Please check the basic_deployment_guide to get familiar with the configurations.
The details of training and validation can be found at yolov5_tutorial.
Please check the installation document of MMDeploy at build_from_source. Please build both MMDeploy and the customized Ops to your specific platform.
Note: please check at MMDeploy FAQ or create new issues in MMDeploy when you come across any problems.
This deployment guide uses the YOLOv5 model trained on COCO dataset in MMYOLO to illustrate the whole process, including both static and dynamic inputs and different procedures for TensorRT and ONNXRuntime.
To deploy the model with static inputs, you need to ensure that the model inputs are in fixed size, e.g. the input size is set to 640x640 while uploading data in the test pipeline and test dataloader.
Here is a example in yolov5_s-static.py
_base_ = '../../yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py'
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile', file_client_args=_base_.file_client_args),
dict(
type='LetterResize',
scale=_base_.img_scale,
allow_scale_up=False,
use_mini_pad=False,
),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True, _scope_='mmdet'),
dict(
type='mmdet.PackDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_id', 'img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape',
'scale_factor', 'pad_param'))
]
test_dataloader = dict(
dataset=dict(pipeline=test_pipeline, batch_shapes_cfg=None))As the YOLOv5 will turn on allow_scale_up and use_mini_pad during the test to change the size of the input image in order to achieve higher accuracy. However, it will cause the input size mismatch problem when deploying in the static input model.
Compared with the original configuration file, this configuration has been modified as follows:
- turn off the settings related to reshaping the image in
test_pipeline, e.g. settingallow_scale_up=Falseanduse_mini_pad=FalseinLetterResize - turn off the
batch_shapesintest_dataloaderasbatch_shapes_cfg=None.
To deploy the model to ONNXRuntime, please refer to the detection_onnxruntime_static.py as follows:
_base_ = ['./base_static.py']
codebase_config = dict(
type='mmyolo',
task='ObjectDetection',
model_type='end2end',
post_processing=dict(
score_threshold=0.05,
confidence_threshold=0.005,
iou_threshold=0.5,
max_output_boxes_per_class=200,
pre_top_k=5000,
keep_top_k=100,
background_label_id=-1),
module=['mmyolo.deploy'])
backend_config = dict(type='onnxruntime')The post_processing in the default configuration aligns the accuracy of the current model with the trained pytorch model. If you need to modify the relevant parameters, you can refer to the detailed introduction of dasic_deployment_guide.
To deploy the model to TensorRT, please refer to the detection_tensorrt_static-640x640.py.
_base_ = ['./base_static.py']
onnx_config = dict(input_shape=(640, 640))
backend_config = dict(
type='tensorrt',
common_config=dict(fp16_mode=False, max_workspace_size=1 << 30),
model_inputs=[
dict(
input_shapes=dict(
input=dict(
min_shape=[1, 3, 640, 640],
opt_shape=[1, 3, 640, 640],
max_shape=[1, 3, 640, 640])))
])
use_efficientnms = FalseIn this guide, we use the default settings such as input_shape=(640, 640) and fp16_mode=False to build in network in fp32 mode. Moreover, we set max_workspace_size=1 << 30 for the gpu memory which allows TensorRT to build the engine with maximum 1GB memory.
As TensorRT limits the minimum and maximum input size, we can use any size for the inputs when deploy the model in dynamic mode. In this way, we can keep the default settings in yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py. The data processing and dataloader parts are as follows.
batch_shapes_cfg = dict(
type='BatchShapePolicy',
batch_size=val_batch_size_per_gpu,
img_size=img_scale[0],
size_divisor=32,
extra_pad_ratio=0.5)
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile', file_client_args=_base_.file_client_args),
dict(type='YOLOv5KeepRatioResize', scale=img_scale),
dict(
type='LetterResize',
scale=img_scale,
allow_scale_up=False,
pad_val=dict(img=114)),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True, _scope_='mmdet'),
dict(
type='mmdet.PackDetInputs',
meta_keys=('img_id', 'img_path', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape',
'scale_factor', 'pad_param'))
]
val_dataloader = dict(
batch_size=val_batch_size_per_gpu,
num_workers=val_num_workers,
persistent_workers=persistent_workers,
pin_memory=True,
drop_last=False,
sampler=dict(type='DefaultSampler', shuffle=False),
dataset=dict(
type=dataset_type,
data_root=data_root,
test_mode=True,
data_prefix=dict(img='val2017/'),
ann_file='annotations/instances_val2017.json',
pipeline=test_pipeline,
batch_shapes_cfg=batch_shapes_cfg))We use allow_scale_up=False to control when the input small images will be upsampled or not in the initialization of LetterResize. At the same time, the default use_mini_pad=False turns off the minimum padding strategy of the image, and val_dataloader['dataset'] is passed in batch_shapes_cfg=batch_shapes_cfg to ensure that the minimum padding is performed according to the input size in batch. These configs will change the dimensions of the input image, so the converted model can support dynamic inputs according to the above dataset loader when testing.
