1, 20],"_default": 1},
"bootstrap": {"_type": "choice","_value": [True, False],"_default": True},
"random_state": 42
},
"KNeighborsClassifier": {
"n_neighbors": {"_type": "int_loguniform", "_value": [1,100],"_default": 3},
"weights" : {"_type": "choice", "_value": ["uniform", "distance"],"_default": "uniform"},
"p": {"_type": "choice", "_value": [1, 2],"_default": 2},
},
}
}然后,定义一个附加budget参数的目标函数,以适应HyperBand[6]评估策略:
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
import numpy as np
def evaluate(config: dict, budget: float) -> float:
layered_dict = layering_config(config)
AS_HP = layered_dict['classifier'].copy()
AS, HP = AS_HP.popitem()
ML_model = eval(AS)(**HP)
scores = []
for i, (train_ix, valid_ix) in enumerate(cv.split(X, y)):
rng = np.random.RandomState(i)
size = int(train_ix.size * budget)
train_ix = rng.choice(train_ix, size, replace=False)
X_train,y_train = X[train_ix, :],y[train_ix]
X_valid,y_valid = X[valid_ix, :],y[valid_ix]
ML_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores.append(ML_model.score(X_valid, y_valid))
score = np.mean(scores)
return 1 - score你应该实例化一个multi_fidelity_iter_generator对象,用来使用HyperBand[6]评估策略:
from ultraopt.multi_fidelity import HyperBandIterGenerator
hb = HyperBandIterGenerator(min_budget=1/4, max_budget=1, eta=2)
hb.get_table()| iter 0 | iter 1 | iter 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| stage 0 | stage 1 | stage 2 | stage 0 | stage 1 | stage 0 | |
| num_config | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| budget | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1 | 1/2 | 1 | 1 |
让我们将 HyperBand 评估策略和 UltraOpt的 ETPE 优化器结合在一起 , 然后开启一个优化过程:
result = fmin(eval_func=evaluate, config_space=HDL,
optimizer="ETPE", # using bayesian optimizer: ETPE
multi_fidelity_iter_generator=hb, # using HyperBand
n_jobs=3, # 3 threads
n_iterations=20)
result100%|██████████| 88/88 [00:11<00:00, 7.48trial/s, max budget: 1.0, best loss: 0.012]
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| HyperParameters | Optimal Value |
+-----------------------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| classifier:__choice__ | KNeighborsClassifier | KNeighborsClassifier | KNeighborsClassifier |
| classifier:KNeighborsClassifier:n_neighbors | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| classifier:KNeighborsClassifier:p | 2:int | 2:int | 2:int |
| classifier:KNeighborsClassifier:weights | distance | uniform | uniform |
| classifier:RandomForestClassifier:bootstrap | - | - | - |
| classifier:RandomForestClassifier:criterion | - | - | - |
| classifier:RandomForestClassifier:max_features | - | - | - |
| classifier:RandomForestClassifier:min_samples_leaf | - | - | - |
| classifier:RandomForestClassifier:min_samples_split | - | - | - |
| classifier:RandomForestClassifier:n_estimators | - | - | - |
| classifier:RandomForestClassifier:random_state | - | - | - |
+-----------------------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| Budgets | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1 (max) |