To deploy the model to ONNXRuntime, please refer to the detection_onnxruntime_dynamic.py for more details.
_base_ = ['./base_dynamic.py']
codebase_config = dict(
type='mmyolo',
task='ObjectDetection',
model_type='end2end',
post_processing=dict(
score_threshold=0.05,
confidence_threshold=0.005,
iou_threshold=0.5,
max_output_boxes_per_class=200,
pre_top_k=5000,
keep_top_k=100,
background_label_id=-1),
module=['mmyolo.deploy'])
backend_config = dict(type='onnxruntime')Differs from the static input config we introduced in previous section, dynamic input config additionally inherits the dynamic_axes. The rest of the configuration stays the same as the static inputs.
To deploy the model to TensorRT, please refer to the detection_tensorrt_dynamic-192x192-960x960.py for more details.
_base_ = ['./base_dynamic.py']
backend_config = dict(
type='tensorrt',
common_config=dict(fp16_mode=False, max_workspace_size=1 << 30),
model_inputs=[
dict(
input_shapes=dict(
input=dict(
min_shape=[1, 3, 192, 192],
opt_shape=[1, 3, 640, 640],
max_shape=[1, 3, 960, 960])))
])
use_efficientnms = FalseIn our example, the network is built in fp32 mode as fp16_mode=False, and the maximum graphic memory is 1GB for building the TensorRT engine as max_workspace_size=1 << 30.
At the same time, min_shape=[1, 3, 192, 192], opt_shape=[1, 3, 640, 640], and max_shape=[1, 3, 960, 960] in the default setting set the model with minimum input size to 192x192, the maximum size to 960x960, and the most common size to 640x640.
When you deploy the model, it can adopt to the input image dimensions automatically.
Note: The MMDeploy root directory used in this guide is /home/openmmlab/dev/mmdeploy, please modify it to your MMDeploy directory.
Use the following command to download the pretrained YOLOv5 weight and save it to your device:
wget https://download.openmmlab.com/mmyolo/v0/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220918_084700-86e02187.pth -O /home/openmmlab/dev/mmdeploy/yolov5s.pthSet the relevant env parameters using the following command as well:
export MMDEPLOY_DIR=/home/openmmlab/dev/mmdeploy
export PATH_TO_CHECKPOINTS=/home/openmmlab/dev/mmdeploy/yolov5s.pthpython3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/deploy.py \
configs/deploy/detection_onnxruntime_static.py \
configs/deploy/model/yolov5_s-static.py \
${PATH_TO_CHECKPOINTS} \
demo/demo.jpg \
--work-dir work_dir \
--show \
--device cpupython3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/deploy.py \
configs/deploy/detection_tensorrt_static-640x640.py \
configs/deploy/model/yolov5_s-static.py \
${PATH_TO_CHECKPOINTS} \
demo/demo.jpg \
--work-dir work_dir \
--show \
--device cuda:0python3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/deploy.py \
configs/deploy/detection_onnxruntime_dynamic.py \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
${PATH_TO_CHECKPOINTS} \
demo/demo.jpg \
--work-dir work_dir \
--show \
--device cpupython3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/deploy.py \
configs/deploy/detection_tensorrt_dynamic-192x192-960x960.py \
configs/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_8xb16-300e_coco.py \
${PATH_TO_CHECKPOINTS} \
demo/demo.jpg \
--work-dir work_dir \
--show \
--device cuda:0When convert the model using the above commands, you will find the following files under the work_dir folder:
or
After exporting to onnxruntime, you will get three files as shown in Figure 1, where end2end.onnx represents the exported onnxruntime model.
After exporting to TensorRT, you will get the four files as shown in Figure 2, where end2end.onnx represents the exported intermediate model. MMDeploy uses this model to automatically continue to convert the end2end.engine model for TensorRT Deployment.