+-----------------------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| Optimal Loss | 0.0328 | 0.0178 | 0.0122 |
+-----------------------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| Num Configs | 28 | 28 | 32 |
+-----------------------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
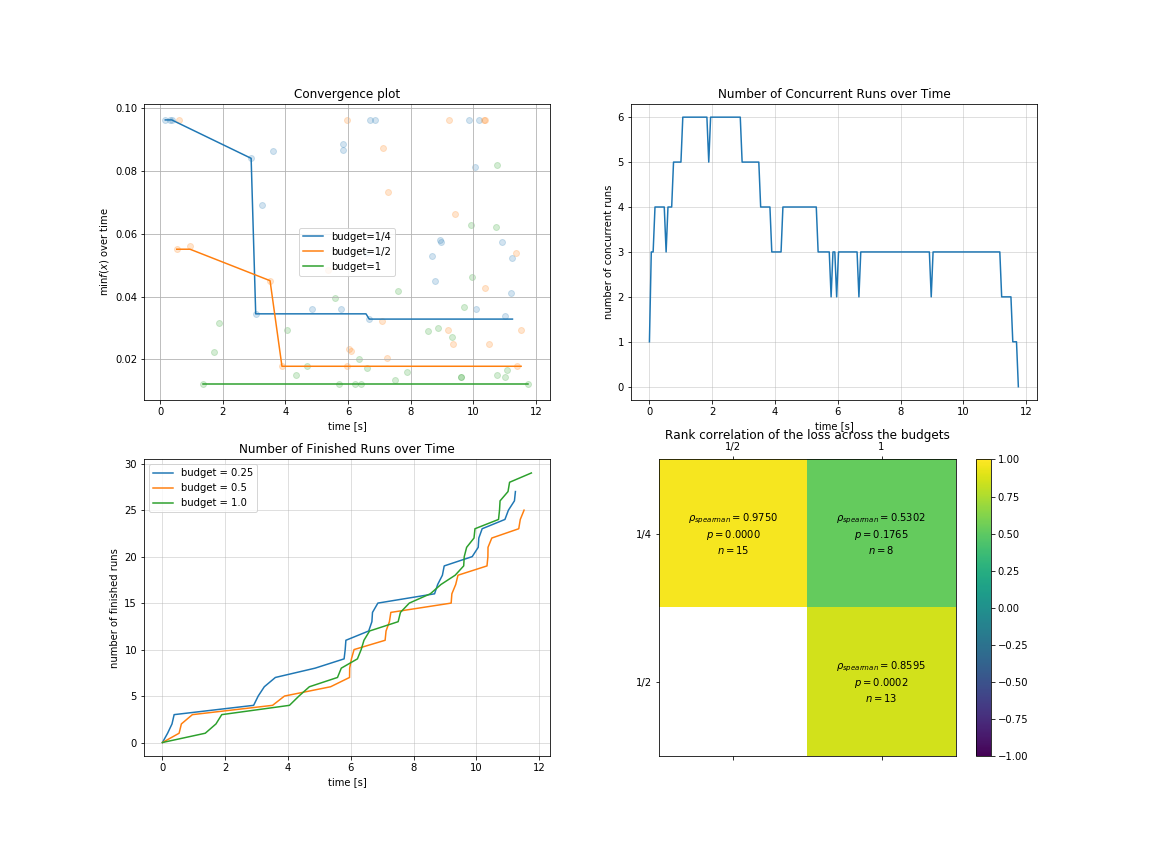
你可以对 多保真度 场景下的优化过程与结果进行可视化:
import pylab as plt
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (16, 12)
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
result.plot_convergence_over_time();
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
result.plot_concurrent_over_time(num_points=200);
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
result.plot_finished_over_time();
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
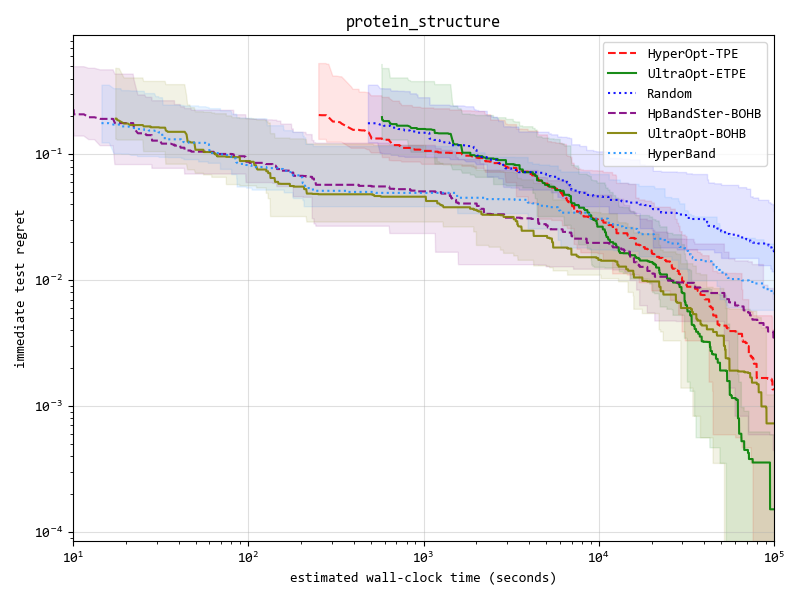
result.plot_correlation_across_budgets();我们实现了4种优化器(在下表中列出), 并且 ETPE 优化器是我们原创的优化器, 在我们的试验中,它比其他基于TPE的优化器如 HyperOpt的TPE 和 HpBandSter的BOHB 要表现更好。
Our experimental code is public available in here, experimental documentation can be found in here .
| Optimizer | Description |
|---|---|
| ETPE | Embedding-Tree-Parzen-Estimator, is our original creation, converting high-cardinality categorical variables to low-dimension continuous variables based on TPE algorithm, and some other aspects have also been improved, is proved to be better than HyperOpt's TPE in our experiments. |
| Forest | Bayesian Optimization based on Random Forest. Surrogate model import scikit-optimize 's skopt.learning.forest model, and integrate Local Search methods in SMAC3 |
| GBRT | Bayesian Optimization based on Gradient Boosting Resgression Tree. Surrogate model import scikit-optimize 's skopt.learning.gbrt model. |
| Random | Random Search for baseline or dummy model. |
Key result figure in experiment (you can see details in experimental documentation ) :
You can see this section in the documentation:
UltraOpt is more function comlete and user friendly than other optimize library:
| UltraOpt | HyperOpt | Scikit-Optimize | SMAC3 | HpBandSter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
调用方便,如 fmin 函数 |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × |
简单的 配置空间 定义 |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | × |
支持 条件配置空间 |
✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ |
配置空间 可序列化 |
✓ | × | × | × | × |
支持 配置空间 可视化 |
✓ | ✓ | × | × | × |
| 可以分析优化结果与优化过程 | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | ✓ |
| 能够在集群中分布式运行 | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | ✓ |
| 支持HyperBand[6]与连续减半[7] | ✓ | × | × | ✓ | ✓ |
@misc{Tang_UltraOpt,
author = {Qichun Tang},
title = {UltraOpt : Distributed Asynchronous Hyperparameter Optimization better than HyperOpt},
month = January,
year = 2021,
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.4430148},
version = {v0.1.0},
publisher = {Zenodo},
url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4430148}
}Reference