After successfully convert the model, you can use ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/test.py to evaluate the converted model. The following part shows how to evaluate the static models of ONNXRuntime and TensorRT. For dynamic model evaluation, please modify the configuration of the inputs.
python3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/test.py \
configs/deploy/detection_onnxruntime_static.py \
configs/deploy/model/yolov5_s-static.py \
--model work_dir/end2end.onnx \
--device cpu \
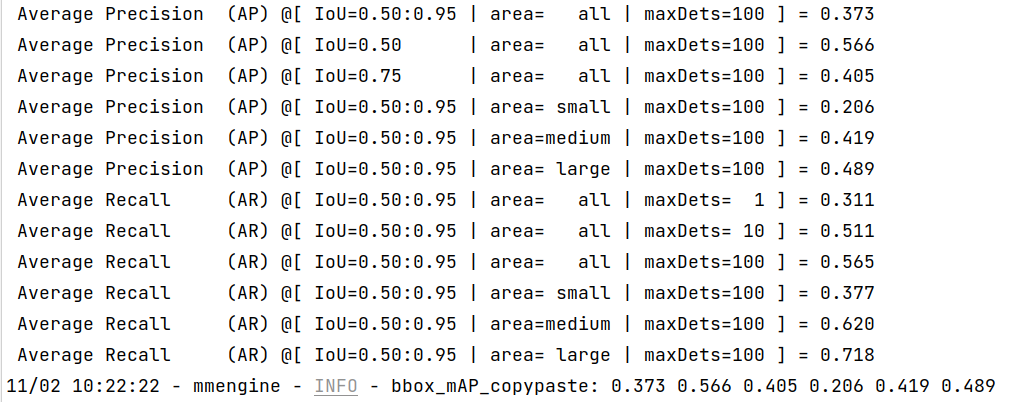
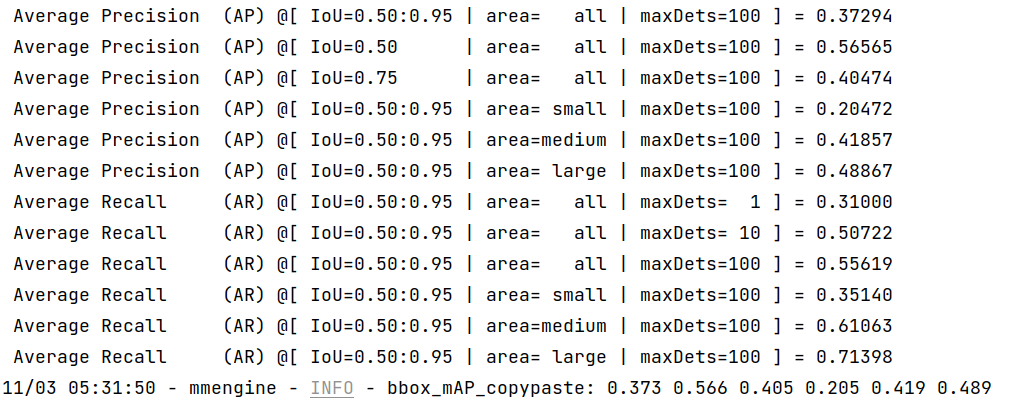
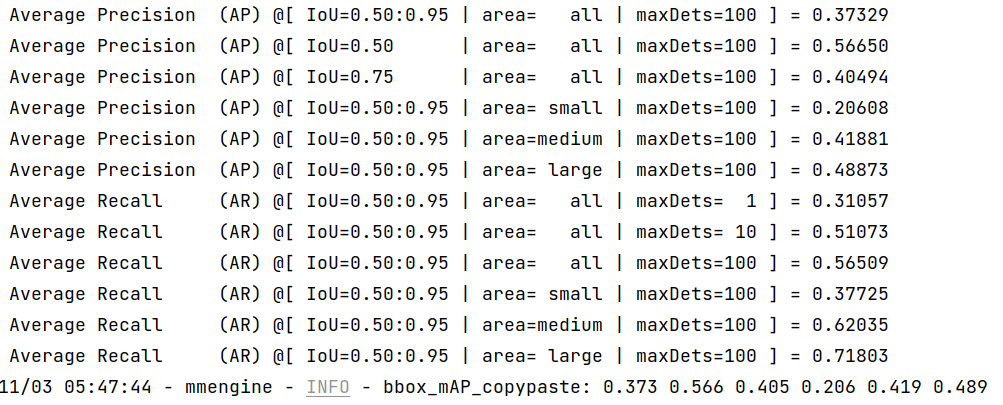
--work-dir work_dirOnce the process is done, you can get the output results as this:
Note: TensorRT must run on CUDA devices!
python3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/test.py \
configs/deploy/detection_tensorrt_static-640x640.py \
configs/deploy/model/yolov5_s-static.py \
--model work_dir/end2end.engine \
--device cuda:0 \
--work-dir work_dirOnce the process is done, you can get the output results as this:
More useful evaluation tools will be released in the future.
MMYOLO provides a deployment Dockerfile for deployment purpose. Please make sure your local docker version is greater than 19.03.
Note: users in mainland China can comment out the Optional part in the dockerfile for better experience.
# (Optional)
RUN sed -i 's/http:\/\/archive.ubuntu.com\/ubuntu\//http:\/\/mirrors.aliyun.com\/ubuntu\//g' /etc/apt/sources.list && \
pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simpleTo build the docker image,
# build an image with PyTorch 1.12, CUDA 11.6, TensorRT 8.2.4 ONNXRuntime 1.8.1
docker build -f docker/Dockerfile_deployment -t mmyolo:v1 .To run the docker image,
export DATA_DIR=/path/to/your/dataset
docker run --gpus all --shm-size=8g -it --name mmyolo -v ${DATA_DIR}:/openmmlab/mmyolo/data/coco mmyolo:v1DATA_DIR is the path of your COCO dataset.
We provide a script.sh file for you which runs the whole pipeline. Create the script under /openmmlab/mmyolo directory in your docker container using the following content.
#!/bin/bash
wget -q https://download.openmmlab.com/mmyolo/v0/yolov5/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco/yolov5_s-v61_syncbn_fast_8xb16-300e_coco_20220918_084700-86e02187.pth \
-O yolov5s.pth
export MMDEPLOY_DIR=/openmmlab/mmdeploy
export PATH_TO_CHECKPOINTS=/openmmlab/mmyolo/yolov5s.pth
python3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/deploy.py \
configs/deploy/detection_tensorrt_static-640x640.py \
configs/deploy/model/yolov5_s-static.py \
${PATH_TO_CHECKPOINTS} \
demo/demo.jpg \
--work-dir work_dir_trt \
--device cuda:0
python3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/test.py \
configs/deploy/detection_tensorrt_static-640x640.py \
configs/deploy/model/yolov5_s-static.py \
--model work_dir_trt/end2end.engine \
--device cuda:0 \
--work-dir work_dir_trt
python3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/deploy.py \
configs/deploy/detection_onnxruntime_static.py \
configs/deploy/model/yolov5_s-static.py \
${PATH_TO_CHECKPOINTS} \
demo/demo.jpg \
--work-dir work_dir_ort \
--device cpu
python3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/test.py \
configs/deploy/detection_onnxruntime_static.py \
configs/deploy/model/yolov5_s-static.py \
--model work_dir_ort/end2end.onnx \
--device cpu \
--work-dir work_dir_ortThen run the script under /openmmlab/mmyolo.
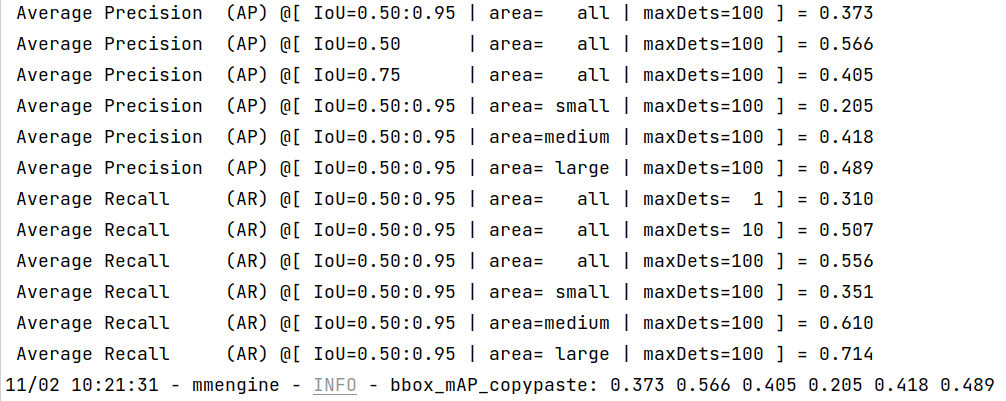
sh script.shThis script automatically downloads the YOLOv5 pretrained weights in MMYOLO and convert the model using MMDeploy. You will get the output result as follows.
We can see from the above images that the accuracy of converted models shrink within 1% compared with the pytorch MMYOLO-YOLOv5 models.
If you need to test the inference speed of the converted model, you can use the following commands.
- TensorRT
python3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/profiler.py \
configs/deploy/detection_tensorrt_static-640x640.py \
configs/deploy/model/yolov5_s-static.py \
data/coco/val2017 \
--model work_dir_trt/end2end.engine \
--device cuda:0- ONNXRuntime
python3 ${MMDEPLOY_DIR}/tools/profiler.py \
configs/deploy/detection_onnxruntime_static.py \
configs/deploy/model/yolov5_s-static.py \
data/coco/val2017 \
--model work_dir_ort/end2end.onnx \
--device cpuTODO